Jillur Rahman Saurav
Dual Codebook VQ: Enhanced Image Reconstruction with Reduced Codebook Size
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Vector Quantization (VQ) techniques face significant challenges in codebook utilization, limiting reconstruction fidelity in image modeling. We introduce a Dual Codebook mechanism that effectively addresses this limitation by partitioning the representation into complementary global and local components. The global codebook employs a lightweight transformer for concurrent updates of all code vectors, while the local codebook maintains precise feature representation through deterministic selection. This complementary approach is trained from scratch without requiring pre-trained knowledge. Experimental evaluation across multiple standard benchmark datasets demonstrates state-of-the-art reconstruction quality while using a compact codebook of size 512 - half the size of previous methods that require pre-training. Our approach achieves significant FID improvements across diverse image domains, particularly excelling in scene and face reconstruction tasks. These results establish Dual Codebook VQ as an efficient paradigm for high-fidelity image reconstruction with significantly reduced computational requirements.
Peptide Sequencing Via Protein Language Models
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a protein language model for determining the complete sequence of a peptide based on measurement of a limited set of amino acids. To date, protein sequencing relies on mass spectrometry, with some novel edman degregation based platforms able to sequence non-native peptides. Current protein sequencing techniques face limitations in accurately identifying all amino acids, hindering comprehensive proteome analysis. Our method simulates partial sequencing data by selectively masking amino acids that are experimentally difficult to identify in protein sequences from the UniRef database. This targeted masking mimics real-world sequencing limitations. We then modify and finetune a ProtBert derived transformer-based model, for a new downstream task predicting these masked residues, providing an approximation of the complete sequence. Evaluating on three bacterial Escherichia species, we achieve per-amino-acid accuracy up to 90.5% when only four amino acids ([KCYM]) are known. Structural assessment using AlphaFold and TM-score validates the biological relevance of our predictions. The model also demonstrates potential for evolutionary analysis through cross-species performance. This integration of simulated experimental constraints with computational predictions offers a promising avenue for enhancing protein sequence analysis, potentially accelerating advancements in proteomics and structural biology by providing a probabilistic reconstruction of the complete protein sequence from limited experimental data.
Predicting Future States with Spatial Point Processes in Single Molecule Resolution Spatial Transcriptomics
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a pipeline based on Random Forest Regression to predict the future distribution of cells that are expressed by the Sog-D gene (active cells) in both the Anterior to posterior (AP) and the Dorsal to Ventral (DV) axis of the Drosophila in embryogenesis process. This method provides insights about how cells and living organisms control gene expression in super resolution whole embryo spatial transcriptomics imaging at sub cellular, single molecule resolution. A Random Forest Regression model was used to predict the next stage active distribution based on the previous one. To achieve this goal, we leveraged temporally resolved, spatial point processes by including Ripley's K-function in conjunction with the cell's state in each stage of embryogenesis, and found average predictive accuracy of active cell distribution. This tool is analogous to RNA Velocity for spatially resolved developmental biology, from one data point we can predict future spatially resolved gene expression using features from the spatial point processes.
Real-Time Diagnostic Integrity Meets Efficiency: A Novel Platform-Agnostic Architecture for Physiological Signal Compression
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Head-based signals such as EEG, EMG, EOG, and ECG collected by wearable systems will play a pivotal role in clinical diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of important brain disorder diseases. However, the real-time transmission of the significant corpus physiological signals over extended periods consumes substantial power and time, limiting the viability of battery-dependent physiological monitoring wearables. This paper presents a novel deep-learning framework employing a variational autoencoder (VAE) for physiological signal compression to reduce wearables' computational complexity and energy consumption. Our approach achieves an impressive compression ratio of 1:293 specifically for spectrogram data, surpassing state-of-the-art compression techniques such as JPEG2000, H.264, Direct Cosine Transform (DCT), and Huffman Encoding, which do not excel in handling physiological signals. We validate the efficacy of the compressed algorithms using collected physiological signals from real patients in the Hospital and deploy the solution on commonly used embedded AI chips (i.e., ARM Cortex V8 and Jetson Nano). The proposed framework achieves a 91% seizure detection accuracy using XGBoost, confirming the approach's reliability, practicality, and scalability.
Clinically Relevant Latent Space Embedding of Cancer Histopathology Slides through Variational Autoencoder Based Image Compression
Mar 23, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) based training approach that can compress and decompress cancer pathology slides at a compression ratio of 1:512, which is better than the previously reported state of the art (SOTA) in the literature, while still maintaining accuracy in clinical validation tasks. The compression approach was tested on more common computer vision datasets such as CIFAR10, and we explore which image characteristics enable this compression ratio on cancer imaging data but not generic images. We generate and visualize embeddings from the compressed latent space and demonstrate how they are useful for clinical interpretation of data, and how in the future such latent embeddings can be used to accelerate search of clinical imaging data.
A SSIM Guided cGAN Architecture For Clinically Driven Generative Image Synthesis of Multiplexed Spatial Proteomics Channels
May 20, 2022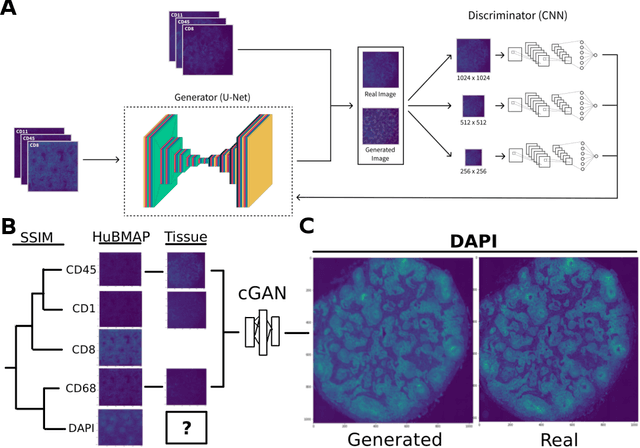
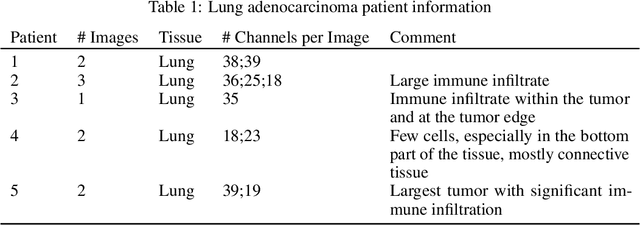

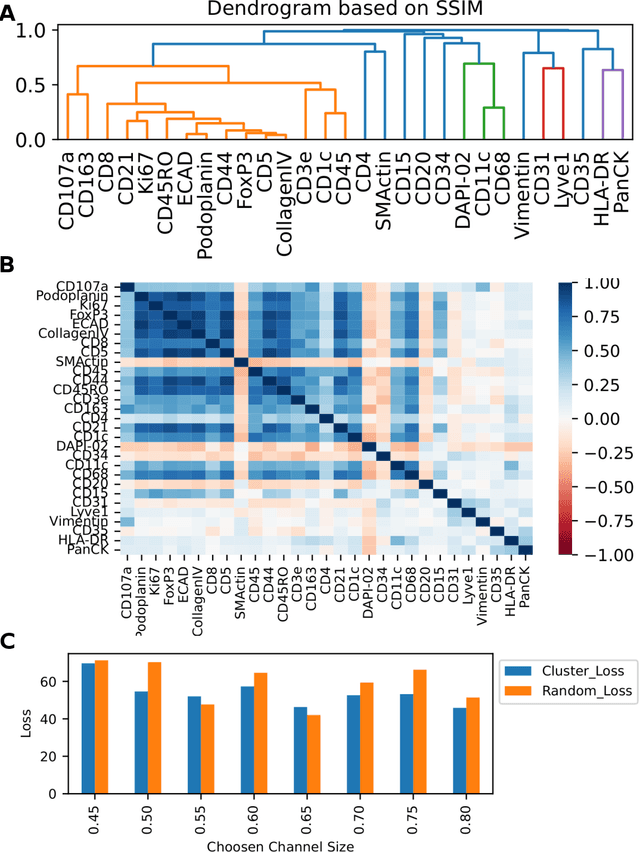
Abstract:Here we present a structural similarity index measure (SSIM) guided conditional Generative Adversarial Network (cGAN) that generatively performs image-to-image (i2i) synthesis to generate photo-accurate protein channels in multiplexed spatial proteomics images. This approach can be utilized to accurately generate missing spatial proteomics channels that were not included during experimental data collection either at the bench or the clinic. Experimental spatial proteomic data from the Human BioMolecular Atlas Program (HuBMAP) was used to generate spatial representations of missing proteins through a U-Net based image synthesis pipeline. HuBMAP channels were hierarchically clustered by the (SSIM) as a heuristic to obtain the minimal set needed to recapitulate the underlying biology represented by the spatial landscape of proteins. We subsequently prove that our SSIM based architecture allows for scaling of generative image synthesis to slides with up to 100 channels, which is better than current state of the art algorithms which are limited to data with 11 channels. We validate these claims by generating a new experimental spatial proteomics data set from human lung adenocarcinoma tissue sections and show that a model trained on HuBMAP can accurately synthesize channels from our new data set. The ability to recapitulate experimental data from sparsely stained multiplexed histological slides containing spatial proteomic will have tremendous impact on medical diagnostics and drug development, and also raises important questions on the medical ethics of utilizing data produced by generative image synthesis in the clinical setting. The algorithm that we present in this paper will allow researchers and clinicians to save time and costs in proteomics based histological staining while also increasing the amount of data that they can generate through their experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge