Atsuhiro Takasu
KG20C & KG20C-QA: Scholarly Knowledge Graph Benchmarks for Link Prediction and Question Answering
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present KG20C and KG20C-QA, two curated datasets for advancing question answering (QA) research on scholarly data. KG20C is a high-quality scholarly knowledge graph constructed from the Microsoft Academic Graph through targeted selection of venues, quality-based filtering, and schema definition. Although KG20C has been available online in non-peer-reviewed sources such as GitHub repository, this paper provides the first formal, peer-reviewed description of the dataset, including clear documentation of its construction and specifications. KG20C-QA is built upon KG20C to support QA tasks on scholarly data. We define a set of QA templates that convert graph triples into natural language question--answer pairs, producing a benchmark that can be used both with graph-based models such as knowledge graph embeddings and with text-based models such as large language models. We benchmark standard knowledge graph embedding methods on KG20C-QA, analyze performance across relation types, and provide reproducible evaluation protocols. By officially releasing these datasets with thorough documentation, we aim to contribute a reusable, extensible resource for the research community, enabling future work in QA, reasoning, and knowledge-driven applications in the scholarly domain. The full datasets will be released at https://github.com/tranhungnghiep/KG20C/ upon paper publication.
Format Matters: The Robustness of Multimodal LLMs in Reviewing Evidence from Tables and Charts
Nov 13, 2025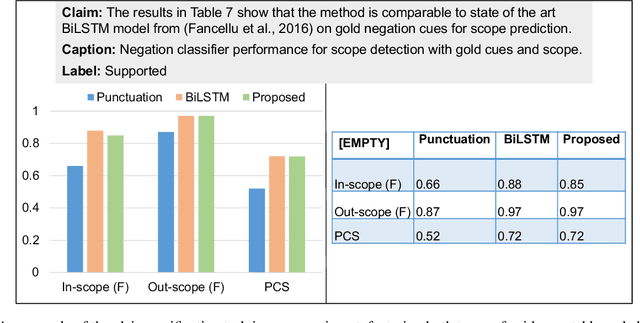
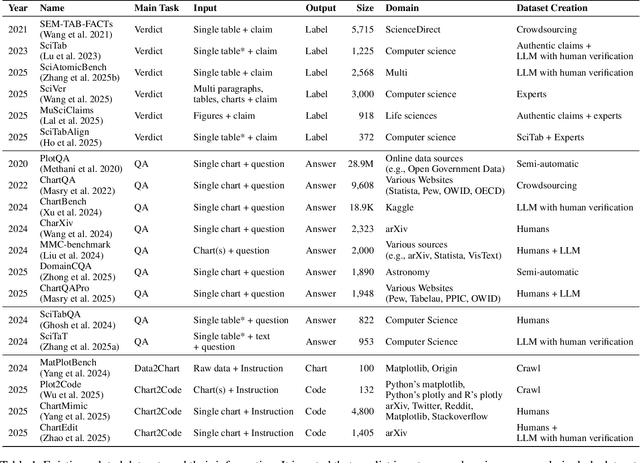
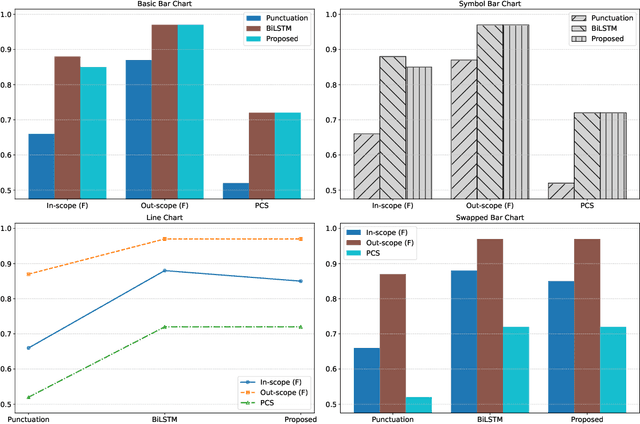
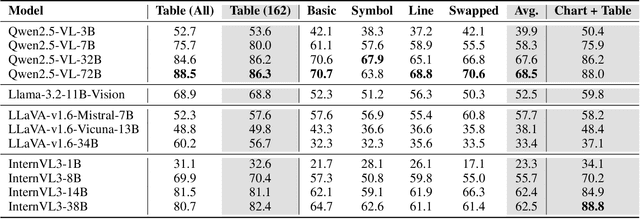
Abstract:With the growing number of submitted scientific papers, there is an increasing demand for systems that can assist reviewers in evaluating research claims. Experimental results are a core component of scientific work, often presented in varying formats such as tables or charts. Understanding how robust current multimodal large language models (multimodal LLMs) are at verifying scientific claims across different evidence formats remains an important and underexplored challenge. In this paper, we design and conduct a series of experiments to assess the ability of multimodal LLMs to verify scientific claims using both tables and charts as evidence. To enable this evaluation, we adapt two existing datasets of scientific papers by incorporating annotations and structures necessary for a multimodal claim verification task. Using this adapted dataset, we evaluate 12 multimodal LLMs and find that current models perform better with table-based evidence while struggling with chart-based evidence. We further conduct human evaluations and observe that humans maintain strong performance across both formats, unlike the models. Our analysis also reveals that smaller multimodal LLMs (under 8B) show weak correlation in performance between table-based and chart-based tasks, indicating limited cross-modal generalization. These findings highlight a critical gap in current models' multimodal reasoning capabilities. We suggest that future multimodal LLMs should place greater emphasis on improving chart understanding to better support scientific claim verification.
Table-Text Alignment: Explaining Claim Verification Against Tables in Scientific Papers
Jun 12, 2025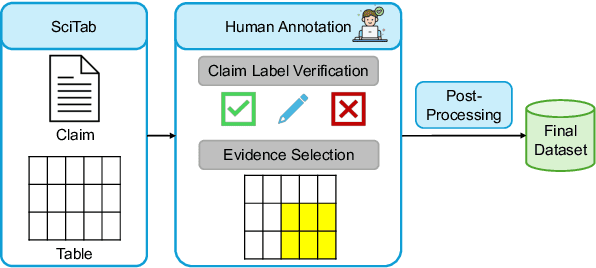
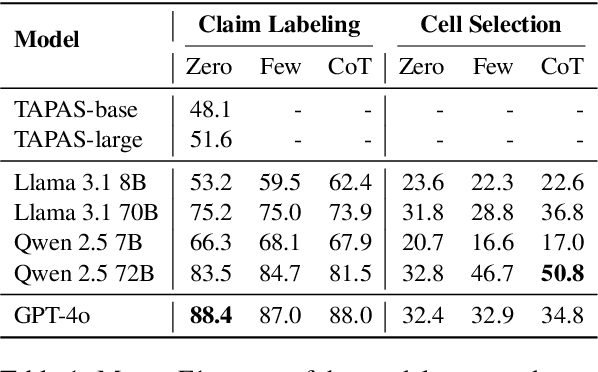
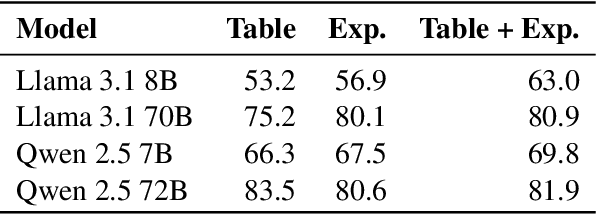
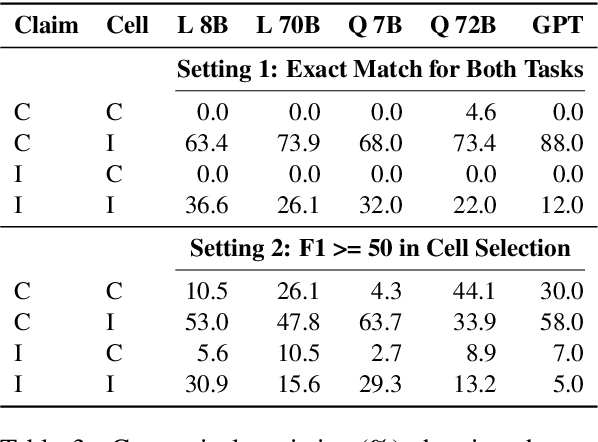
Abstract:Scientific claim verification against tables typically requires predicting whether a claim is supported or refuted given a table. However, we argue that predicting the final label alone is insufficient: it reveals little about the model's reasoning and offers limited interpretability. To address this, we reframe table-text alignment as an explanation task, requiring models to identify the table cells essential for claim verification. We build a new dataset by extending the SciTab benchmark with human-annotated cell-level rationales. Annotators verify the claim label and highlight the minimal set of cells needed to support their decision. After the annotation process, we utilize the collected information and propose a taxonomy for handling ambiguous cases. Our experiments show that (i) incorporating table alignment information improves claim verification performance, and (ii) most LLMs, while often predicting correct labels, fail to recover human-aligned rationales, suggesting that their predictions do not stem from faithful reasoning.
An Encoding--Searching Separation Perspective on Bi-Encoder Neural Search
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:This paper reviews, analyzes, and proposes a new perspective on the bi-encoder architecture for neural search. While the bi-encoder architecture is widely used due to its simplicity and scalability at test time, it has some notable issues such as low performance on seen datasets and weak zero-shot performance on new datasets. In this paper, we analyze these issues and summarize two main critiques: the encoding information bottleneck problem and limitations of the basic assumption of embedding search. We then construct a thought experiment to logically analyze the encoding and searching operations and challenge the basic assumption of embedding search. Building on these observations, we propose a new perspective on the bi-encoder architecture called the \textit{encoding--searching separation} perspective, which conceptually and practically separates the encoding and searching operations. This new perspective is applied to explain the root cause of the identified issues and discuss ways to mitigate the problems. Finally, we discuss the implications of the ideas underlying the new perspective, the design surface that it exposes and the potential research directions arising from it.
On the Trade-off between the Number of Nodes and the Number of Trees in a Random Forest
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we focus on the prediction phase of a random forest and study the problem of representing a bag of decision trees using a smaller bag of decision trees, where we only consider binary decision problems on the binary domain and simple decision trees in which an internal node is limited to querying the Boolean value of a single variable. As a main result, we show that the majority function of $n$ variables can be represented by a bag of $T$ ($< n$) decision trees each with polynomial size if $n-T$ is a constant, where $n$ and $T$ must be odd (in order to avoid the tie break). We also show that a bag of $n$ decision trees can be represented by a bag of $T$ decision trees each with polynomial size if $n-T$ is a constant and a small classification error is allowed. A related result on the $k$-out-of-$n$ functions is presented too.
Melody-conditioned lyrics generation via fine-tuning language model and its evaluation with ChatGPT
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:We leverage character-level language models for syllable-level lyrics generation from symbolic melody. By fine-tuning a character-level pre-trained model, we integrate language knowledge into the beam search of a syllable-level Transformer generator. Using ChatGPT-based evaluations, we demonstrate enhanced coherence and correctness in the generated lyrics.
Controllable Lyrics-to-Melody Generation
Jun 05, 2023Abstract:Lyrics-to-melody generation is an interesting and challenging topic in AI music research field. Due to the difficulty of learning the correlations between lyrics and melody, previous methods suffer from low generation quality and lack of controllability. Controllability of generative models enables human interaction with models to generate desired contents, which is especially important in music generation tasks towards human-centered AI that can facilitate musicians in creative activities. To address these issues, we propose a controllable lyrics-to-melody generation network, ConL2M, which is able to generate realistic melodies from lyrics in user-desired musical style. Our work contains three main novelties: 1) To model the dependencies of music attributes cross multiple sequences, inter-branch memory fusion (Memofu) is proposed to enable information flow between multi-branch stacked LSTM architecture; 2) Reference style embedding (RSE) is proposed to improve the quality of generation as well as control the musical style of generated melodies; 3) Sequence-level statistical loss (SeqLoss) is proposed to help the model learn sequence-level features of melodies given lyrics. Verified by evaluation metrics for music quality and controllability, initial study of controllable lyrics-to-melody generation shows better generation quality and the feasibility of interacting with users to generate the melodies in desired musical styles when given lyrics.
An End-to-End Multi-Task Learning Model for Image-based Table Recognition
Mar 29, 2023



Abstract:Image-based table recognition is a challenging task due to the diversity of table styles and the complexity of table structures. Most of the previous methods focus on a non-end-to-end approach which divides the problem into two separate sub-problems: table structure recognition; and cell-content recognition and then attempts to solve each sub-problem independently using two separate systems. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end multi-task learning model for image-based table recognition. The proposed model consists of one shared encoder, one shared decoder, and three separate decoders which are used for learning three sub-tasks of table recognition: table structure recognition, cell detection, and cell-content recognition. The whole system can be easily trained and inferred in an end-to-end approach. In the experiments, we evaluate the performance of the proposed model on two large-scale datasets: FinTabNet and PubTabNet. The experiment results show that the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in all benchmark datasets.
* 10 pages, VISAPP2023. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2303.07641
TabIQA: Table Questions Answering on Business Document Images
Mar 27, 2023



Abstract:Table answering questions from business documents has many challenges that require understanding tabular structures, cross-document referencing, and additional numeric computations beyond simple search queries. This paper introduces a novel pipeline, named TabIQA, to answer questions about business document images. TabIQA combines state-of-the-art deep learning techniques 1) to extract table content and structural information from images and 2) to answer various questions related to numerical data, text-based information, and complex queries from structured tables. The evaluation results on VQAonBD 2023 dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of TabIQA in achieving promising performance in answering table-related questions. The TabIQA repository is available at https://github.com/phucty/itabqa.
Rethinking Image-based Table Recognition Using Weakly Supervised Methods
Mar 14, 2023



Abstract:Most of the previous methods for table recognition rely on training datasets containing many richly annotated table images. Detailed table image annotation, e.g., cell or text bounding box annotation, however, is costly and often subjective. In this paper, we propose a weakly supervised model named WSTabNet for table recognition that relies only on HTML (or LaTeX) code-level annotations of table images. The proposed model consists of three main parts: an encoder for feature extraction, a structure decoder for generating table structure, and a cell decoder for predicting the content of each cell in the table. Our system is trained end-to-end by stochastic gradient descent algorithms, requiring only table images and their ground-truth HTML (or LaTeX) representations. To facilitate table recognition with deep learning, we create and release WikiTableSet, the largest publicly available image-based table recognition dataset built from Wikipedia. WikiTableSet contains nearly 4 million English table images, 590K Japanese table images, and 640k French table images with corresponding HTML representation and cell bounding boxes. The extensive experiments on WikiTableSet and two large-scale datasets: FinTabNet and PubTabNet demonstrate that the proposed weakly supervised model achieves better, or similar accuracies compared to the state-of-the-art models on all benchmark datasets.
* 10 pages, ICPRAM2023
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge