Xanh Ho
Format Matters: The Robustness of Multimodal LLMs in Reviewing Evidence from Tables and Charts
Nov 13, 2025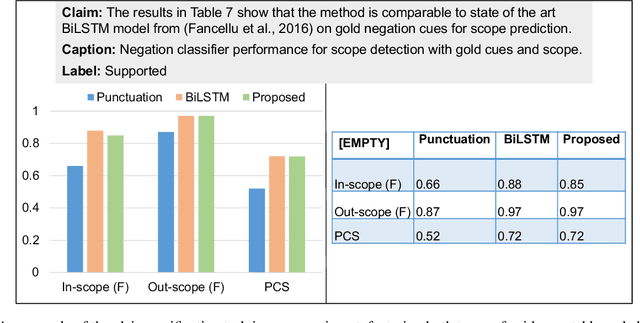
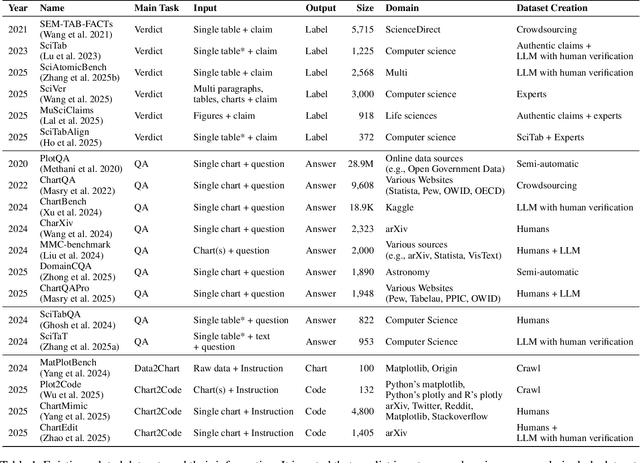
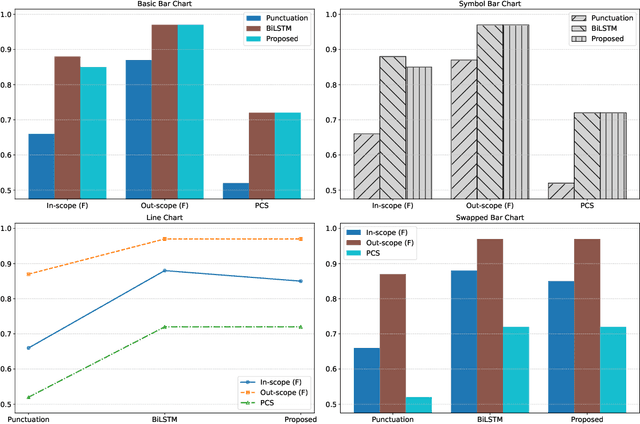
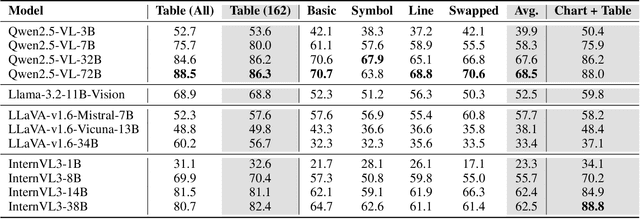
Abstract:With the growing number of submitted scientific papers, there is an increasing demand for systems that can assist reviewers in evaluating research claims. Experimental results are a core component of scientific work, often presented in varying formats such as tables or charts. Understanding how robust current multimodal large language models (multimodal LLMs) are at verifying scientific claims across different evidence formats remains an important and underexplored challenge. In this paper, we design and conduct a series of experiments to assess the ability of multimodal LLMs to verify scientific claims using both tables and charts as evidence. To enable this evaluation, we adapt two existing datasets of scientific papers by incorporating annotations and structures necessary for a multimodal claim verification task. Using this adapted dataset, we evaluate 12 multimodal LLMs and find that current models perform better with table-based evidence while struggling with chart-based evidence. We further conduct human evaluations and observe that humans maintain strong performance across both formats, unlike the models. Our analysis also reveals that smaller multimodal LLMs (under 8B) show weak correlation in performance between table-based and chart-based tasks, indicating limited cross-modal generalization. These findings highlight a critical gap in current models' multimodal reasoning capabilities. We suggest that future multimodal LLMs should place greater emphasis on improving chart understanding to better support scientific claim verification.
Table-Text Alignment: Explaining Claim Verification Against Tables in Scientific Papers
Jun 12, 2025
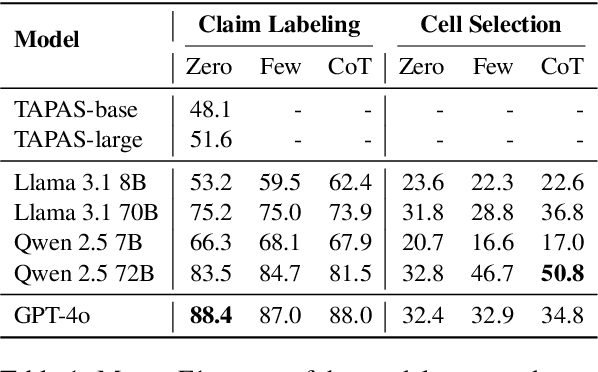
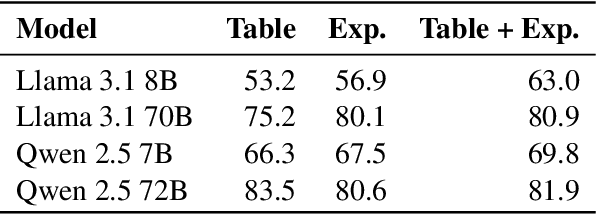
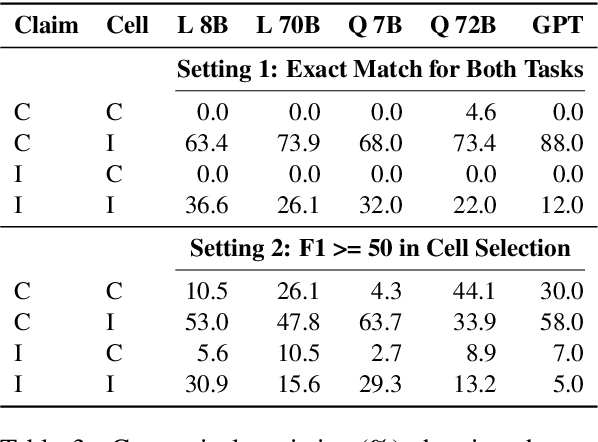
Abstract:Scientific claim verification against tables typically requires predicting whether a claim is supported or refuted given a table. However, we argue that predicting the final label alone is insufficient: it reveals little about the model's reasoning and offers limited interpretability. To address this, we reframe table-text alignment as an explanation task, requiring models to identify the table cells essential for claim verification. We build a new dataset by extending the SciTab benchmark with human-annotated cell-level rationales. Annotators verify the claim label and highlight the minimal set of cells needed to support their decision. After the annotation process, we utilize the collected information and propose a taxonomy for handling ambiguous cases. Our experiments show that (i) incorporating table alignment information improves claim verification performance, and (ii) most LLMs, while often predicting correct labels, fail to recover human-aligned rationales, suggesting that their predictions do not stem from faithful reasoning.
LLM-as-a-Judge: Reassessing the Performance of LLMs in Extractive QA
Apr 16, 2025
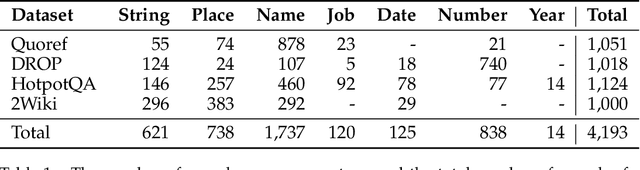
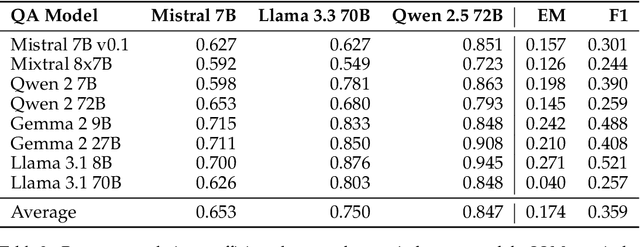
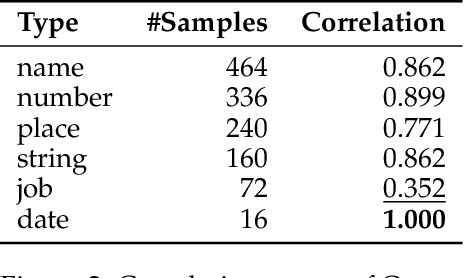
Abstract:Extractive reading comprehension question answering (QA) datasets are typically evaluated using Exact Match (EM) and F1-score, but these metrics often fail to fully capture model performance. With the success of large language models (LLMs), they have been employed in various tasks, including serving as judges (LLM-as-a-judge). In this paper, we reassess the performance of QA models using LLM-as-a-judge across four reading comprehension QA datasets. We examine different families of LLMs and various answer types to evaluate the effectiveness of LLM-as-a-judge in these tasks. Our results show that LLM-as-a-judge is highly correlated with human judgments and can replace traditional EM/F1 metrics. By using LLM-as-a-judge, the correlation with human judgments improves significantly, from 0.17 (EM) and 0.36 (F1-score) to 0.85. These findings confirm that EM and F1 metrics underestimate the true performance of the QA models. While LLM-as-a-judge is not perfect for more difficult answer types (e.g., job), it still outperforms EM/F1, and we observe no bias issues, such as self-preference, when the same model is used for both the QA and judgment tasks.
MoreHopQA: More Than Multi-hop Reasoning
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Most existing multi-hop datasets are extractive answer datasets, where the answers to the questions can be extracted directly from the provided context. This often leads models to use heuristics or shortcuts instead of performing true multi-hop reasoning. In this paper, we propose a new multi-hop dataset, MoreHopQA, which shifts from extractive to generative answers. Our dataset is created by utilizing three existing multi-hop datasets: HotpotQA, 2WikiMultihopQA, and MuSiQue. Instead of relying solely on factual reasoning, we enhance the existing multi-hop questions by adding another layer of questioning that involves one, two, or all three of the following types of reasoning: commonsense, arithmetic, and symbolic. Our dataset is created through a semi-automated process, resulting in a dataset with 1,118 samples that have undergone human verification. We then use our dataset to evaluate five different large language models: Mistral 7B, Gemma 7B, Llama 3 (8B and 70B), and GPT-4. We also design various cases to analyze the reasoning steps in the question-answering process. Our results show that models perform well on initial multi-hop questions but struggle with our extended questions, indicating that our dataset is more challenging than previous ones. Our analysis of question decomposition reveals that although models can correctly answer questions, only a portion - 38.7% for GPT-4 and 33.4% for Llama3-70B - achieve perfect reasoning, where all corresponding sub-questions are answered correctly. Evaluation code and data are available at https://github.com/Alab-NII/morehopqa
A Survey of Pre-trained Language Models for Processing Scientific Text
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:The number of Language Models (LMs) dedicated to processing scientific text is on the rise. Keeping pace with the rapid growth of scientific LMs (SciLMs) has become a daunting task for researchers. To date, no comprehensive surveys on SciLMs have been undertaken, leaving this issue unaddressed. Given the constant stream of new SciLMs, appraising the state-of-the-art and how they compare to each other remain largely unknown. This work fills that gap and provides a comprehensive review of SciLMs, including an extensive analysis of their effectiveness across different domains, tasks and datasets, and a discussion on the challenges that lie ahead.
Solving Label Variation in Scientific Information Extraction via Multi-Task Learning
Dec 25, 2023
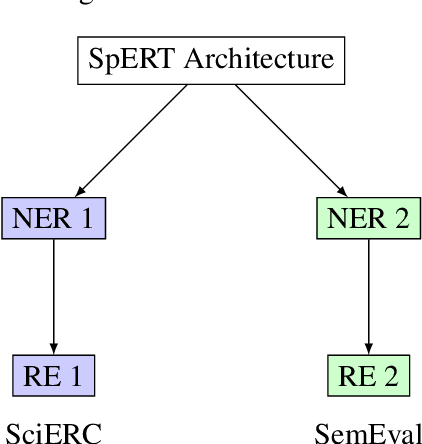


Abstract:Scientific Information Extraction (ScientificIE) is a critical task that involves the identification of scientific entities and their relationships. The complexity of this task is compounded by the necessity for domain-specific knowledge and the limited availability of annotated data. Two of the most popular datasets for ScientificIE are SemEval-2018 Task-7 and SciERC. They have overlapping samples and differ in their annotation schemes, which leads to conflicts. In this study, we first introduced a novel approach based on multi-task learning to address label variations. We then proposed a soft labeling technique that converts inconsistent labels into probabilistic distributions. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed method can enhance the model robustness to label noise and improve the end-to-end performance in both ScientificIE tasks. The analysis revealed that label variations can be particularly effective in handling ambiguous instances. Furthermore, the richness of the information captured by label variations can potentially reduce data size requirements. The findings highlight the importance of releasing variation labels and promote future research on other tasks in other domains. Overall, this study demonstrates the effectiveness of multi-task learning and the potential of label variations to enhance the performance of ScientificIE.
Analyzing the Effectiveness of the Underlying Reasoning Tasks in Multi-hop Question Answering
Feb 12, 2023

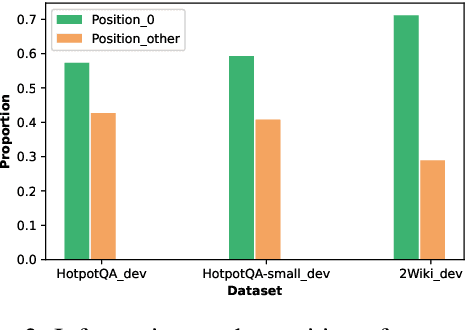

Abstract:To explain the predicted answers and evaluate the reasoning abilities of models, several studies have utilized underlying reasoning (UR) tasks in multi-hop question answering (QA) datasets. However, it remains an open question as to how effective UR tasks are for the QA task when training models on both tasks in an end-to-end manner. In this study, we address this question by analyzing the effectiveness of UR tasks (including both sentence-level and entity-level tasks) in three aspects: (1) QA performance, (2) reasoning shortcuts, and (3) robustness. While the previous models have not been explicitly trained on an entity-level reasoning prediction task, we build a multi-task model that performs three tasks together: sentence-level supporting facts prediction, entity-level reasoning prediction, and answer prediction. Experimental results on 2WikiMultiHopQA and HotpotQA-small datasets reveal that (1) UR tasks can improve QA performance. Using four debiased datasets that are newly created, we demonstrate that (2) UR tasks are helpful in preventing reasoning shortcuts in the multi-hop QA task. However, we find that (3) UR tasks do not contribute to improving the robustness of the model on adversarial questions, such as sub-questions and inverted questions. We encourage future studies to investigate the effectiveness of entity-level reasoning in the form of natural language questions (e.g., sub-question forms).
How Well Do Multi-hop Reading Comprehension Models Understand Date Information?
Oct 11, 2022



Abstract:Several multi-hop reading comprehension datasets have been proposed to resolve the issue of reasoning shortcuts by which questions can be answered without performing multi-hop reasoning. However, the ability of multi-hop models to perform step-by-step reasoning when finding an answer to a comparison question remains unclear. It is also unclear how questions about the internal reasoning process are useful for training and evaluating question-answering (QA) systems. To evaluate the model precisely in a hierarchical manner, we first propose a dataset, \textit{HieraDate}, with three probing tasks in addition to the main question: extraction, reasoning, and robustness. Our dataset is created by enhancing two previous multi-hop datasets, HotpotQA and 2WikiMultiHopQA, focusing on multi-hop questions on date information that involve both comparison and numerical reasoning. We then evaluate the ability of existing models to understand date information. Our experimental results reveal that the multi-hop models do not have the ability to subtract two dates even when they perform well in date comparison and number subtraction tasks. Other results reveal that our probing questions can help to improve the performance of the models (e.g., by +10.3 F1) on the main QA task and our dataset can be used for data augmentation to improve the robustness of the models.
A Survey on Measuring and Mitigating Reasoning Shortcuts in Machine Reading Comprehension
Sep 05, 2022

Abstract:The issue of shortcut learning is widely known in NLP and has been an important research focus in recent years. Unintended correlations in the data enable models to easily solve tasks that were meant to exhibit advanced language understanding and reasoning capabilities. In this survey paper, we focus on the field of machine reading comprehension (MRC), an important task for showcasing high-level language understanding that also suffers from a range of shortcuts. We summarize the available techniques for measuring and mitigating shortcuts and conclude with suggestions for further progress in shortcut research. Most importantly, we highlight two main concerns for shortcut mitigation in MRC: the lack of public challenge sets, a necessary component for effective and reusable evaluation, and the lack of certain mitigation techniques that are prominent in other areas.
Constructing A Multi-hop QA Dataset for Comprehensive Evaluation of Reasoning Steps
Nov 12, 2020



Abstract:A multi-hop question answering (QA) dataset aims to test reasoning and inference skills by requiring a model to read multiple paragraphs to answer a given question. However, current datasets do not provide a complete explanation for the reasoning process from the question to the answer. Further, previous studies revealed that many examples in existing multi-hop datasets do not require multi-hop reasoning to answer a question. In this study, we present a new multi-hop QA dataset, called 2WikiMultiHopQA, which uses structured and unstructured data. In our dataset, we introduce the evidence information containing a reasoning path for multi-hop questions. The evidence information has two benefits: (i) providing a comprehensive explanation for predictions and (ii) evaluating the reasoning skills of a model. We carefully design a pipeline and a set of templates when generating a question-answer pair that guarantees the multi-hop steps and the quality of the questions. We also exploit the structured format in Wikidata and use logical rules to create questions that are natural but still require multi-hop reasoning. Through experiments, we demonstrate that our dataset is challenging for multi-hop models and it ensures that multi-hop reasoning is required.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge