Patrick Ruhkamp
UnReflectAnything: RGB-Only Highlight Removal by Rendering Synthetic Specular Supervision
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Specular highlights distort appearance, obscure texture, and hinder geometric reasoning in both natural and surgical imagery. We present UnReflectAnything, an RGB-only framework that removes highlights from a single image by predicting a highlight map together with a reflection-free diffuse reconstruction. The model uses a frozen vision transformer encoder to extract multi-scale features, a lightweight head to localize specular regions, and a token-level inpainting module that restores corrupted feature patches before producing the final diffuse image. To overcome the lack of paired supervision, we introduce a Virtual Highlight Synthesis pipeline that renders physically plausible specularities using monocular geometry, Fresnel-aware shading, and randomized lighting which enables training on arbitrary RGB images with correct geometric structure. UnReflectAnything generalizes across natural and surgical domains where non-Lambertian surfaces and non-uniform lighting create severe highlights and it achieves competitive performance with state-of-the-art results on several benchmarks. Project Page: https://alberto-rota.github.io/UnReflectAnything/
S2P3: Self-Supervised Polarimetric Pose Prediction
Dec 02, 2023



Abstract:This paper proposes the first self-supervised 6D object pose prediction from multimodal RGB+polarimetric images. The novel training paradigm comprises 1) a physical model to extract geometric information of polarized light, 2) a teacher-student knowledge distillation scheme and 3) a self-supervised loss formulation through differentiable rendering and an invertible physical constraint. Both networks leverage the physical properties of polarized light to learn robust geometric representations by encoding shape priors and polarization characteristics derived from our physical model. Geometric pseudo-labels from the teacher support the student network without the need for annotated real data. Dense appearance and geometric information of objects are obtained through a differentiable renderer with the predicted pose for self-supervised direct coupling. The student network additionally features our proposed invertible formulation of the physical shape priors that enables end-to-end self-supervised training through physical constraints of derived polarization characteristics compared against polarimetric input images. We specifically focus on photometrically challenging objects with texture-less or reflective surfaces and transparent materials for which the most prominent performance gain is reported.
Multi-Modal Dataset Acquisition for Photometrically Challenging Object
Aug 21, 2023Abstract:This paper addresses the limitations of current datasets for 3D vision tasks in terms of accuracy, size, realism, and suitable imaging modalities for photometrically challenging objects. We propose a novel annotation and acquisition pipeline that enhances existing 3D perception and 6D object pose datasets. Our approach integrates robotic forward-kinematics, external infrared trackers, and improved calibration and annotation procedures. We present a multi-modal sensor rig, mounted on a robotic end-effector, and demonstrate how it is integrated into the creation of highly accurate datasets. Additionally, we introduce a freehand procedure for wider viewpoint coverage. Both approaches yield high-quality 3D data with accurate object and camera pose annotations. Our methods overcome the limitations of existing datasets and provide valuable resources for 3D vision research.
Polarimetric Information for Multi-Modal 6D Pose Estimation of Photometrically Challenging Objects with Limited Data
Aug 21, 2023



Abstract:6D pose estimation pipelines that rely on RGB-only or RGB-D data show limitations for photometrically challenging objects with e.g. textureless surfaces, reflections or transparency. A supervised learning-based method utilising complementary polarisation information as input modality is proposed to overcome such limitations. This supervised approach is then extended to a self-supervised paradigm by leveraging physical characteristics of polarised light, thus eliminating the need for annotated real data. The methods achieve significant advancements in pose estimation by leveraging geometric information from polarised light and incorporating shape priors and invertible physical constraints.
On the Importance of Accurate Geometry Data for Dense 3D Vision Tasks
Mar 26, 2023



Abstract:Learning-based methods to solve dense 3D vision problems typically train on 3D sensor data. The respectively used principle of measuring distances provides advantages and drawbacks. These are typically not compared nor discussed in the literature due to a lack of multi-modal datasets. Texture-less regions are problematic for structure from motion and stereo, reflective material poses issues for active sensing, and distances for translucent objects are intricate to measure with existing hardware. Training on inaccurate or corrupt data induces model bias and hampers generalisation capabilities. These effects remain unnoticed if the sensor measurement is considered as ground truth during the evaluation. This paper investigates the effect of sensor errors for the dense 3D vision tasks of depth estimation and reconstruction. We rigorously show the significant impact of sensor characteristics on the learned predictions and notice generalisation issues arising from various technologies in everyday household environments. For evaluation, we introduce a carefully designed dataset\footnote{dataset available at https://github.com/Junggy/HAMMER-dataset} comprising measurements from commodity sensors, namely D-ToF, I-ToF, passive/active stereo, and monocular RGB+P. Our study quantifies the considerable sensor noise impact and paves the way to improved dense vision estimates and targeted data fusion.
HouseCat6D -- A Large-Scale Multi-Modal Category Level 6D Object Pose Dataset with Household Objects in Realistic Scenarios
Dec 21, 2022Abstract:Estimating the 6D pose of objects is one of the major fields in 3D computer vision. Since the promising outcomes from instance-level pose estimation, the research trends are heading towards category-level pose estimation for more practical application scenarios. However, unlike well-established instance-level pose datasets, available category-level datasets lack annotation quality and provided pose quantity. We propose the new category level 6D pose dataset HouseCat6D featuring 1) Multi-modality of Polarimetric RGB+P and Depth, 2) Highly diverse 194 objects of 10 household object categories including 2 photometrically challenging categories, 3) High-quality pose annotation with an error range of only 1.35 mm to 1.74 mm, 4) 41 large scale scenes with extensive viewpoint coverage, 5) Checkerboard-free environment throughout the entire scene. We also provide benchmark results of state-of-the-art category-level pose estimation networks.
Is my Depth Ground-Truth Good Enough? HAMMER -- Highly Accurate Multi-Modal Dataset for DEnse 3D Scene Regression
May 09, 2022
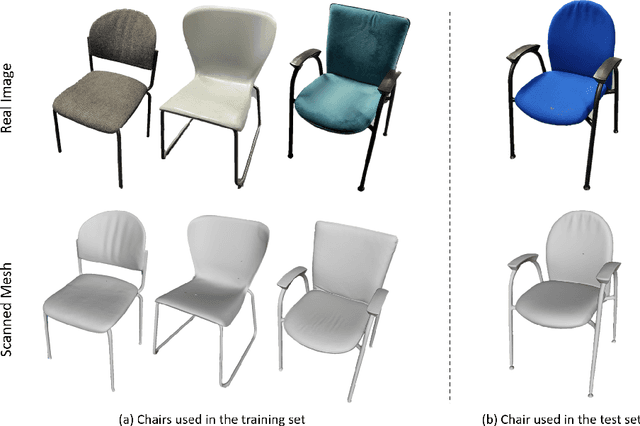
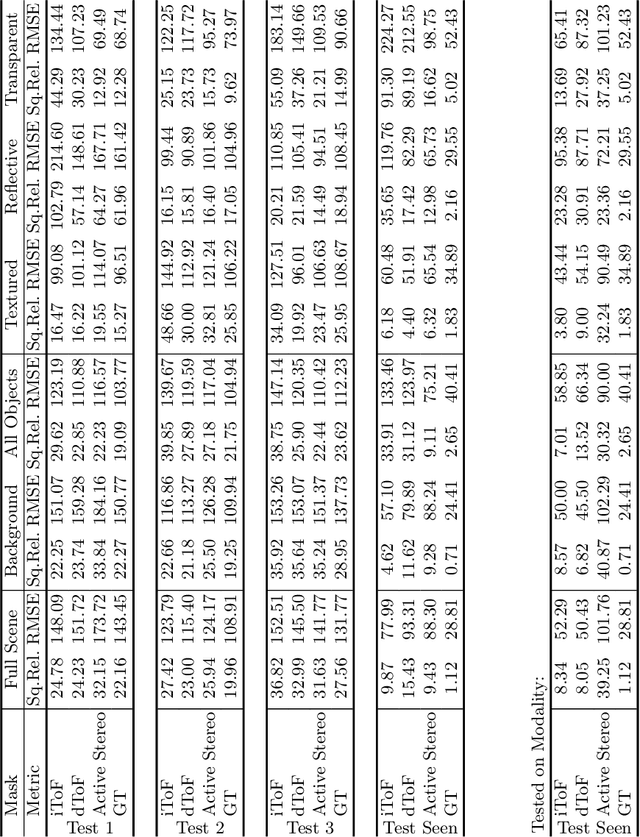
Abstract:Depth estimation is a core task in 3D computer vision. Recent methods investigate the task of monocular depth trained with various depth sensor modalities. Every sensor has its advantages and drawbacks caused by the nature of estimates. In the literature, mostly mean average error of the depth is investigated and sensor capabilities are typically not discussed. Especially indoor environments, however, pose challenges for some devices. Textureless regions pose challenges for structure from motion, reflective materials are problematic for active sensing, and distances for translucent material are intricate to measure with existing sensors. This paper proposes HAMMER, a dataset comprising depth estimates from multiple commonly used sensors for indoor depth estimation, namely ToF, stereo, structured light together with monocular RGB+P data. We construct highly reliable ground truth depth maps with the help of 3D scanners and aligned renderings. A popular depth estimators is trained on this data and typical depth senosors. The estimates are extensively analyze on different scene structures. We notice generalization issues arising from various sensor technologies in household environments with challenging but everyday scene content. HAMMER, which we make publicly available, provides a reliable base to pave the way to targeted depth improvements and sensor fusion approaches.
Towards Remote Robotic Competitions: An Internet-Connected Task Board and Dashboard
Jan 24, 2022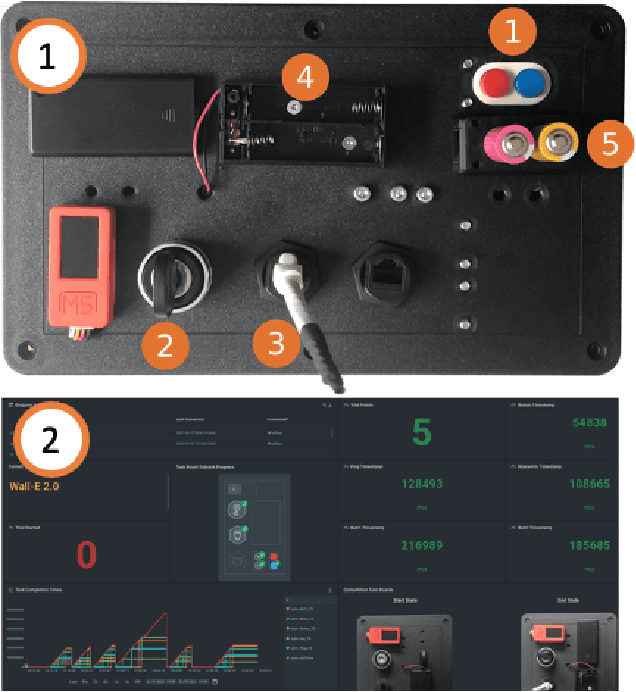
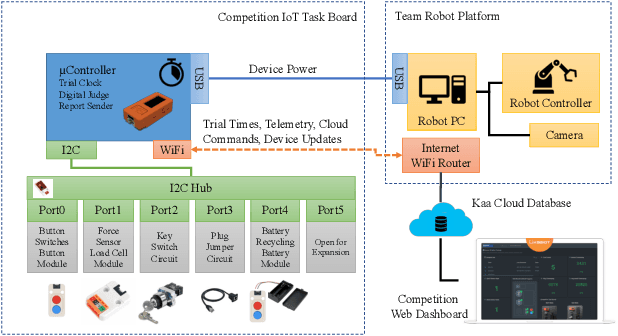
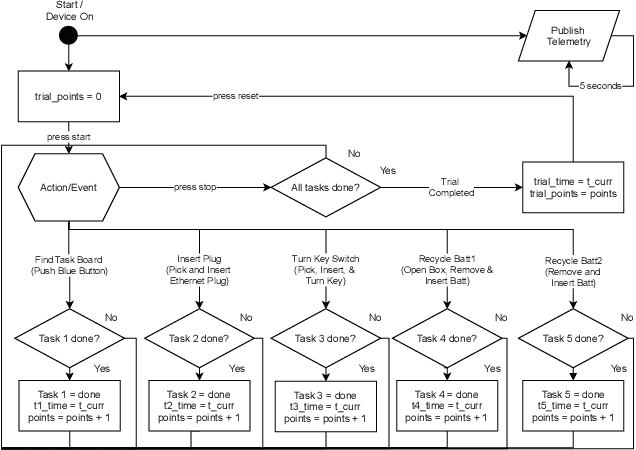
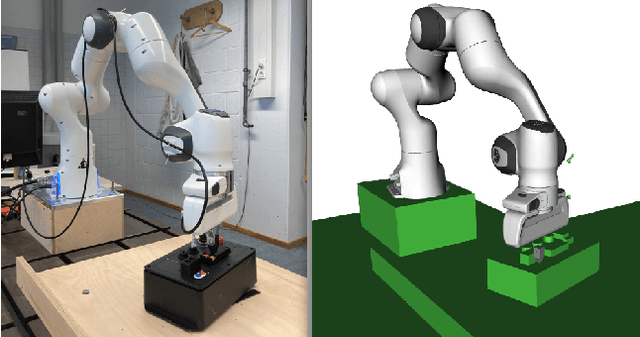
Abstract:In this work we present a platform to assess robot platform skills using an internet-of-things (IoT) task board device to aggregate performances across remote sites. We demonstrate a concept for a modular, scale-able device and web dashboard enabling remote competitions as an alternative to in-person robot competitions. We share data from nine robot platforms located across four continents in three manipulation task categories of object localization, object insertion, and component disassembly through an organized international robot competition - the Robothon Grand Challenge. This paper discusses the design of an electronic task board, the strategies implemented by the top-performing teams and compares their results with a benchmark solution to the presented task board. Through this platform, we demonstrate fully remote, online competitions can generate innovative robotic solutions and tested a tool for measuring remote performances. Using the open-sourced task board code and design files, the reader can reproduce the benchmark solution or configure the platform for their own use case and share their results transparently without transporting their robot platform.
Looking Beyond Corners: Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations for Keypoint Detection and Description Extraction
Dec 22, 2021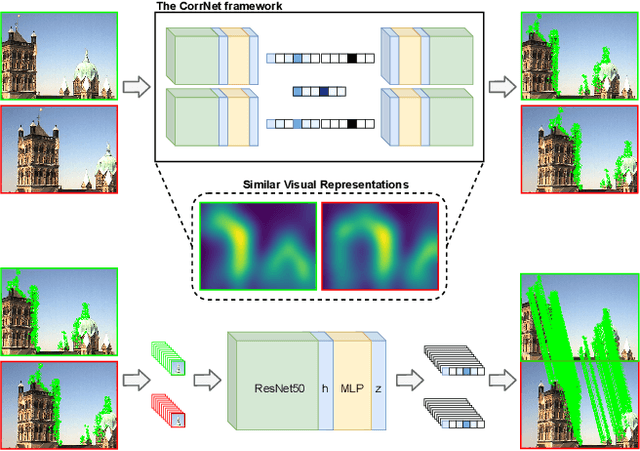
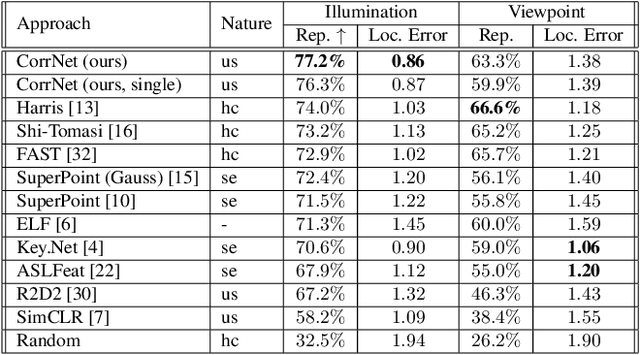

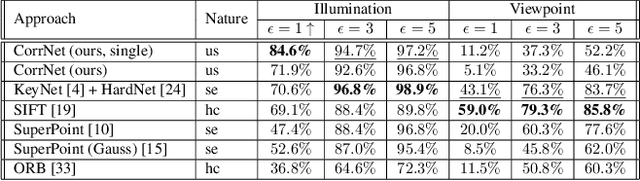
Abstract:Learnable keypoint detectors and descriptors are beginning to outperform classical hand-crafted feature extraction methods. Recent studies on self-supervised learning of visual representations have driven the increasing performance of learnable models based on deep networks. By leveraging traditional data augmentations and homography transformations, these networks learn to detect corners under adverse conditions such as extreme illumination changes. However, their generalization capabilities are limited to corner-like features detected a priori by classical methods or synthetically generated data. In this paper, we propose the Correspondence Network (CorrNet) that learns to detect repeatable keypoints and to extract discriminative descriptions via unsupervised contrastive learning under spatial constraints. Our experiments show that CorrNet is not only able to detect low-level features such as corners, but also high-level features that represent similar objects present in a pair of input images through our proposed joint guided backpropagation of their latent space. Our approach obtains competitive results under viewpoint changes and achieves state-of-the-art performance under illumination changes.
Polarimetric Pose Prediction
Dec 07, 2021
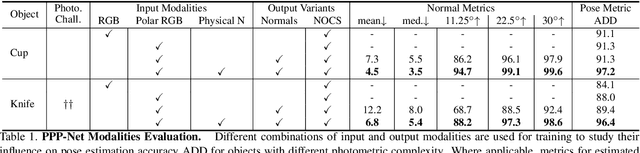
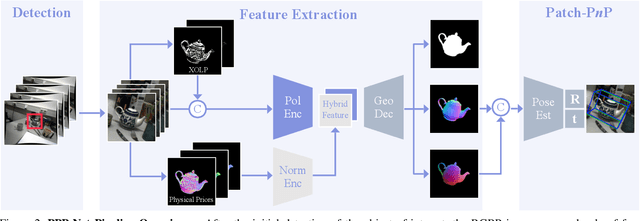
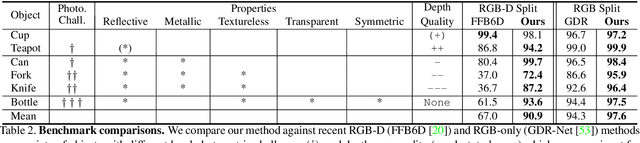
Abstract:Light has many properties that can be passively measured by vision sensors. Colour-band separated wavelength and intensity are arguably the most commonly used ones for monocular 6D object pose estimation. This paper explores how complementary polarisation information, i.e. the orientation of light wave oscillations, can influence the accuracy of pose predictions. A hybrid model that leverages physical priors jointly with a data-driven learning strategy is designed and carefully tested on objects with different amount of photometric complexity. Our design not only significantly improves the pose accuracy in relation to photometric state-of-the-art approaches, but also enables object pose estimation for highly reflective and transparent objects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge