Markus Karmann
M2N2V2: Multi-Modal Unsupervised and Training-free Interactive Segmentation
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:We present Markov Map Nearest Neighbor V2 (M2N2V2), a novel and simple, yet effective approach which leverages depth guidance and attention maps for unsupervised and training-free point-prompt-based interactive segmentation. Following recent trends in supervised multimodal approaches, we carefully integrate depth as an additional modality to create novel depth-guided Markov-maps. Furthermore, we observe occasional segment size fluctuations in M2N2 during the interactive process, which can decrease the overall mIoU's. To mitigate this problem, we model the prompting as a sequential process and propose a novel adaptive score function which considers the previous segmentation and the current prompt point in order to prevent unreasonable segment size changes. Using Stable Diffusion 2 and Depth Anything V2 as backbones, we empirically show that our proposed M2N2V2 significantly improves the Number of Clicks (NoC) and mIoU compared to M2N2 in all datasets except those from the medical domain. Interestingly, our unsupervised approach achieves competitive results compared to supervised methods like SAM and SimpleClick in the more challenging DAVIS and HQSeg44K datasets in the NoC metric, reducing the gap between supervised and unsupervised methods.
Repurposing Stable Diffusion Attention for Training-Free Unsupervised Interactive Segmentation
Nov 15, 2024

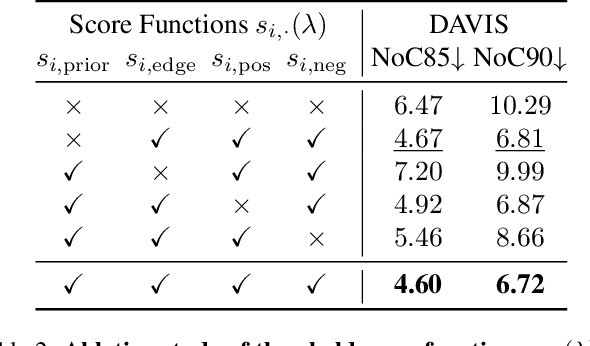

Abstract:Recent progress in interactive point prompt based Image Segmentation allows to significantly reduce the manual effort to obtain high quality semantic labels. State-of-the-art unsupervised methods use self-supervised pre-trained models to obtain pseudo-labels which are used in training a prompt-based segmentation model. In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised and training-free approach based solely on the self-attention of Stable Diffusion. We interpret the self-attention tensor as a Markov transition operator, which enables us to iteratively construct a Markov chain. Pixel-wise counting of the required number of iterations along the Markov-chain to reach a relative probability threshold yields a Markov-iteration-map, which we simply call a Markov-map. Compared to the raw attention maps, we show that our proposed Markov-map has less noise, sharper semantic boundaries and more uniform values within semantically similar regions. We integrate the Markov-map in a simple yet effective truncated nearest neighbor framework to obtain interactive point prompt based segmentation. Despite being training-free, we experimentally show that our approach yields excellent results in terms of Number of Clicks (NoC), even outperforming state-of-the-art training based unsupervised methods in most of the datasets.
MLV$^2$-Net: Rater-Based Majority-Label Voting for Consistent Meningeal Lymphatic Vessel Segmentation
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:Meningeal lymphatic vessels (MLVs) are responsible for the drainage of waste products from the human brain. An impairment in their functionality has been associated with aging as well as brain disorders like multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. However, MLVs have only recently been described for the first time in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and their ramified structure renders manual segmentation particularly difficult. Further, as there is no consistent notion of their appearance, human-annotated MLV structures contain a high inter-rater variability that most automatic segmentation methods cannot take into account. In this work, we propose a new rater-aware training scheme for the popular nnU-Net model, and we explore rater-based ensembling strategies for accurate and consistent segmentation of MLVs. This enables us to boost nnU-Net's performance while obtaining explicit predictions in different annotation styles and a rater-based uncertainty estimation. Our final model, MLV$^2$-Net, achieves a Dice similarity coefficient of 0.806 with respect to the human reference standard. The model further matches the human inter-rater reliability and replicates age-related associations with MLV volume.
Looking Beyond Corners: Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations for Keypoint Detection and Description Extraction
Dec 22, 2021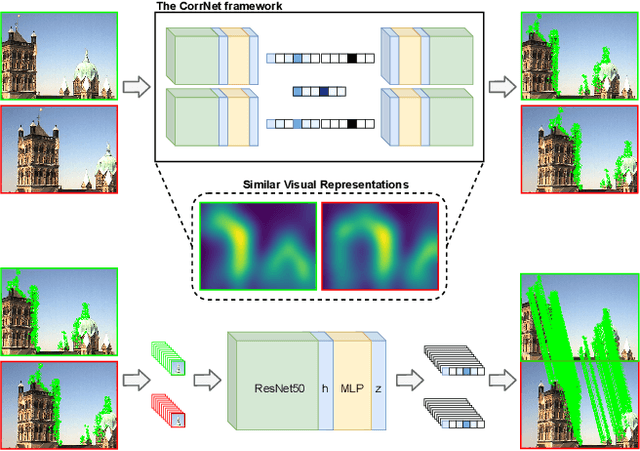
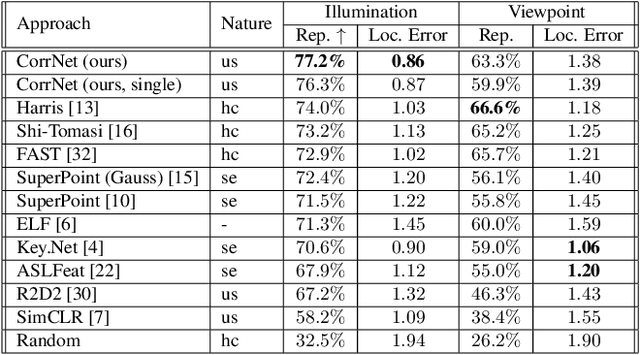

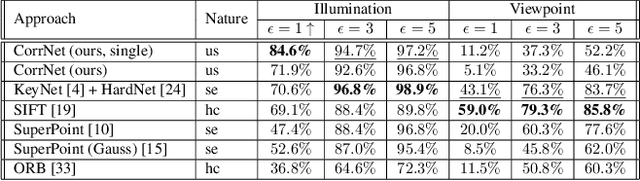
Abstract:Learnable keypoint detectors and descriptors are beginning to outperform classical hand-crafted feature extraction methods. Recent studies on self-supervised learning of visual representations have driven the increasing performance of learnable models based on deep networks. By leveraging traditional data augmentations and homography transformations, these networks learn to detect corners under adverse conditions such as extreme illumination changes. However, their generalization capabilities are limited to corner-like features detected a priori by classical methods or synthetically generated data. In this paper, we propose the Correspondence Network (CorrNet) that learns to detect repeatable keypoints and to extract discriminative descriptions via unsupervised contrastive learning under spatial constraints. Our experiments show that CorrNet is not only able to detect low-level features such as corners, but also high-level features that represent similar objects present in a pair of input images through our proposed joint guided backpropagation of their latent space. Our approach obtains competitive results under viewpoint changes and achieves state-of-the-art performance under illumination changes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge