Luca Zancato
Maximally-Informative Retrieval for State Space Model Generation
Jun 13, 2025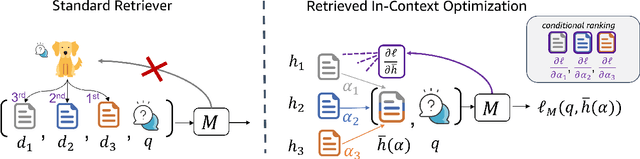
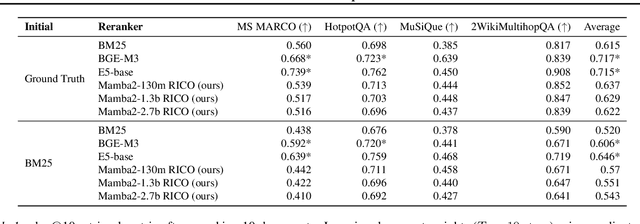
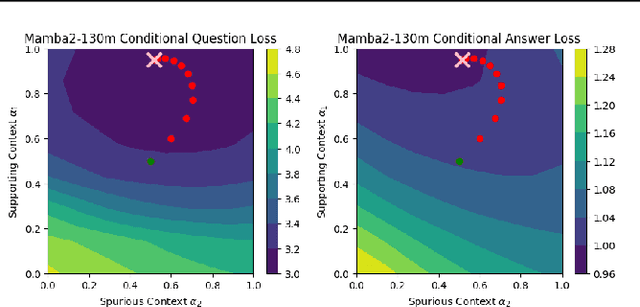
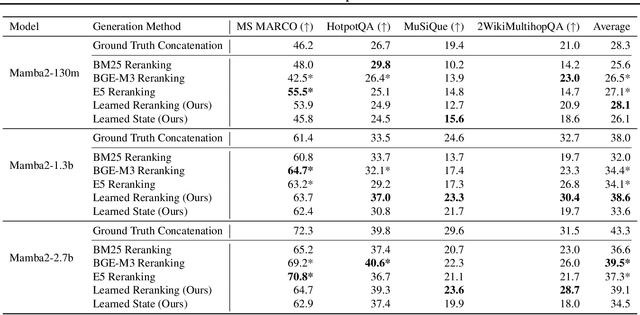
Abstract:Given a query and dataset, the optimal way of answering the query is to make use all the information available. Modern LLMs exhibit impressive ability to memorize training data, but data not deemed important during training is forgotten, and information outside that training set cannot be made use of. Processing an entire dataset at inference time is infeasible due to the bounded nature of model resources (e.g. context size in transformers or states in state space models), meaning we must resort to external memory. This constraint naturally leads to the following problem: How can we decide based on the present query and model, what among a virtually unbounded set of known data matters for inference? To minimize model uncertainty for a particular query at test-time, we introduce Retrieval In-Context Optimization (RICO), a retrieval method that uses gradients from the LLM itself to learn the optimal mixture of documents for answer generation. Unlike traditional retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which relies on external heuristics for document retrieval, our approach leverages direct feedback from the model. Theoretically, we show that standard top-$k$ retrieval with model gradients can approximate our optimization procedure, and provide connections to the leave-one-out loss. We demonstrate empirically that by minimizing an unsupervised loss objective in the form of question perplexity, we can achieve comparable retriever metric performance to BM25 with \emph{no finetuning}. Furthermore, when evaluated on quality of the final prediction, our method often outperforms fine-tuned dense retrievers such as E5.
PICASO: Permutation-Invariant Context Composition with State Space Models
Feb 24, 2025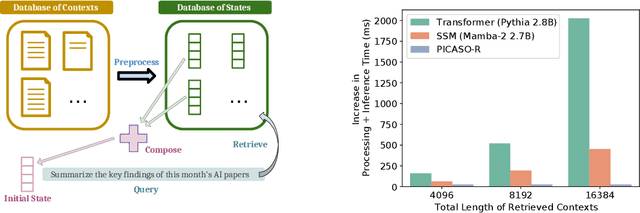

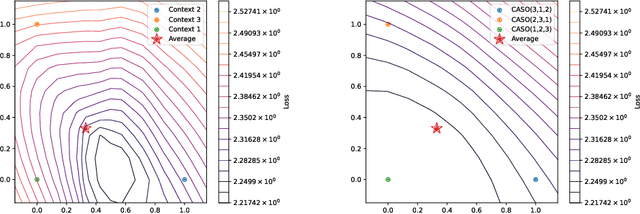

Abstract:Providing Large Language Models with relevant contextual knowledge at inference time has been shown to greatly improve the quality of their generations. This is often achieved by prepending informative passages of text, or 'contexts', retrieved from external knowledge bases to their input. However, processing additional contexts online incurs significant computation costs that scale with their length. State Space Models (SSMs) offer a promising solution by allowing a database of contexts to be mapped onto fixed-dimensional states from which to start the generation. A key challenge arises when attempting to leverage information present across multiple contexts, since there is no straightforward way to condition generation on multiple independent states in existing SSMs. To address this, we leverage a simple mathematical relation derived from SSM dynamics to compose multiple states into one that efficiently approximates the effect of concatenating textual contexts. Since the temporal ordering of contexts can often be uninformative, we enforce permutation-invariance by efficiently averaging states obtained via our composition algorithm across all possible context orderings. We evaluate our resulting method on WikiText and MSMARCO in both zero-shot and fine-tuned settings, and show that we can match the strongest performing baseline while enjoying on average 5.4x speedup.
Descriminative-Generative Custom Tokens for Vision-Language Models
Feb 17, 2025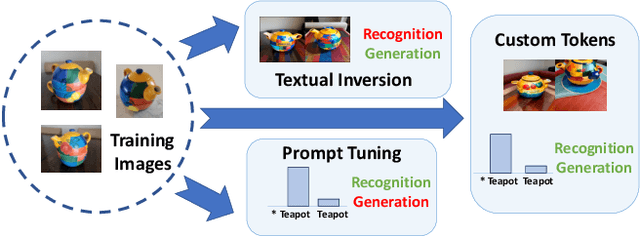

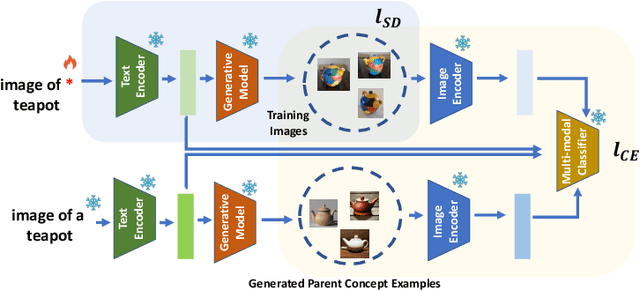
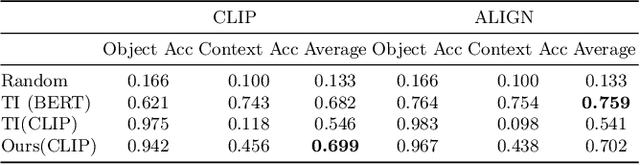
Abstract:This paper explores the possibility of learning custom tokens for representing new concepts in Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Our aim is to learn tokens that can be effective for both discriminative and generative tasks while composing well with words to form new input queries. The targeted concept is specified in terms of a small set of images and a parent concept described using text. We operate on CLIP text features and propose to use a combination of a textual inversion loss and a classification loss to ensure that text features of the learned token are aligned with image features of the concept in the CLIP embedding space. We restrict the learned token to a low-dimensional subspace spanned by tokens for attributes that are appropriate for the given super-class. These modifications improve the quality of compositions of the learned token with natural language for generating new scenes. Further, we show that learned custom tokens can be used to form queries for text-to-image retrieval task, and also have the important benefit that composite queries can be visualized to ensure that the desired concept is faithfully encoded. Based on this, we introduce the method of Generation Aided Image Retrieval, where the query is modified at inference time to better suit the search intent. On the DeepFashion2 dataset, our method improves Mean Reciprocal Retrieval (MRR) over relevant baselines by 7%.
Expansion Span: Combining Fading Memory and Retrieval in Hybrid State Space Models
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:The "state" of State Space Models (SSMs) represents their memory, which fades exponentially over an unbounded span. By contrast, Attention-based models have "eidetic" (i.e., verbatim, or photographic) memory over a finite span (context size). Hybrid architectures combine State Space layers with Attention, but still cannot recall the distant past and can access only the most recent tokens eidetically. Unlike current methods of combining SSM and Attention layers, we allow the state to be allocated based on relevancy rather than recency. In this way, for every new set of query tokens, our models can "eidetically" access tokens from beyond the Attention span of current Hybrid SSMs without requiring extra hardware resources. We describe a method to expand the memory span of the hybrid state by "reserving" a fraction of the Attention context for tokens retrieved from arbitrarily distant in the past, thus expanding the eidetic memory span of the overall state. We call this reserved fraction of tokens the "expansion span," and the mechanism to retrieve and aggregate it "Span-Expanded Attention" (SE-Attn). To adapt Hybrid models to using SE-Attn, we propose a novel fine-tuning method that extends LoRA to Hybrid models (HyLoRA) and allows efficient adaptation on long spans of tokens. We show that SE-Attn enables us to efficiently adapt pre-trained Hybrid models on sequences of tokens up to 8 times longer than the ones used for pre-training. We show that HyLoRA with SE-Attn is cheaper and more performant than alternatives like LongLoRA when applied to Hybrid models on natural language benchmarks with long-range dependencies, such as PG-19, RULER, and other common natural language downstream tasks.
Marconi: Prefix Caching for the Era of Hybrid LLMs
Nov 28, 2024



Abstract:Hybrid models that combine the language modeling capabilities of Attention layers with the efficiency of Recurrent layers (e.g., State Space Models) have gained traction in practically supporting long contexts in Large Language Model serving. Yet, the unique properties of these models complicate the usage of complementary efficiency optimizations such as prefix caching that skip redundant computations across requests. Most notably, their use of in-place state updates for recurrent layers precludes rolling back cache entries for partial sequence overlaps, and instead mandates only exact-match cache hits; the effect is a deluge of (large) cache entries per sequence, most of which yield minimal reuse opportunities. We present Marconi, the first system that supports efficient prefix caching with Hybrid LLMs. Key to Marconi are its novel admission and eviction policies that more judiciously assess potential cache entries based not only on recency, but also on (1) forecasts of their reuse likelihood across a taxonomy of different hit scenarios, and (2) the compute savings that hits deliver relative to memory footprints. Across diverse workloads and Hybrid models, Marconi achieves up to 34.4$\times$ higher token hit rates (71.1% or 617 ms lower TTFT) compared to state-of-the-art prefix caching systems.
Compositional Structures in Neural Embedding and Interaction Decompositions
Jul 12, 2024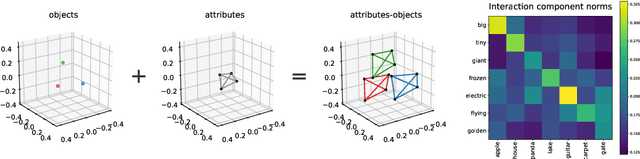
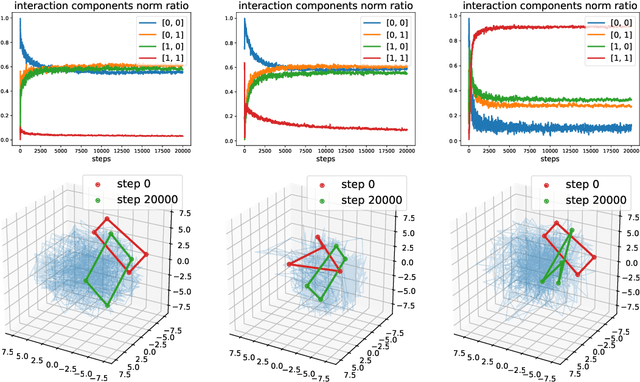
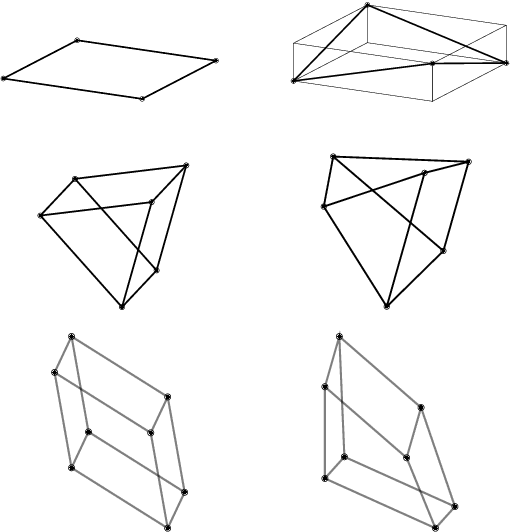
Abstract:We describe a basic correspondence between linear algebraic structures within vector embeddings in artificial neural networks and conditional independence constraints on the probability distributions modeled by these networks. Our framework aims to shed light on the emergence of structural patterns in data representations, a phenomenon widely acknowledged but arguably still lacking a solid formal grounding. Specifically, we introduce a characterization of compositional structures in terms of "interaction decompositions," and we establish necessary and sufficient conditions for the presence of such structures within the representations of a model.
B'MOJO: Hybrid State Space Realizations of Foundation Models with Eidetic and Fading Memory
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:We describe a family of architectures to support transductive inference by allowing memory to grow to a finite but a-priori unknown bound while making efficient use of finite resources for inference. Current architectures use such resources to represent data either eidetically over a finite span ("context" in Transformers), or fading over an infinite span (in State Space Models, or SSMs). Recent hybrid architectures have combined eidetic and fading memory, but with limitations that do not allow the designer or the learning process to seamlessly modulate the two, nor to extend the eidetic memory span. We leverage ideas from Stochastic Realization Theory to develop a class of models called B'MOJO to seamlessly combine eidetic and fading memory within an elementary composable module. The overall architecture can be used to implement models that can access short-term eidetic memory "in-context," permanent structural memory "in-weights," fading memory "in-state," and long-term eidetic memory "in-storage" by natively incorporating retrieval from an asynchronously updated memory. We show that Transformers, existing SSMs such as Mamba, and hybrid architectures such as Jamba are special cases of B'MOJO and describe a basic implementation, to be open sourced, that can be stacked and scaled efficiently in hardware. We test B'MOJO on transductive inference tasks, such as associative recall, where it outperforms existing SSMs and Hybrid models; as a baseline, we test ordinary language modeling where B'MOJO achieves perplexity comparable to similarly-sized Transformers and SSMs up to 1.4B parameters, while being up to 10% faster to train. Finally, we show that B'MOJO's ability to modulate eidetic and fading memory results in better inference on longer sequences tested up to 32K tokens, four-fold the length of the longest sequences seen during training.
CPR: Retrieval Augmented Generation for Copyright Protection
Mar 27, 2024Abstract:Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is emerging as a flexible and robust technique to adapt models to private users data without training, to handle credit attribution, and to allow efficient machine unlearning at scale. However, RAG techniques for image generation may lead to parts of the retrieved samples being copied in the model's output. To reduce risks of leaking private information contained in the retrieved set, we introduce Copy-Protected generation with Retrieval (CPR), a new method for RAG with strong copyright protection guarantees in a mixed-private setting for diffusion models.CPR allows to condition the output of diffusion models on a set of retrieved images, while also guaranteeing that unique identifiable information about those example is not exposed in the generated outputs. In particular, it does so by sampling from a mixture of public (safe) distribution and private (user) distribution by merging their diffusion scores at inference. We prove that CPR satisfies Near Access Freeness (NAF) which bounds the amount of information an attacker may be able to extract from the generated images. We provide two algorithms for copyright protection, CPR-KL and CPR-Choose. Unlike previously proposed rejection-sampling-based NAF methods, our methods enable efficient copyright-protected sampling with a single run of backward diffusion. We show that our method can be applied to any pre-trained conditional diffusion model, such as Stable Diffusion or unCLIP. In particular, we empirically show that applying CPR on top of unCLIP improves quality and text-to-image alignment of the generated results (81.4 to 83.17 on TIFA benchmark), while enabling credit attribution, copy-right protection, and deterministic, constant time, unlearning.
Multi-Modal Hallucination Control by Visual Information Grounding
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:Generative Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are prone to generate plausible-sounding textual answers that, however, are not always grounded in the input image. We investigate this phenomenon, usually referred to as "hallucination" and show that it stems from an excessive reliance on the language prior. In particular, we show that as more tokens are generated, the reliance on the visual prompt decreases, and this behavior strongly correlates with the emergence of hallucinations. To reduce hallucinations, we introduce Multi-Modal Mutual-Information Decoding (M3ID), a new sampling method for prompt amplification. M3ID amplifies the influence of the reference image over the language prior, hence favoring the generation of tokens with higher mutual information with the visual prompt. M3ID can be applied to any pre-trained autoregressive VLM at inference time without necessitating further training and with minimal computational overhead. If training is an option, we show that M3ID can be paired with Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to improve the model's reliance on the prompt image without requiring any labels. Our empirical findings show that our algorithms maintain the fluency and linguistic capabilities of pre-trained VLMs while reducing hallucinations by mitigating visually ungrounded answers. Specifically, for the LLaVA 13B model, M3ID and M3ID+DPO reduce the percentage of hallucinated objects in captioning tasks by 25% and 28%, respectively, and improve the accuracy on VQA benchmarks such as POPE by 21% and 24%.
SemiGPC: Distribution-Aware Label Refinement for Imbalanced Semi-Supervised Learning Using Gaussian Processes
Nov 03, 2023
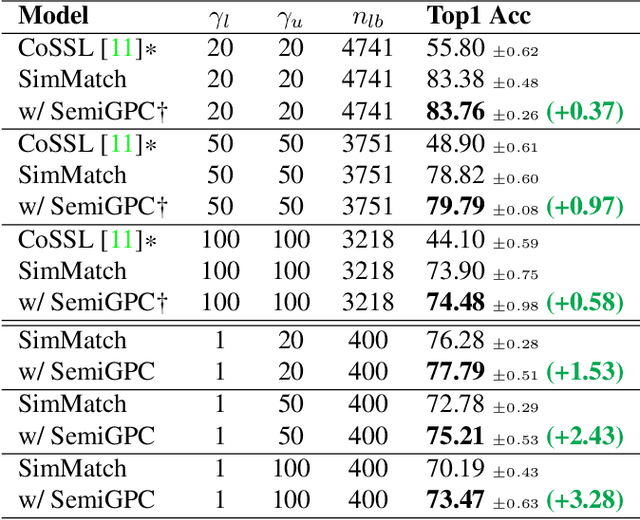

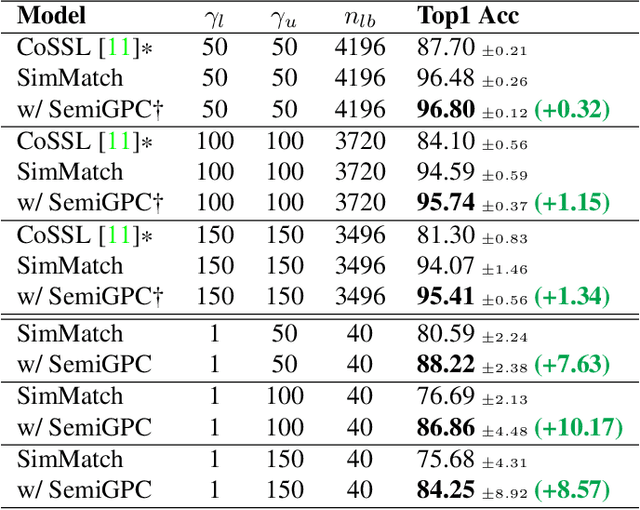
Abstract:In this paper we introduce SemiGPC, a distribution-aware label refinement strategy based on Gaussian Processes where the predictions of the model are derived from the labels posterior distribution. Differently from other buffer-based semi-supervised methods such as CoMatch and SimMatch, our SemiGPC includes a normalization term that addresses imbalances in the global data distribution while maintaining local sensitivity. This explicit control allows SemiGPC to be more robust to confirmation bias especially under class imbalance. We show that SemiGPC improves performance when paired with different Semi-Supervised methods such as FixMatch, ReMixMatch, SimMatch and FreeMatch and different pre-training strategies including MSN and Dino. We also show that SemiGPC achieves state of the art results under different degrees of class imbalance on standard CIFAR10-LT/CIFAR100-LT especially in the low data-regime. Using SemiGPC also results in about 2% avg.accuracy increase compared to a new competitive baseline on the more challenging benchmarks SemiAves, SemiCUB, SemiFungi and Semi-iNat.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge