Davide Modolo
Self-Supervised Multi-Object Tracking with Path Consistency
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel concept of path consistency to learn robust object matching without using manual object identity supervision. Our key idea is that, to track a object through frames, we can obtain multiple different association results from a model by varying the frames it can observe, i.e., skipping frames in observation. As the differences in observations do not alter the identities of objects, the obtained association results should be consistent. Based on this rationale, we generate multiple observation paths, each specifying a different set of frames to be skipped, and formulate the Path Consistency Loss that enforces the association results are consistent across different observation paths. We use the proposed loss to train our object matching model with only self-supervision. By extensive experiments on three tracking datasets (MOT17, PersonPath22, KITTI), we demonstrate that our method outperforms existing unsupervised methods with consistent margins on various evaluation metrics, and even achieves performance close to supervised methods.
Hyperbolic Learning with Synthetic Captions for Open-World Detection
Apr 07, 2024



Abstract:Open-world detection poses significant challenges, as it requires the detection of any object using either object class labels or free-form texts. Existing related works often use large-scale manual annotated caption datasets for training, which are extremely expensive to collect. Instead, we propose to transfer knowledge from vision-language models (VLMs) to enrich the open-vocabulary descriptions automatically. Specifically, we bootstrap dense synthetic captions using pre-trained VLMs to provide rich descriptions on different regions in images, and incorporate these captions to train a novel detector that generalizes to novel concepts. To mitigate the noise caused by hallucination in synthetic captions, we also propose a novel hyperbolic vision-language learning approach to impose a hierarchy between visual and caption embeddings. We call our detector ``HyperLearner''. We conduct extensive experiments on a wide variety of open-world detection benchmarks (COCO, LVIS, Object Detection in the Wild, RefCOCO) and our results show that our model consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, such as GLIP, GLIPv2 and Grounding DINO, when using the same backbone.
Early Action Recognition with Action Prototypes
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Early action recognition is an important and challenging problem that enables the recognition of an action from a partially observed video stream where the activity is potentially unfinished or even not started. In this work, we propose a novel model that learns a prototypical representation of the full action for each class and uses it to regularize the architecture and the visual representations of the partial observations. Our model is very simple in design and also efficient. We decompose the video into short clips, where a visual encoder extracts features from each clip independently. Later, a decoder aggregates together in an online fashion features from all the clips for the final class prediction. During training, for each partial observation, the model is jointly trained to both predict the label as well as the action prototypical representation which acts as a regularizer. We evaluate our method on multiple challenging real-world datasets and outperform the current state-of-the-art by a significant margin. For example, on early recognition observing only the first 10% of each video, our method improves the SOTA by +2.23 Top-1 accuracy on Something-Something-v2, +3.55 on UCF-101, +3.68 on SSsub21, and +5.03 on EPIC-Kitchens-55, where prior work used either multi-modal inputs (e.g. optical-flow) or batched inference. Finally, we also present exhaustive ablation studies to motivate the design choices we made, as well as gather insights regarding what our model is learning semantically.
SemiGPC: Distribution-Aware Label Refinement for Imbalanced Semi-Supervised Learning Using Gaussian Processes
Nov 03, 2023
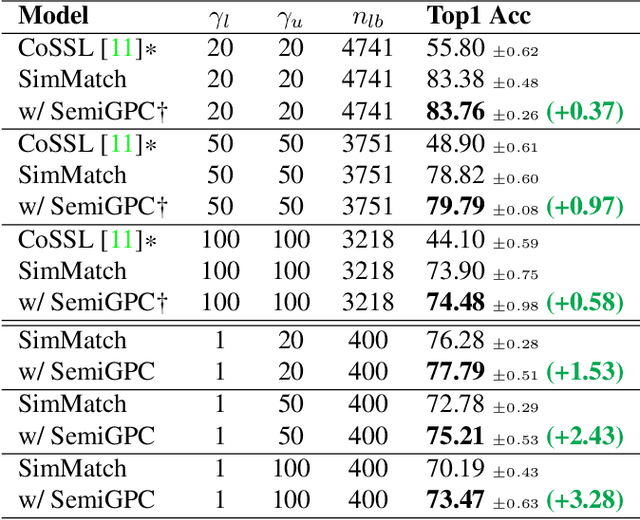

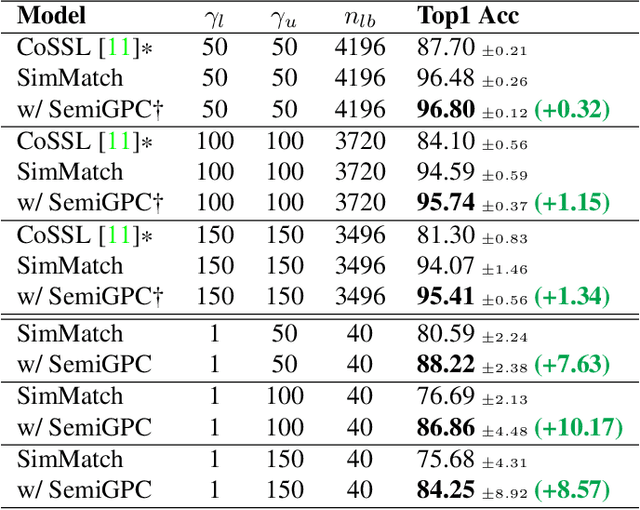
Abstract:In this paper we introduce SemiGPC, a distribution-aware label refinement strategy based on Gaussian Processes where the predictions of the model are derived from the labels posterior distribution. Differently from other buffer-based semi-supervised methods such as CoMatch and SimMatch, our SemiGPC includes a normalization term that addresses imbalances in the global data distribution while maintaining local sensitivity. This explicit control allows SemiGPC to be more robust to confirmation bias especially under class imbalance. We show that SemiGPC improves performance when paired with different Semi-Supervised methods such as FixMatch, ReMixMatch, SimMatch and FreeMatch and different pre-training strategies including MSN and Dino. We also show that SemiGPC achieves state of the art results under different degrees of class imbalance on standard CIFAR10-LT/CIFAR100-LT especially in the low data-regime. Using SemiGPC also results in about 2% avg.accuracy increase compared to a new competitive baseline on the more challenging benchmarks SemiAves, SemiCUB, SemiFungi and Semi-iNat.
Denoising and Selecting Pseudo-Heatmaps for Semi-Supervised Human Pose Estimation
Sep 29, 2023Abstract:We propose a new semi-supervised learning design for human pose estimation that revisits the popular dual-student framework and enhances it two ways. First, we introduce a denoising scheme to generate reliable pseudo-heatmaps as targets for learning from unlabeled data. This uses multi-view augmentations and a threshold-and-refine procedure to produce a pool of pseudo-heatmaps. Second, we select the learning targets from these pseudo-heatmaps guided by the estimated cross-student uncertainty. We evaluate our proposed method on multiple evaluation setups on the COCO benchmark. Our results show that our model outperforms previous state-of-the-art semi-supervised pose estimators, especially in extreme low-data regime. For example with only 0.5K labeled images our method is capable of surpassing the best competitor by 7.22 mAP (+25% absolute improvement). We also demonstrate that our model can learn effectively from unlabeled data in the wild to further boost its generalization and performance.
SkeleTR: Towrads Skeleton-based Action Recognition in the Wild
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:We present SkeleTR, a new framework for skeleton-based action recognition. In contrast to prior work, which focuses mainly on controlled environments, we target more general scenarios that typically involve a variable number of people and various forms of interaction between people. SkeleTR works with a two-stage paradigm. It first models the intra-person skeleton dynamics for each skeleton sequence with graph convolutions, and then uses stacked Transformer encoders to capture person interactions that are important for action recognition in general scenarios. To mitigate the negative impact of inaccurate skeleton associations, SkeleTR takes relative short skeleton sequences as input and increases the number of sequences. As a unified solution, SkeleTR can be directly applied to multiple skeleton-based action tasks, including video-level action classification, instance-level action detection, and group-level activity recognition. It also enables transfer learning and joint training across different action tasks and datasets, which result in performance improvement. When evaluated on various skeleton-based action recognition benchmarks, SkeleTR achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
Challenges of Zero-Shot Recognition with Vision-Language Models: Granularity and Correctness
Jun 28, 2023



Abstract:This paper investigates the challenges of applying vision-language models (VLMs) to zero-shot visual recognition tasks in an open-world setting, with a focus on contrastive vision-language models such as CLIP. We first examine the performance of VLMs on concepts of different granularity levels. We propose a way to fairly evaluate the performance discrepancy under two experimental setups and find that VLMs are better at recognizing fine-grained concepts. Furthermore, we find that the similarity scores from VLMs do not strictly reflect the correctness of the textual inputs given visual input. We propose an evaluation protocol to test our hypothesis that the scores can be biased towards more informative descriptions, and the nature of the similarity score between embedding makes it challenging for VLMs to recognize the correctness between similar but wrong descriptions. Our study highlights the challenges of using VLMs in open-world settings and suggests directions for future research to improve their zero-shot capabilities.
ScaleDet: A Scalable Multi-Dataset Object Detector
Jun 08, 2023



Abstract:Multi-dataset training provides a viable solution for exploiting heterogeneous large-scale datasets without extra annotation cost. In this work, we propose a scalable multi-dataset detector (ScaleDet) that can scale up its generalization across datasets when increasing the number of training datasets. Unlike existing multi-dataset learners that mostly rely on manual relabelling efforts or sophisticated optimizations to unify labels across datasets, we introduce a simple yet scalable formulation to derive a unified semantic label space for multi-dataset training. ScaleDet is trained by visual-textual alignment to learn the label assignment with label semantic similarities across datasets. Once trained, ScaleDet can generalize well on any given upstream and downstream datasets with seen and unseen classes. We conduct extensive experiments using LVIS, COCO, Objects365, OpenImages as upstream datasets, and 13 datasets from Object Detection in the Wild (ODinW) as downstream datasets. Our results show that ScaleDet achieves compelling strong model performance with an mAP of 50.7 on LVIS, 58.8 on COCO, 46.8 on Objects365, 76.2 on OpenImages, and 71.8 on ODinW, surpassing state-of-the-art detectors with the same backbone.
Musketeer (All for One, and One for All): A Generalist Vision-Language Model with Task Explanation Prompts
May 11, 2023Abstract:We present a sequence-to-sequence vision-language model whose parameters are jointly trained on all tasks (all for one) and fully shared among multiple tasks (one for all), resulting in a single model which we named Musketeer. The integration of knowledge across heterogeneous tasks is enabled by a novel feature called Task Explanation Prompt (TEP). TEP reduces interference among tasks, allowing the model to focus on their shared structure. With a single model, Musketeer achieves results comparable to or better than strong baselines trained on single tasks, almost uniformly across multiple tasks.
Semi-supervised Vision Transformers at Scale
Aug 11, 2022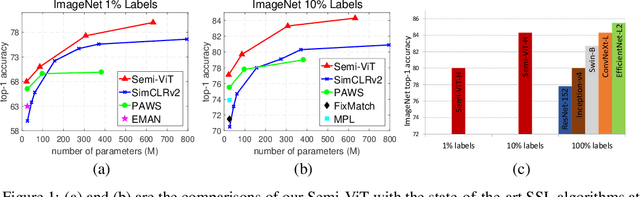
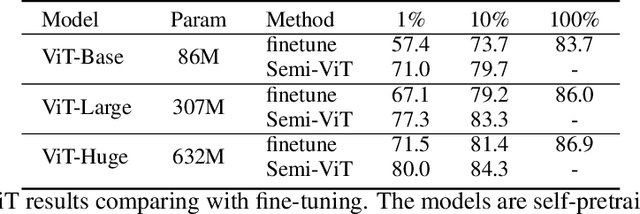

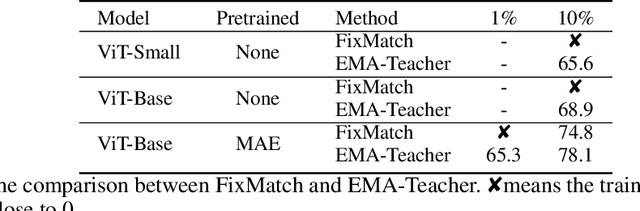
Abstract:We study semi-supervised learning (SSL) for vision transformers (ViT), an under-explored topic despite the wide adoption of the ViT architectures to different tasks. To tackle this problem, we propose a new SSL pipeline, consisting of first un/self-supervised pre-training, followed by supervised fine-tuning, and finally semi-supervised fine-tuning. At the semi-supervised fine-tuning stage, we adopt an exponential moving average (EMA)-Teacher framework instead of the popular FixMatch, since the former is more stable and delivers higher accuracy for semi-supervised vision transformers. In addition, we propose a probabilistic pseudo mixup mechanism to interpolate unlabeled samples and their pseudo labels for improved regularization, which is important for training ViTs with weak inductive bias. Our proposed method, dubbed Semi-ViT, achieves comparable or better performance than the CNN counterparts in the semi-supervised classification setting. Semi-ViT also enjoys the scalability benefits of ViTs that can be readily scaled up to large-size models with increasing accuracies. For example, Semi-ViT-Huge achieves an impressive 80% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet using only 1% labels, which is comparable with Inception-v4 using 100% ImageNet labels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge