Alessandro Bergamo
Optimal Transport-Guided Source-Free Adaptation for Face Anti-Spoofing
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Developing a face anti-spoofing model that meets the security requirements of clients worldwide is challenging due to the domain gap between training datasets and diverse end-user test data. Moreover, for security and privacy reasons, it is undesirable for clients to share a large amount of their face data with service providers. In this work, we introduce a novel method in which the face anti-spoofing model can be adapted by the client itself to a target domain at test time using only a small sample of data while keeping model parameters and training data inaccessible to the client. Specifically, we develop a prototype-based base model and an optimal transport-guided adaptor that enables adaptation in either a lightweight training or training-free fashion, without updating base model's parameters. Furthermore, we propose geodesic mixup, an optimal transport-based synthesis method that generates augmented training data along the geodesic path between source prototypes and target data distribution. This allows training a lightweight classifier to effectively adapt to target-specific characteristics while retaining essential knowledge learned from the source domain. In cross-domain and cross-attack settings, compared with recent methods, our method achieves average relative improvements of 19.17% in HTER and 8.58% in AUC, respectively.
Early Action Recognition with Action Prototypes
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Early action recognition is an important and challenging problem that enables the recognition of an action from a partially observed video stream where the activity is potentially unfinished or even not started. In this work, we propose a novel model that learns a prototypical representation of the full action for each class and uses it to regularize the architecture and the visual representations of the partial observations. Our model is very simple in design and also efficient. We decompose the video into short clips, where a visual encoder extracts features from each clip independently. Later, a decoder aggregates together in an online fashion features from all the clips for the final class prediction. During training, for each partial observation, the model is jointly trained to both predict the label as well as the action prototypical representation which acts as a regularizer. We evaluate our method on multiple challenging real-world datasets and outperform the current state-of-the-art by a significant margin. For example, on early recognition observing only the first 10% of each video, our method improves the SOTA by +2.23 Top-1 accuracy on Something-Something-v2, +3.55 on UCF-101, +3.68 on SSsub21, and +5.03 on EPIC-Kitchens-55, where prior work used either multi-modal inputs (e.g. optical-flow) or batched inference. Finally, we also present exhaustive ablation studies to motivate the design choices we made, as well as gather insights regarding what our model is learning semantically.
SkeleTR: Towrads Skeleton-based Action Recognition in the Wild
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:We present SkeleTR, a new framework for skeleton-based action recognition. In contrast to prior work, which focuses mainly on controlled environments, we target more general scenarios that typically involve a variable number of people and various forms of interaction between people. SkeleTR works with a two-stage paradigm. It first models the intra-person skeleton dynamics for each skeleton sequence with graph convolutions, and then uses stacked Transformer encoders to capture person interactions that are important for action recognition in general scenarios. To mitigate the negative impact of inaccurate skeleton associations, SkeleTR takes relative short skeleton sequences as input and increases the number of sequences. As a unified solution, SkeleTR can be directly applied to multiple skeleton-based action tasks, including video-level action classification, instance-level action detection, and group-level activity recognition. It also enables transfer learning and joint training across different action tasks and datasets, which result in performance improvement. When evaluated on various skeleton-based action recognition benchmarks, SkeleTR achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
Large Scale Real-World Multi-Person Tracking
Nov 03, 2022Abstract:This paper presents a new large scale multi-person tracking dataset -- \texttt{PersonPath22}, which is over an order of magnitude larger than currently available high quality multi-object tracking datasets such as MOT17, HiEve, and MOT20 datasets. The lack of large scale training and test data for this task has limited the community's ability to understand the performance of their tracking systems on a wide range of scenarios and conditions such as variations in person density, actions being performed, weather, and time of day. \texttt{PersonPath22} dataset was specifically sourced to provide a wide variety of these conditions and our annotations include rich meta-data such that the performance of a tracker can be evaluated along these different dimensions. The lack of training data has also limited the ability to perform end-to-end training of tracking systems. As such, the highest performing tracking systems all rely on strong detectors trained on external image datasets. We hope that the release of this dataset will enable new lines of research that take advantage of large scale video based training data.
Self-taught Object Localization with Deep Networks
Feb 02, 2016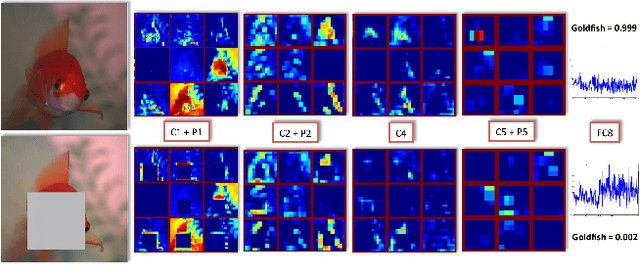
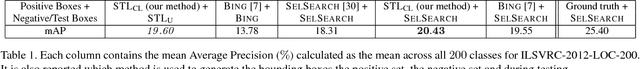
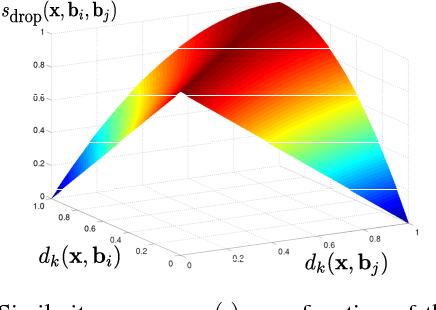
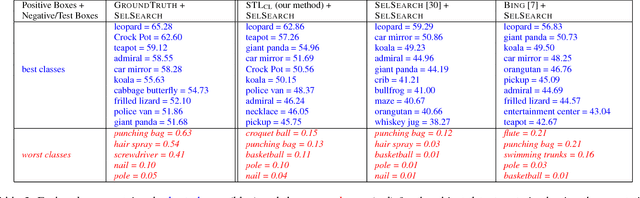
Abstract:This paper introduces self-taught object localization, a novel approach that leverages deep convolutional networks trained for whole-image recognition to localize objects in images without additional human supervision, i.e., without using any ground-truth bounding boxes for training. The key idea is to analyze the change in the recognition scores when artificially masking out different regions of the image. The masking out of a region that includes the object typically causes a significant drop in recognition score. This idea is embedded into an agglomerative clustering technique that generates self-taught localization hypotheses. Our object localization scheme outperforms existing proposal methods in both precision and recall for small number of subwindow proposals (e.g., on ILSVRC-2012 it produces a relative gain of 23.4% over the state-of-the-art for top-1 hypothesis). Furthermore, our experiments show that the annotations automatically-generated by our method can be used to train object detectors yielding recognition results remarkably close to those obtained by training on manually-annotated bounding boxes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge