Krishnamurthy Dj Dvijotham
Through the Stealth Lens: Rethinking Attacks and Defenses in RAG
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems are vulnerable to attacks that inject poisoned passages into the retrieved set, even at low corruption rates. We show that existing attacks are not designed to be stealthy, allowing reliable detection and mitigation. We formalize stealth using a distinguishability-based security game. If a few poisoned passages are designed to control the response, they must differentiate themselves from benign ones, inherently compromising stealth. This motivates the need for attackers to rigorously analyze intermediate signals involved in generation$\unicode{x2014}$such as attention patterns or next-token probability distributions$\unicode{x2014}$to avoid easily detectable traces of manipulation. Leveraging attention patterns, we propose a passage-level score$\unicode{x2014}$the Normalized Passage Attention Score$\unicode{x2014}$used by our Attention-Variance Filter algorithm to identify and filter potentially poisoned passages. This method mitigates existing attacks, improving accuracy by up to $\sim 20 \%$ over baseline defenses. To probe the limits of attention-based defenses, we craft stealthier adaptive attacks that obscure such traces, achieving up to $35 \%$ attack success rate, and highlight the challenges in improving stealth.
Keeping up with dynamic attackers: Certifying robustness to adaptive online data poisoning
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:The rise of foundation models fine-tuned on human feedback from potentially untrusted users has increased the risk of adversarial data poisoning, necessitating the study of robustness of learning algorithms against such attacks. Existing research on provable certified robustness against data poisoning attacks primarily focuses on certifying robustness for static adversaries who modify a fraction of the dataset used to train the model before the training algorithm is applied. In practice, particularly when learning from human feedback in an online sense, adversaries can observe and react to the learning process and inject poisoned samples that optimize adversarial objectives better than when they are restricted to poisoning a static dataset once, before the learning algorithm is applied. Indeed, it has been shown in prior work that online dynamic adversaries can be significantly more powerful than static ones. We present a novel framework for computing certified bounds on the impact of dynamic poisoning, and use these certificates to design robust learning algorithms. We give an illustration of the framework for the mean estimation and binary classification problems and outline directions for extending this in further work. The code to implement our certificates and replicate our results is available at https://github.com/Avinandan22/Certified-Robustness.
Beyond Thumbs Up/Down: Untangling Challenges of Fine-Grained Feedback for Text-to-Image Generation
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Human feedback plays a critical role in learning and refining reward models for text-to-image generation, but the optimal form the feedback should take for learning an accurate reward function has not been conclusively established. This paper investigates the effectiveness of fine-grained feedback which captures nuanced distinctions in image quality and prompt-alignment, compared to traditional coarse-grained feedback (for example, thumbs up/down or ranking between a set of options). While fine-grained feedback holds promise, particularly for systems catering to diverse societal preferences, we show that demonstrating its superiority to coarse-grained feedback is not automatic. Through experiments on real and synthetic preference data, we surface the complexities of building effective models due to the interplay of model choice, feedback type, and the alignment between human judgment and computational interpretation. We identify key challenges in eliciting and utilizing fine-grained feedback, prompting a reassessment of its assumed benefits and practicality. Our findings -- e.g., that fine-grained feedback can lead to worse models for a fixed budget, in some settings; however, in controlled settings with known attributes, fine grained rewards can indeed be more helpful -- call for careful consideration of feedback attributes and potentially beckon novel modeling approaches to appropriately unlock the potential value of fine-grained feedback in-the-wild.
Rich Human Feedback for Text-to-Image Generation
Dec 15, 2023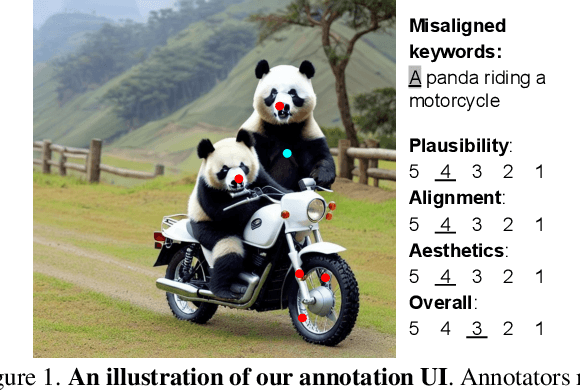
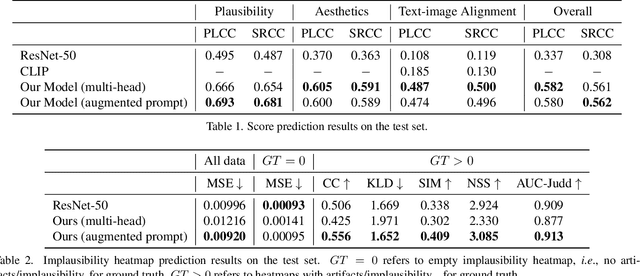
Abstract:Recent Text-to-Image (T2I) generation models such as Stable Diffusion and Imagen have made significant progress in generating high-resolution images based on text descriptions. However, many generated images still suffer from issues such as artifacts/implausibility, misalignment with text descriptions, and low aesthetic quality. Inspired by the success of Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) for large language models, prior works collected human-provided scores as feedback on generated images and trained a reward model to improve the T2I generation. In this paper, we enrich the feedback signal by (i) marking image regions that are implausible or misaligned with the text, and (ii) annotating which words in the text prompt are misrepresented or missing on the image. We collect such rich human feedback on 18K generated images and train a multimodal transformer to predict the rich feedback automatically. We show that the predicted rich human feedback can be leveraged to improve image generation, for example, by selecting high-quality training data to finetune and improve the generative models, or by creating masks with predicted heatmaps to inpaint the problematic regions. Notably, the improvements generalize to models (Muse) beyond those used to generate the images on which human feedback data were collected (Stable Diffusion variants).
Provably Correct Physics-Informed Neural Networks
May 17, 2023Abstract:Recent work provides promising evidence that Physics-informed neural networks (PINN) can efficiently solve partial differential equations (PDE). However, previous works have failed to provide guarantees on the worst-case residual error of a PINN across the spatio-temporal domain - a measure akin to the tolerance of numerical solvers - focusing instead on point-wise comparisons between their solution and the ones obtained by a solver on a set of inputs. In real-world applications, one cannot consider tests on a finite set of points to be sufficient grounds for deployment, as the performance could be substantially worse on a different set. To alleviate this issue, we establish tolerance-based correctness conditions for PINNs over the entire input domain. To verify the extent to which they hold, we introduce $\partial$-CROWN: a general, efficient and scalable post-training framework to bound PINN residual errors. We demonstrate its effectiveness in obtaining tight certificates by applying it to two classically studied PDEs - Burgers' and Schr\"odinger's equations -, and two more challenging ones with real-world applications - the Allan-Cahn and Diffusion-Sorption equations.
Pushing the Accuracy-Group Robustness Frontier with Introspective Self-play
Feb 11, 2023Abstract:Standard empirical risk minimization (ERM) training can produce deep neural network (DNN) models that are accurate on average but under-perform in under-represented population subgroups, especially when there are imbalanced group distributions in the long-tailed training data. Therefore, approaches that improve the accuracy-group robustness trade-off frontier of a DNN model (i.e. improving worst-group accuracy without sacrificing average accuracy, or vice versa) is of crucial importance. Uncertainty-based active learning (AL) can potentially improve the frontier by preferentially sampling underrepresented subgroups to create a more balanced training dataset. However, the quality of uncertainty estimates from modern DNNs tend to degrade in the presence of spurious correlations and dataset bias, compromising the effectiveness of AL for sampling tail groups. In this work, we propose Introspective Self-play (ISP), a simple approach to improve the uncertainty estimation of a deep neural network under dataset bias, by adding an auxiliary introspection task requiring a model to predict the bias for each data point in addition to the label. We show that ISP provably improves the bias-awareness of the model representation and the resulting uncertainty estimates. On two real-world tabular and language tasks, ISP serves as a simple "plug-in" for AL model training, consistently improving both the tail-group sampling rate and the final accuracy-fairness trade-off frontier of popular AL methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge