Khe Chai Sim
Aligner-Encoders: Self-Attention Transformers Can Be Self-Transducers
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Modern systems for automatic speech recognition, including the RNN-Transducer and Attention-based Encoder-Decoder (AED), are designed so that the encoder is not required to alter the time-position of information from the audio sequence into the embedding; alignment to the final text output is processed during decoding. We discover that the transformer-based encoder adopted in recent years is actually capable of performing the alignment internally during the forward pass, prior to decoding. This new phenomenon enables a simpler and more efficient model, the "Aligner-Encoder". To train it, we discard the dynamic programming of RNN-T in favor of the frame-wise cross-entropy loss of AED, while the decoder employs the lighter text-only recurrence of RNN-T without learned cross-attention -- it simply scans embedding frames in order from the beginning, producing one token each until predicting the end-of-message. We conduct experiments demonstrating performance remarkably close to the state of the art, including a special inference configuration enabling long-form recognition. In a representative comparison, we measure the total inference time for our model to be 2x faster than RNN-T and 16x faster than AED. Lastly, we find that the audio-text alignment is clearly visible in the self-attention weights of a certain layer, which could be said to perform "self-transduction".
TransformerFAM: Feedback attention is working memory
Apr 14, 2024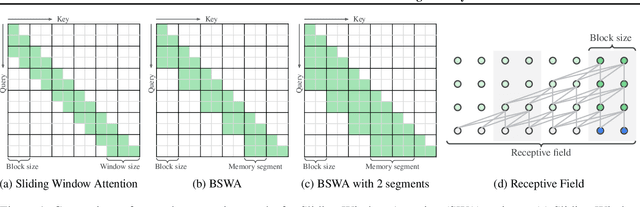
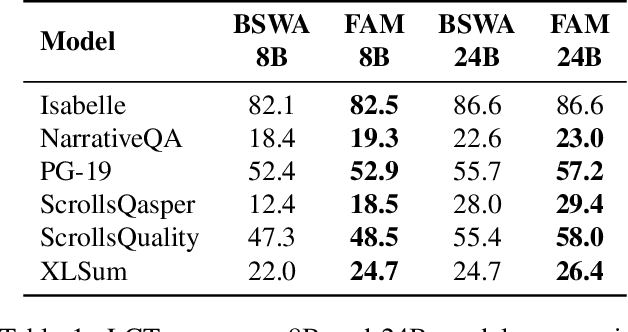
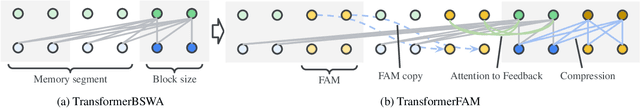
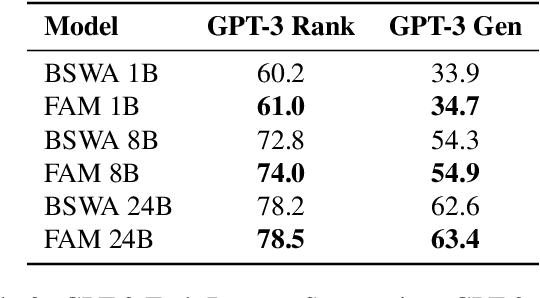
Abstract:While Transformers have revolutionized deep learning, their quadratic attention complexity hinders their ability to process infinitely long inputs. We propose Feedback Attention Memory (FAM), a novel Transformer architecture that leverages a feedback loop to enable the network to attend to its own latent representations. This design fosters the emergence of working memory within the Transformer, allowing it to process indefinitely long sequences. TransformerFAM requires no additional weights, enabling seamless integration with pre-trained models. Our experiments show that TransformerFAM significantly improves Transformer performance on long-context tasks across various model sizes (1B, 8B, and 24B). These results showcase the potential to empower Large Language Models (LLMs) to process sequences of unlimited length.
Hierarchical Recurrent Adapters for Efficient Multi-Task Adaptation of Large Speech Models
Mar 25, 2024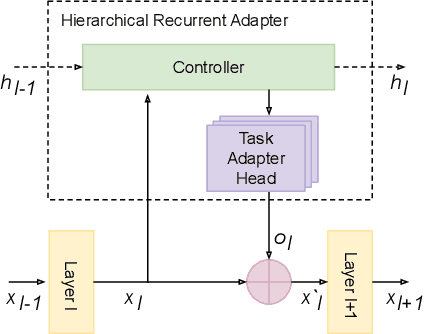
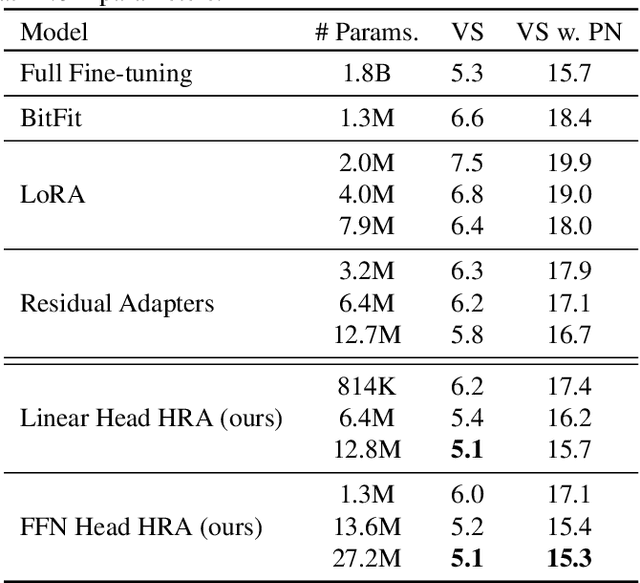
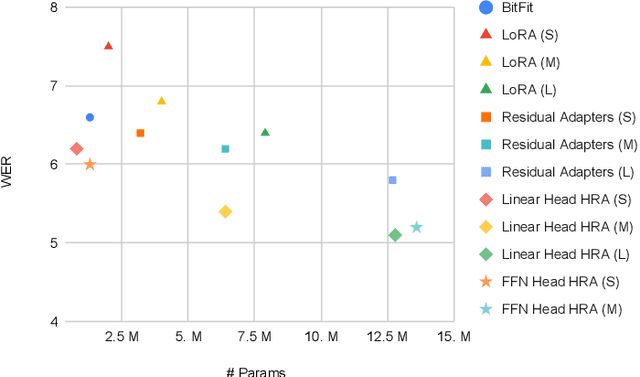
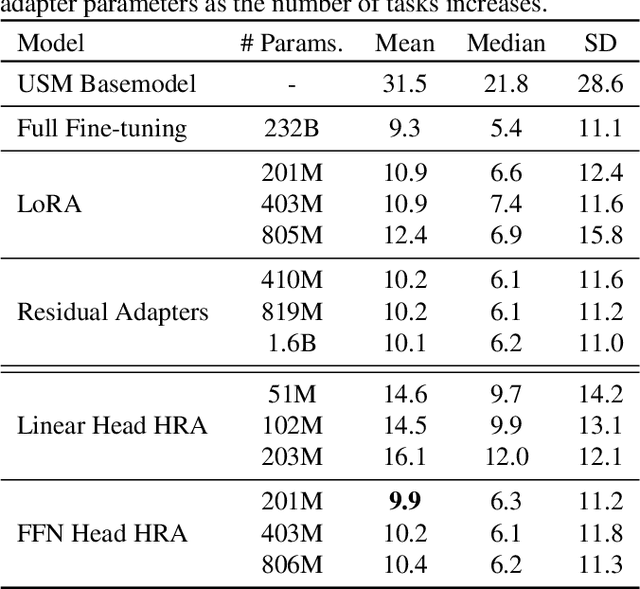
Abstract:Parameter efficient adaptation methods have become a key mechanism to train large pre-trained models for downstream tasks. However, their per-task parameter overhead is considered still high when the number of downstream tasks to adapt for is large. We introduce an adapter module that has a better efficiency in large scale multi-task adaptation scenario. Our adapter is hierarchical in terms of how the adapter parameters are allocated. The adapter consists of a single shared controller network and multiple task-level adapter heads to reduce the per-task parameter overhead without performance regression on downstream tasks. The adapter is also recurrent so the entire adapter parameters are reused across different layers of the pre-trained model. Our Hierarchical Recurrent Adapter (HRA) outperforms the previous adapter-based approaches as well as full model fine-tuning baseline in both single and multi-task adaptation settings when evaluated on automatic speech recognition tasks.
Profit: Benchmarking Personalization and Robustness Trade-off in Federated Prompt Tuning
Oct 06, 2023Abstract:In many applications of federated learning (FL), clients desire models that are personalized using their local data, yet are also robust in the sense that they retain general global knowledge. However, the presence of data heterogeneity across clients induces a fundamental trade-off between personalization (i.e., adaptation to a local distribution) and robustness (i.e., not forgetting previously learned general knowledge). It is critical to understand how to navigate this personalization vs robustness trade-off when designing federated systems, which are increasingly moving towards a paradigm of fine-tuning large foundation models. Due to limited computational and communication capabilities in most federated settings, this foundation model fine-tuning must be done using parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) approaches. While some recent work has studied federated approaches to PEFT, the personalization vs robustness trade-off of federated PEFT has been largely unexplored. In this work, we take a step towards bridging this gap by benchmarking fundamental FL algorithms -- FedAvg and FedSGD plus personalization (via client local fine-tuning) -- applied to one of the most ubiquitous PEFT approaches to large language models (LLMs) -- prompt tuning -- in a multitude of hyperparameter settings under varying levels of data heterogeneity. Our results show that federated-trained prompts can be surprisingly robust when using a small learning rate with many local epochs for personalization, especially when using an adaptive optimizer as the client optimizer during federated training. We also demonstrate that simple approaches such as adding regularization and interpolating two prompts are effective in improving the personalization vs robustness trade-off in computation-limited settings with few local updates allowed for personalization.
Contextual Biasing with the Knuth-Morris-Pratt Matching Algorithm
Sep 29, 2023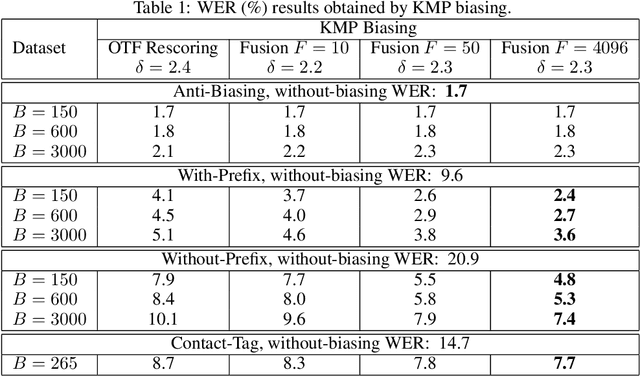
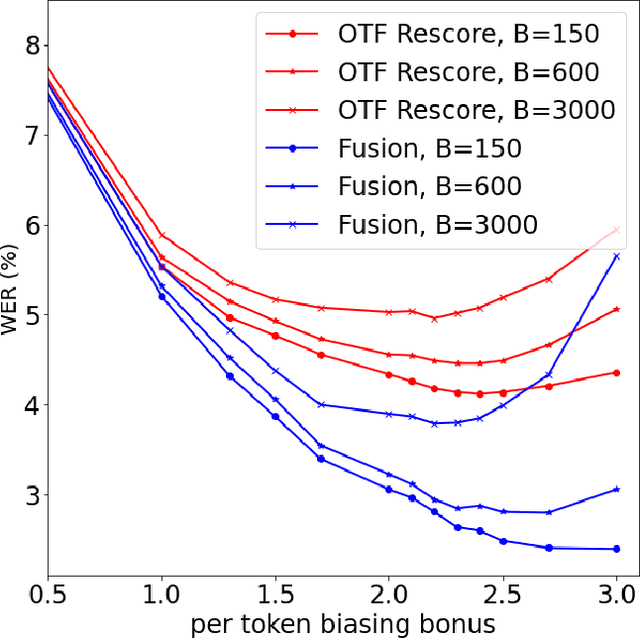
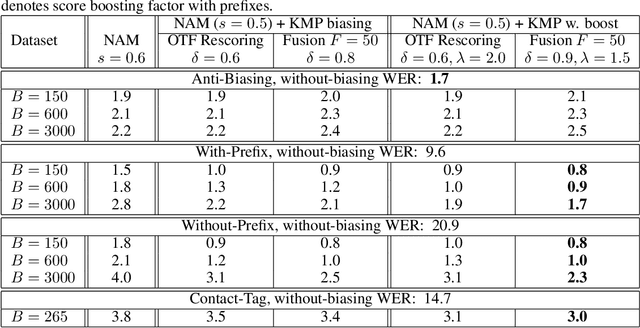
Abstract:Contextual biasing refers to the problem of biasing the automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems towards rare entities that are relevant to the specific user or application scenarios. We propose algorithms for contextual biasing based on the Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm for pattern matching. During beam search, we boost the score of a token extension if it extends matching into a set of biasing phrases. Our method simulates the classical approaches often implemented in the weighted finite state transducer (WFST) framework, but avoids the FST language altogether, with careful considerations on memory footprint and efficiency on tensor processing units (TPUs) by vectorization. Without introducing additional model parameters, our method achieves significant word error rate (WER) reductions on biasing test sets by itself, and yields further performance gain when combined with a model-based biasing method.
Massive End-to-end Models for Short Search Queries
Sep 22, 2023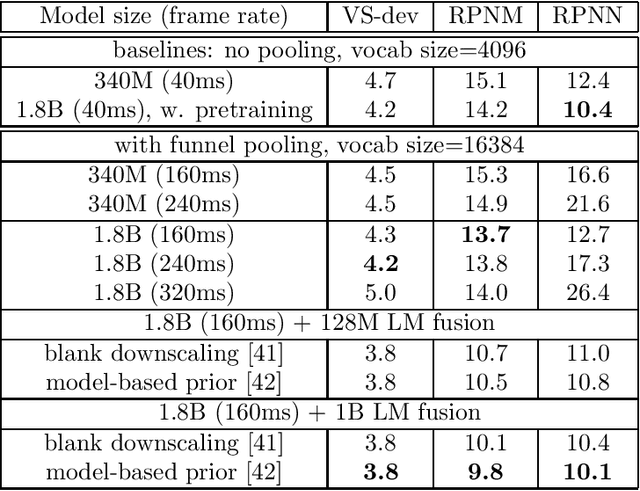
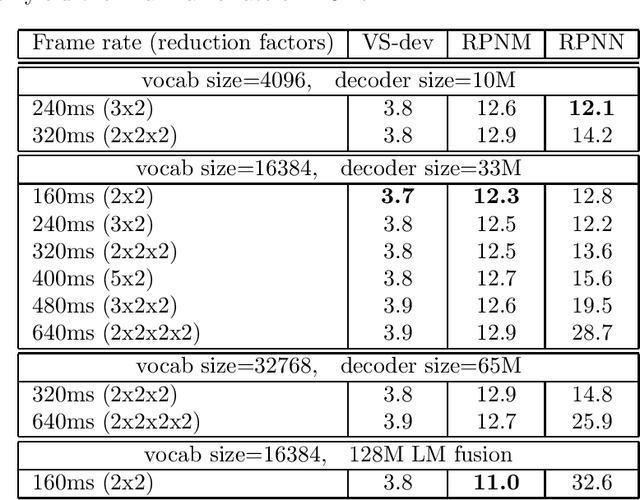
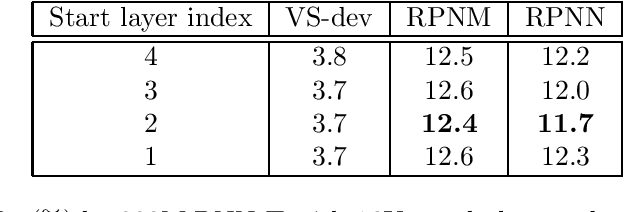
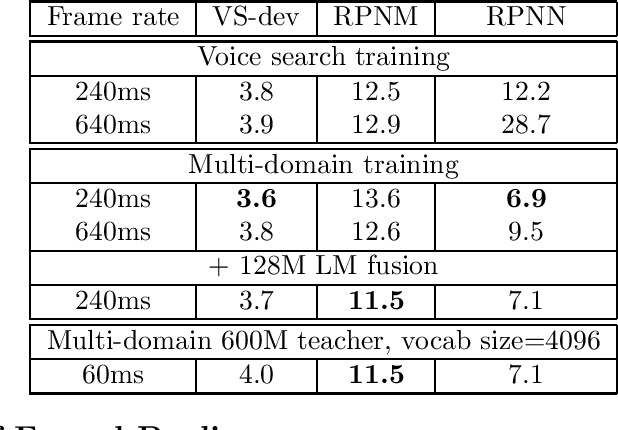
Abstract:In this work, we investigate two popular end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) models, namely Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) and RNN-Transducer (RNN-T), for offline recognition of voice search queries, with up to 2B model parameters. The encoders of our models use the neural architecture of Google's universal speech model (USM), with additional funnel pooling layers to significantly reduce the frame rate and speed up training and inference. We perform extensive studies on vocabulary size, time reduction strategy, and its generalization performance on long-form test sets. Despite the speculation that, as the model size increases, CTC can be as good as RNN-T which builds label dependency into the prediction, we observe that a 900M RNN-T clearly outperforms a 1.8B CTC and is more tolerant to severe time reduction, although the WER gap can be largely removed by LM shallow fusion.
Improving Speech Recognition for African American English With Audio Classification
Sep 16, 2023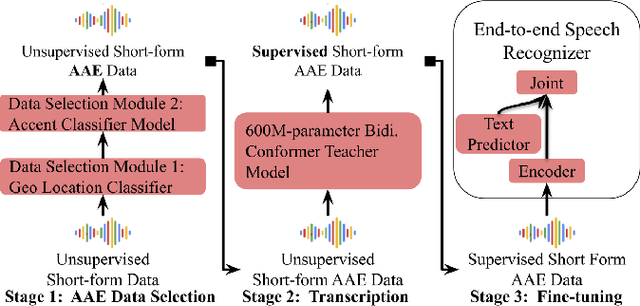
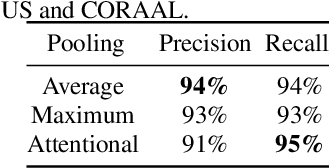
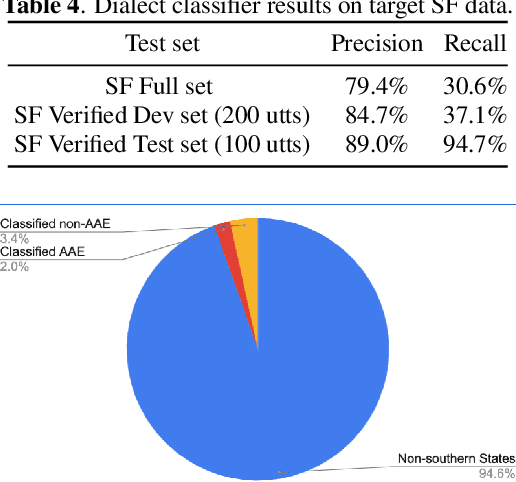
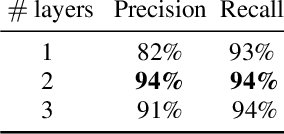
Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems have been shown to have large quality disparities between the language varieties they are intended or expected to recognize. One way to mitigate this is to train or fine-tune models with more representative datasets. But this approach can be hindered by limited in-domain data for training and evaluation. We propose a new way to improve the robustness of a US English short-form speech recognizer using a small amount of out-of-domain (long-form) African American English (AAE) data. We use CORAAL, YouTube and Mozilla Common Voice to train an audio classifier to approximately output whether an utterance is AAE or some other variety including Mainstream American English (MAE). By combining the classifier output with coarse geographic information, we can select a subset of utterances from a large corpus of untranscribed short-form queries for semi-supervised learning at scale. Fine-tuning on this data results in a 38.5% relative word error rate disparity reduction between AAE and MAE without reducing MAE quality.
Edit Distance based RL for RNNT decoding
May 31, 2023Abstract:RNN-T is currently considered the industry standard in ASR due to its exceptional WERs in various benchmark tests and its ability to support seamless streaming and longform transcription. However, its biggest drawback lies in the significant discrepancy between its training and inference objectives. During training, RNN-T maximizes all alignment probabilities by teacher forcing, while during inference, it uses beam search which may not necessarily find the maximum probable alignment. Additionally, RNN-T's inability to experience mistakes during teacher forcing training makes it more problematic when a mistake occurs in inference. To address this issue, this paper proposes a Reinforcement Learning method that minimizes the gap between training and inference time. Our Edit Distance based RL (EDRL) approach computes rewards based on the edit distance, and trains the network at every action level. The proposed approach yielded SoTA WERs on LibriSpeech for the 600M Conformer RNN-T model.
Efficient Domain Adaptation for Speech Foundation Models
Feb 03, 2023Abstract:Foundation models (FMs), that are trained on broad data at scale and are adaptable to a wide range of downstream tasks, have brought large interest in the research community. Benefiting from the diverse data sources such as different modalities, languages and application domains, foundation models have demonstrated strong generalization and knowledge transfer capabilities. In this paper, we present a pioneering study towards building an efficient solution for FM-based speech recognition systems. We adopt the recently developed self-supervised BEST-RQ for pretraining, and propose the joint finetuning with both source and unsupervised target domain data using JUST Hydra. The FM encoder adapter and decoder are then finetuned to the target domain with a small amount of supervised in-domain data. On a large-scale YouTube and Voice Search task, our method is shown to be both data and model parameter efficient. It achieves the same quality with only 21.6M supervised in-domain data and 130.8M finetuned parameters, compared to the 731.1M model trained from scratch on additional 300M supervised in-domain data.
Resource-Efficient Transfer Learning From Speech Foundation Model Using Hierarchical Feature Fusion
Nov 04, 2022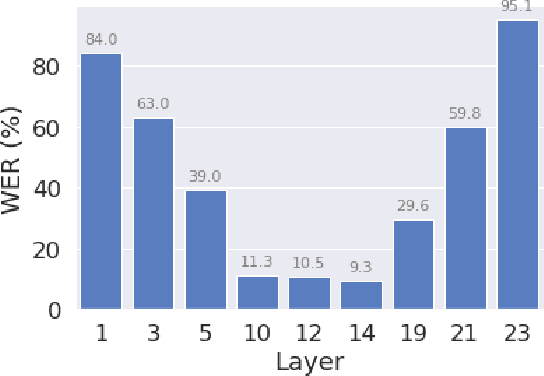
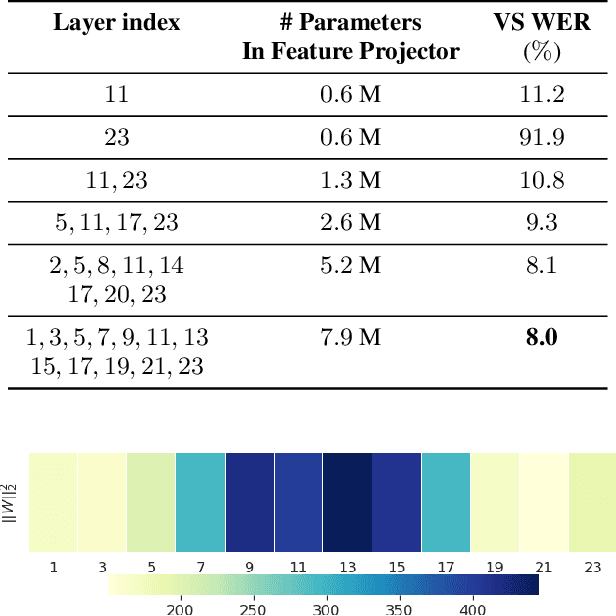
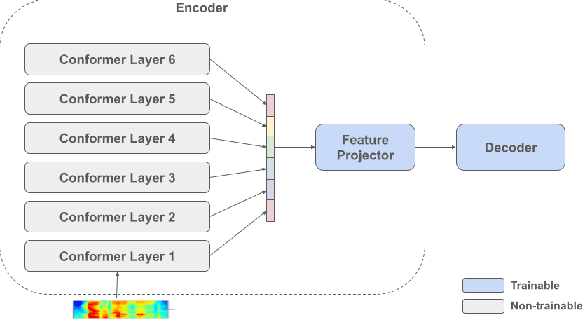
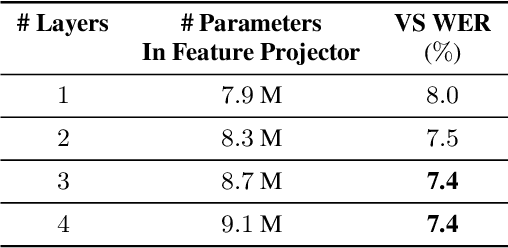
Abstract:Self-supervised pre-training of a speech foundation model, followed by supervised fine-tuning, has shown impressive quality improvements on automatic speech recognition (ASR) tasks. Fine-tuning separate foundation models for many downstream tasks are expensive since the foundation model is usually very big. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods (e.g. adapter, sparse update methods) offer an alternative paradigm where a small set of parameters are updated to adapt the foundation model to new tasks. However, these methods still suffer from a high computational memory cost and slow training speed because they require backpropagation through the entire neural network at each step. In the paper, we analyze the performance of features at different layers of a foundation model on the speech recognition task and propose a novel hierarchical feature fusion method for resource-efficient transfer learning from speech foundation models. Experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve better performance on speech recognition task than existing algorithms with fewer number of trainable parameters, less computational memory cost and faster training speed. After combining with Adapters at all layers, the proposed method can achieve the same performance as fine-tuning the whole model with $97\%$ fewer trainable encoder parameters and $53\%$ faster training speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge