Shefali Garg
Improving Speech Recognition for African American English With Audio Classification
Sep 16, 2023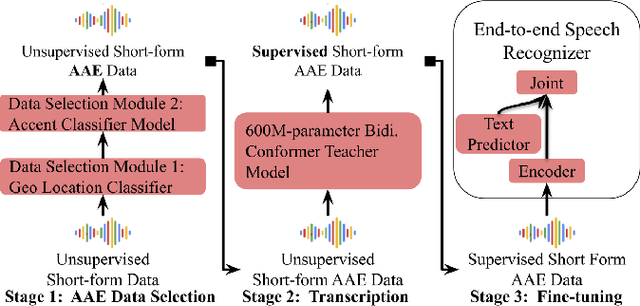
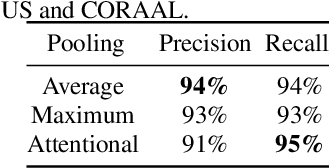
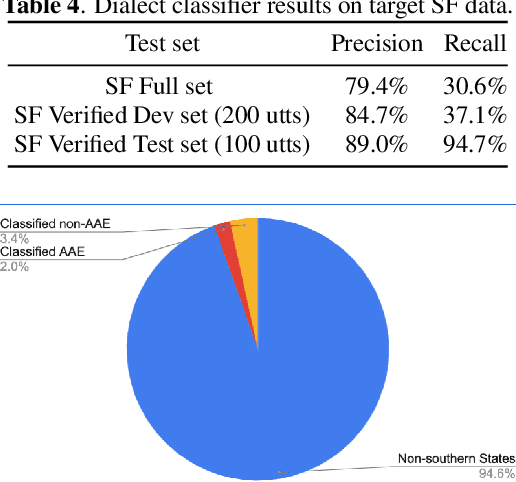
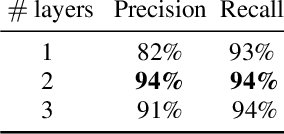
Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems have been shown to have large quality disparities between the language varieties they are intended or expected to recognize. One way to mitigate this is to train or fine-tune models with more representative datasets. But this approach can be hindered by limited in-domain data for training and evaluation. We propose a new way to improve the robustness of a US English short-form speech recognizer using a small amount of out-of-domain (long-form) African American English (AAE) data. We use CORAAL, YouTube and Mozilla Common Voice to train an audio classifier to approximately output whether an utterance is AAE or some other variety including Mainstream American English (MAE). By combining the classifier output with coarse geographic information, we can select a subset of utterances from a large corpus of untranscribed short-form queries for semi-supervised learning at scale. Fine-tuning on this data results in a 38.5% relative word error rate disparity reduction between AAE and MAE without reducing MAE quality.
UserLibri: A Dataset for ASR Personalization Using Only Text
Jul 02, 2022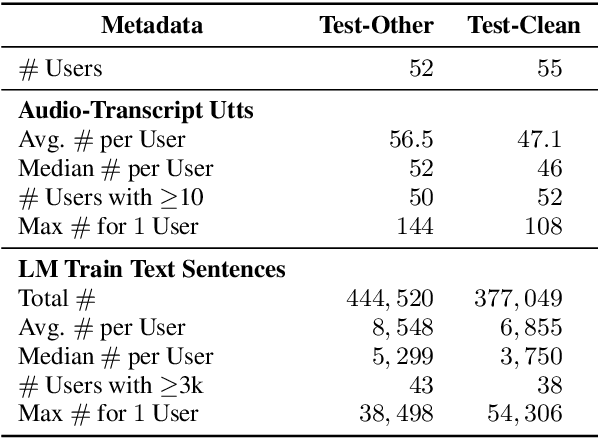
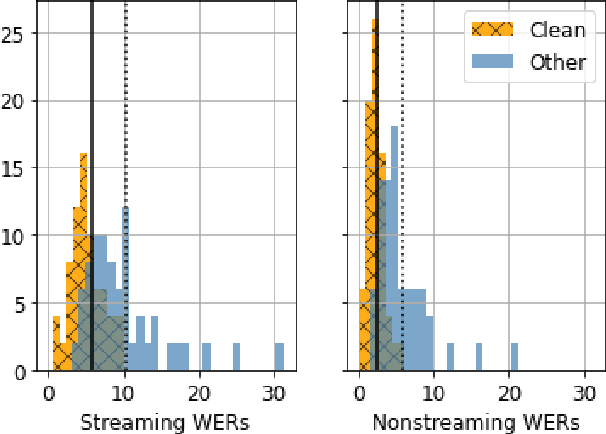
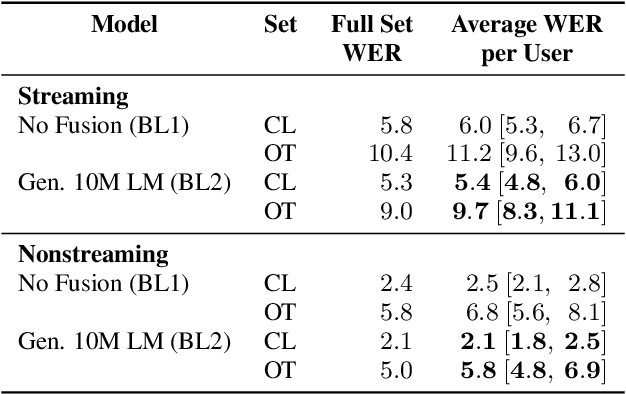
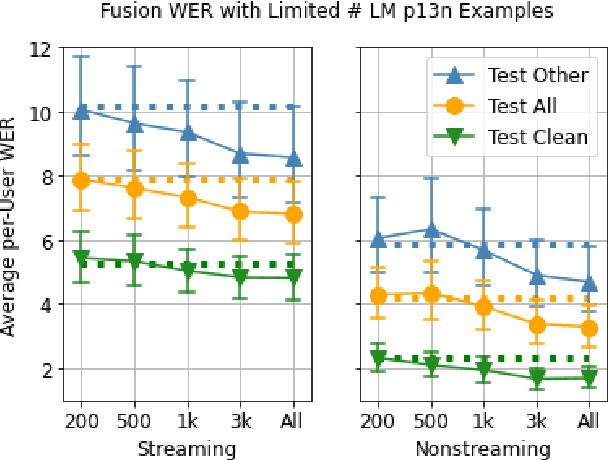
Abstract:Personalization of speech models on mobile devices (on-device personalization) is an active area of research, but more often than not, mobile devices have more text-only data than paired audio-text data. We explore training a personalized language model on text-only data, used during inference to improve speech recognition performance for that user. We experiment on a user-clustered LibriSpeech corpus, supplemented with personalized text-only data for each user from Project Gutenberg. We release this User-Specific LibriSpeech (UserLibri) dataset to aid future personalization research. LibriSpeech audio-transcript pairs are grouped into 55 users from the test-clean dataset and 52 users from test-other. We are able to lower the average word error rate per user across both sets in streaming and nonstreaming models, including an improvement of 2.5 for the harder set of test-other users when streaming.
Large-scale ASR Domain Adaptation using Self- and Semi-supervised Learning
Oct 13, 2021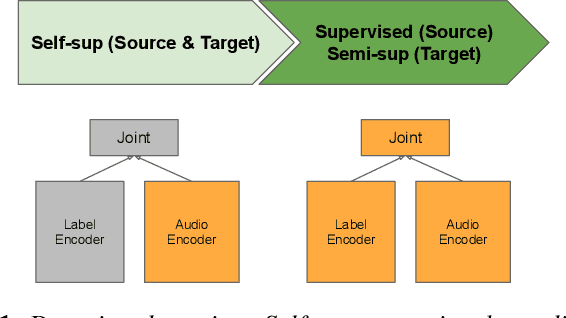
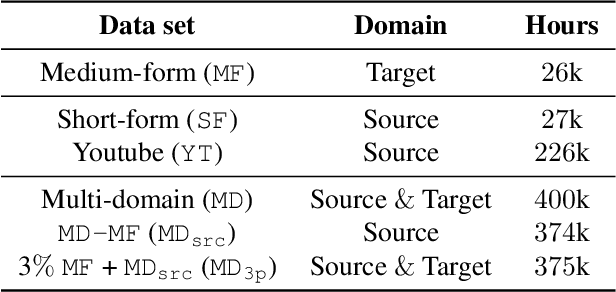
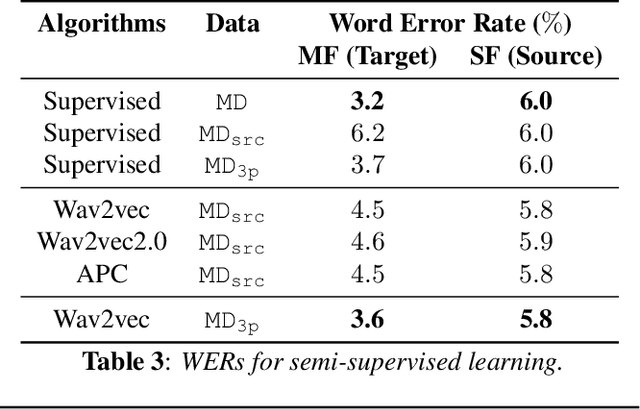
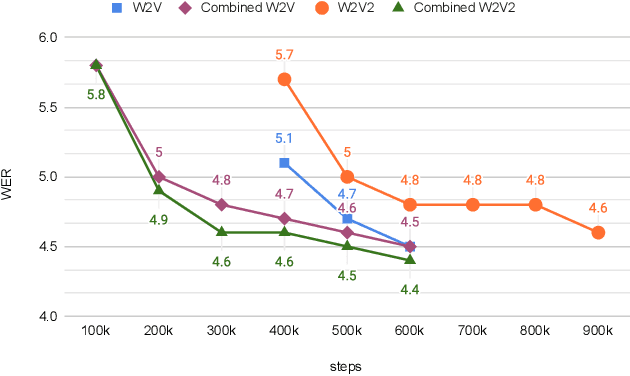
Abstract:Self- and semi-supervised learning methods have been actively investigated to reduce labeled training data or enhance the model performance. However, the approach mostly focus on in-domain performance for public datasets. In this study, we utilize the combination of self- and semi-supervised learning methods to solve unseen domain adaptation problem in a large-scale production setting for online ASR model. This approach demonstrates that using the source domain data with a small fraction of the target domain data (3%) can recover the performance gap compared to a full data baseline: relative 13.5% WER improvement for target domain data.
Incremental Layer-wise Self-Supervised Learning for Efficient Speech Domain Adaptation On Device
Oct 01, 2021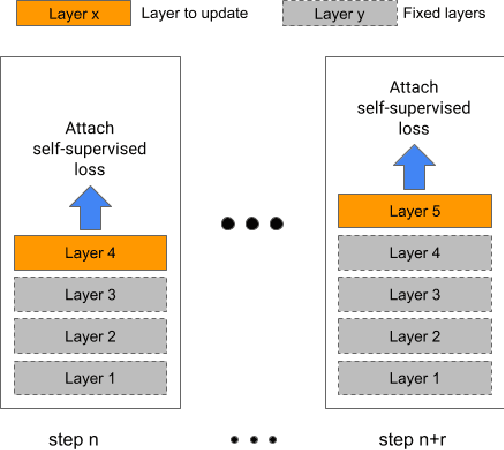
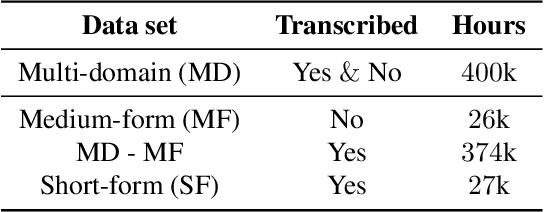
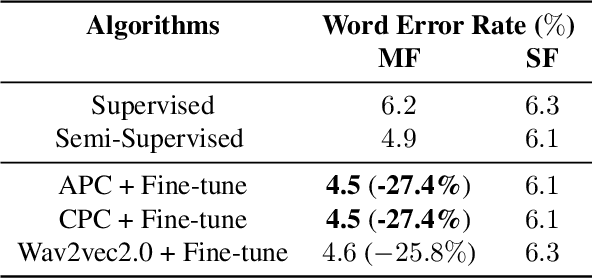
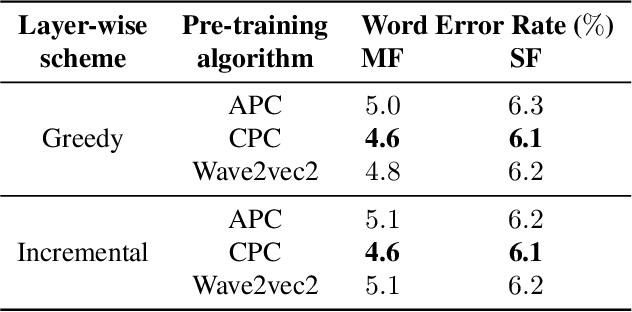
Abstract:Streaming end-to-end speech recognition models have been widely applied to mobile devices and show significant improvement in efficiency. These models are typically trained on the server using transcribed speech data. However, the server data distribution can be very different from the data distribution on user devices, which could affect the model performance. There are two main challenges for on device training, limited reliable labels and limited training memory. While self-supervised learning algorithms can mitigate the mismatch between domains using unlabeled data, they are not applicable on mobile devices directly because of the memory constraint. In this paper, we propose an incremental layer-wise self-supervised learning algorithm for efficient speech domain adaptation on mobile devices, in which only one layer is updated at a time. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm obtains a Word Error Rate (WER) on the target domain $24.2\%$ better than supervised baseline and costs $89.7\%$ less training memory than the end-to-end self-supervised learning algorithm.
Pentagon at MEDIQA 2019: Multi-task Learning for Filtering and Re-ranking Answers using Language Inference and Question Entailment
Jul 01, 2019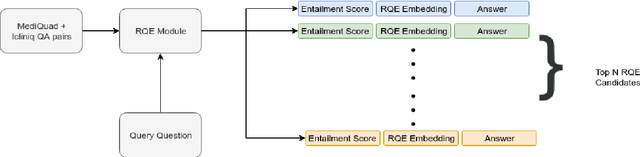
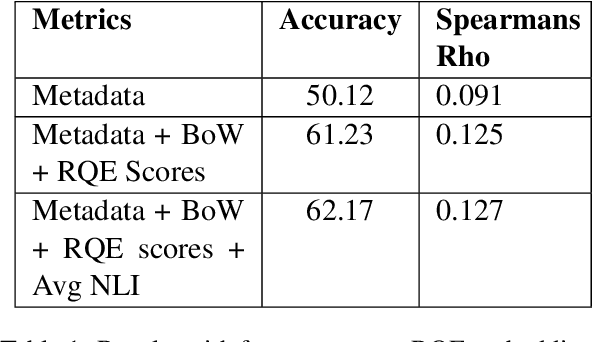
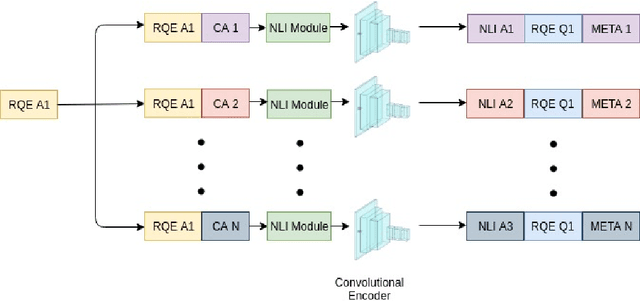
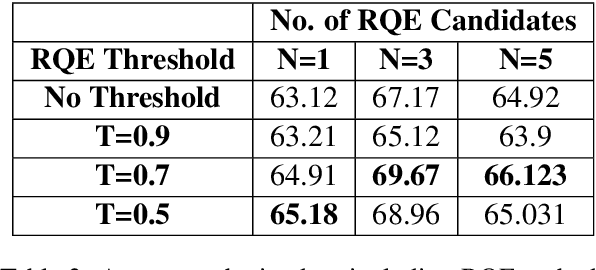
Abstract:Parallel deep learning architectures like fine-tuned BERT and MT-DNN, have quickly become the state of the art, bypassing previous deep and shallow learning methods by a large margin. More recently, pre-trained models from large related datasets have been able to perform well on many downstream tasks by just fine-tuning on domain-specific datasets . However, using powerful models on non-trivial tasks, such as ranking and large document classification, still remains a challenge due to input size limitations of parallel architecture and extremely small datasets (insufficient for fine-tuning). In this work, we introduce an end-to-end system, trained in a multi-task setting, to filter and re-rank answers in the medical domain. We use task-specific pre-trained models as deep feature extractors. Our model achieves the highest Spearman's Rho and Mean Reciprocal Rank of 0.338 and 0.9622 respectively, on the ACL-BioNLP workshop MediQA Question Answering shared-task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge