Theresa Breiner
UserLibri: A Dataset for ASR Personalization Using Only Text
Jul 02, 2022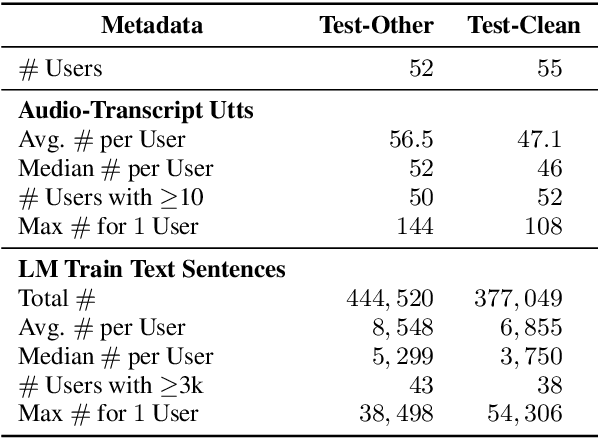
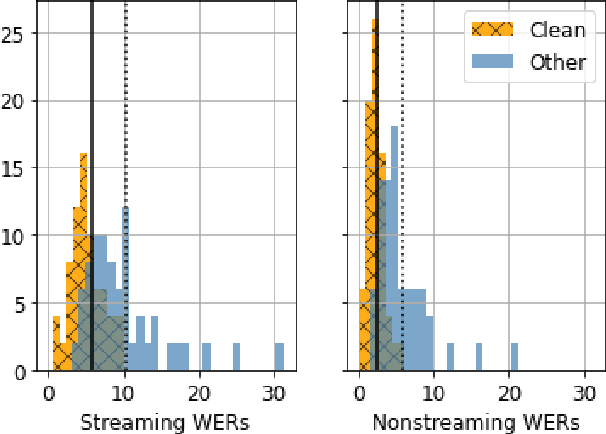
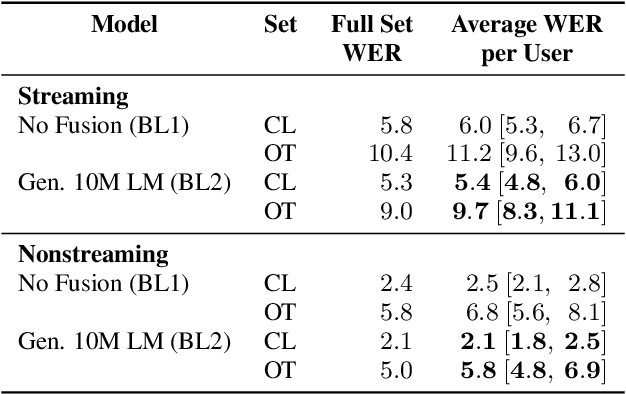
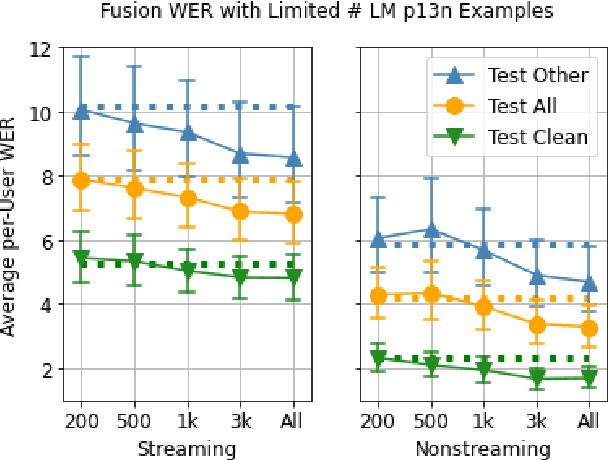
Abstract:Personalization of speech models on mobile devices (on-device personalization) is an active area of research, but more often than not, mobile devices have more text-only data than paired audio-text data. We explore training a personalized language model on text-only data, used during inference to improve speech recognition performance for that user. We experiment on a user-clustered LibriSpeech corpus, supplemented with personalized text-only data for each user from Project Gutenberg. We release this User-Specific LibriSpeech (UserLibri) dataset to aid future personalization research. LibriSpeech audio-transcript pairs are grouped into 55 users from the test-clean dataset and 52 users from test-other. We are able to lower the average word error rate per user across both sets in streaming and nonstreaming models, including an improvement of 2.5 for the harder set of test-other users when streaming.
Building Machine Translation Systems for the Next Thousand Languages
May 16, 2022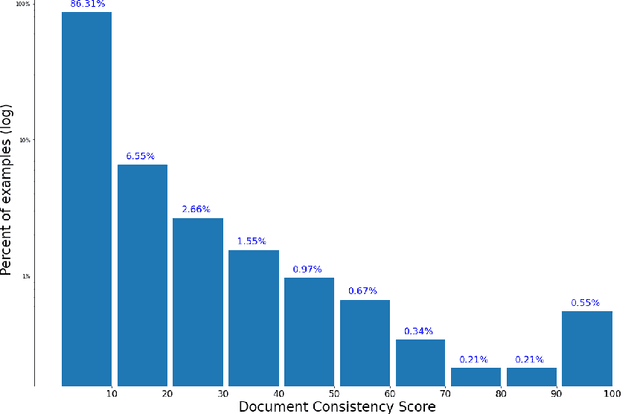
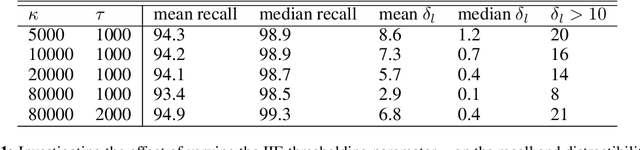
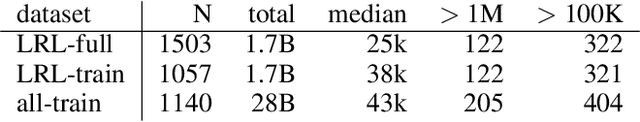
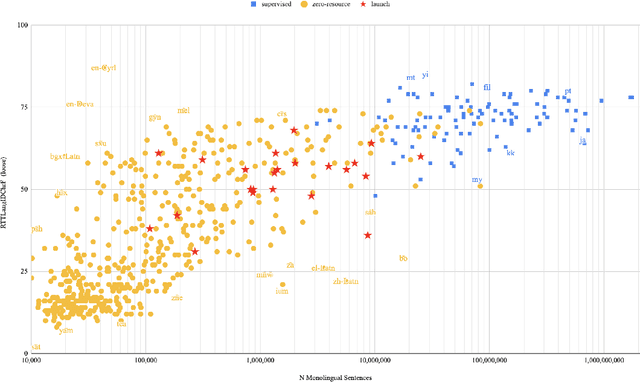
Abstract:In this paper we share findings from our effort to build practical machine translation (MT) systems capable of translating across over one thousand languages. We describe results in three research domains: (i) Building clean, web-mined datasets for 1500+ languages by leveraging semi-supervised pre-training for language identification and developing data-driven filtering techniques; (ii) Developing practical MT models for under-served languages by leveraging massively multilingual models trained with supervised parallel data for over 100 high-resource languages and monolingual datasets for an additional 1000+ languages; and (iii) Studying the limitations of evaluation metrics for these languages and conducting qualitative analysis of the outputs from our MT models, highlighting several frequent error modes of these types of models. We hope that our work provides useful insights to practitioners working towards building MT systems for currently understudied languages, and highlights research directions that can complement the weaknesses of massively multilingual models in data-sparse settings.
Mining Large-Scale Low-Resource Pronunciation Data From Wikipedia
Jan 27, 2021

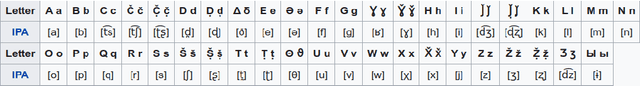

Abstract:Pronunciation modeling is a key task for building speech technology in new languages, and while solid grapheme-to-phoneme (G2P) mapping systems exist, language coverage can stand to be improved. The information needed to build G2P models for many more languages can easily be found on Wikipedia, but unfortunately, it is stored in disparate formats. We report on a system we built to mine a pronunciation data set in 819 languages from loosely structured tables within Wikipedia. The data includes phoneme inventories, and for 63 low-resource languages, also includes the grapheme-to-phoneme (G2P) mapping. 54 of these languages do not have easily findable G2P mappings online otherwise. We turned the information from Wikipedia into a structured, machine-readable TSV format, and make the resulting data set publicly available so it can be improved further and used in a variety of applications involving low-resource languages.
Language ID in the Wild: Unexpected Challenges on the Path to a Thousand-Language Web Text Corpus
Oct 29, 2020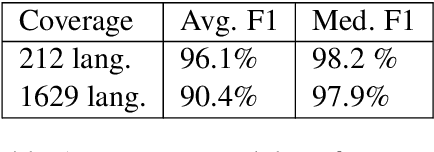
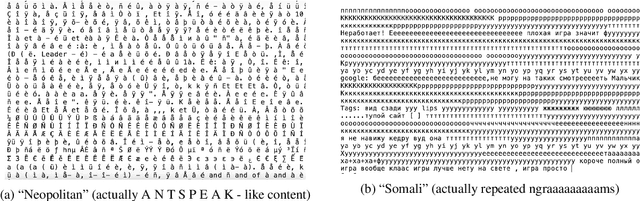

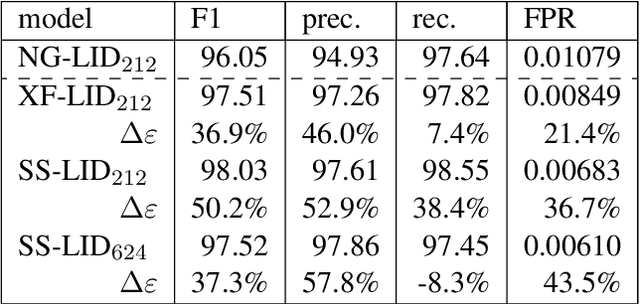
Abstract:Large text corpora are increasingly important for a wide variety of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, and automatic language identification (LangID) is a core technology needed to collect such datasets in a multilingual context. LangID is largely treated as solved in the literature, with models reported that achieve over 90% average F1 on as many as 1,366 languages. We train LangID models on up to 1,629 languages with comparable quality on held-out test sets, but find that human-judged LangID accuracy for web-crawl text corpora created using these models is only around 5% for many lower-resource languages, suggesting a need for more robust evaluation. Further analysis revealed a variety of error modes, arising from domain mismatch, class imbalance, language similarity, and insufficiently expressive models. We propose two classes of techniques to mitigate these errors: wordlist-based tunable-precision filters (for which we release curated lists in about 500 languages) and transformer-based semi-supervised LangID models, which increase median dataset precision from 5.5% to 71.2%. These techniques enable us to create an initial data set covering 100K or more relatively clean sentences in each of 500+ languages, paving the way towards a 1,000-language web text corpus.
Writing Across the World's Languages: Deep Internationalization for Gboard, the Google Keyboard
Dec 03, 2019Abstract:This technical report describes our deep internationalization program for Gboard, the Google Keyboard. Today, Gboard supports 900+ language varieties across 70+ writing systems, and this report describes how and why we have been adding support for hundreds of language varieties from around the globe. Many languages of the world are increasingly used in writing on an everyday basis, and we describe the trends we see. We cover technological and logistical challenges in scaling up a language technology product like Gboard to hundreds of language varieties, and describe how we built systems and processes to operate at scale. Finally, we summarize the key take-aways from user studies we ran with speakers of hundreds of languages from around the world.
Automatic Keyboard Layout Design for Low-Resource Latin-Script Languages
Jan 18, 2019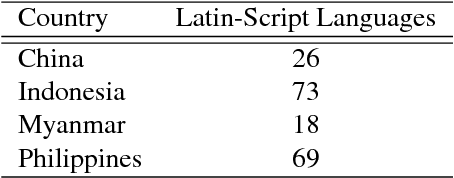


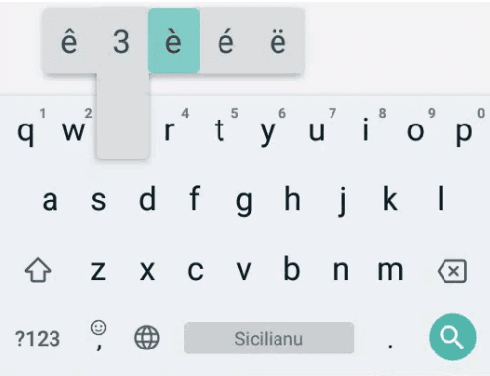
Abstract:We present our approach to automatically designing and implementing keyboard layouts on mobile devices for typing low-resource languages written in the Latin script. For many speakers, one of the barriers in accessing and creating text content on the web is the absence of input tools for their language. Ease in typing in these languages would lower technological barriers to online communication and collaboration, likely leading to the creation of more web content. Unfortunately, it can be time-consuming to develop layouts manually even for language communities that use a keyboard layout very similar to English; starting from scratch requires many configuration files to describe multiple possible behaviors for each key. With our approach, we only need a small amount of data in each language to generate keyboard layouts with very little human effort. This process can help serve speakers of low-resource languages in a scalable way, allowing us to develop input tools for more languages. Having input tools that reflect the linguistic diversity of the world will let as many people as possible use technology to learn, communicate, and express themselves in their own native languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge