Junlin Xie
AdaDrive: Self-Adaptive Slow-Fast System for Language-Grounded Autonomous Driving
Nov 09, 2025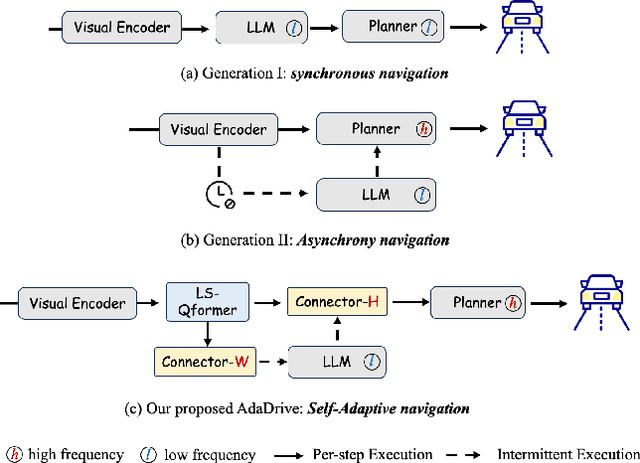
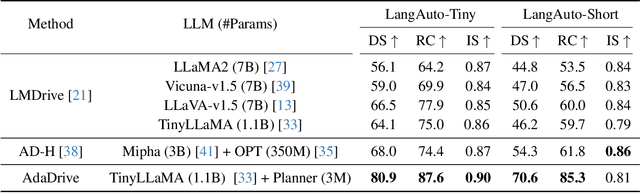
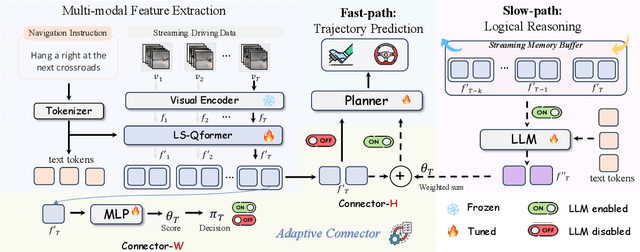
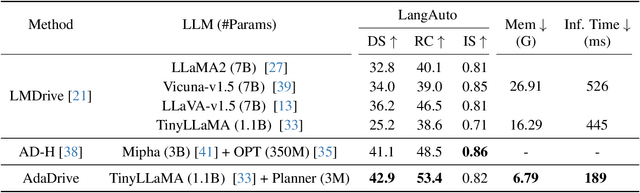
Abstract:Effectively integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) into autonomous driving requires a balance between leveraging high-level reasoning and maintaining real-time efficiency. Existing approaches either activate LLMs too frequently, causing excessive computational overhead, or use fixed schedules, failing to adapt to dynamic driving conditions. To address these challenges, we propose AdaDrive, an adaptively collaborative slow-fast framework that optimally determines when and how LLMs contribute to decision-making. (1) When to activate the LLM: AdaDrive employs a novel adaptive activation loss that dynamically determines LLM invocation based on a comparative learning mechanism, ensuring activation only in complex or critical scenarios. (2) How to integrate LLM assistance: Instead of rigid binary activation, AdaDrive introduces an adaptive fusion strategy that modulates a continuous, scaled LLM influence based on scene complexity and prediction confidence, ensuring seamless collaboration with conventional planners. Through these strategies, AdaDrive provides a flexible, context-aware framework that maximizes decision accuracy without compromising real-time performance. Extensive experiments on language-grounded autonomous driving benchmarks demonstrate that AdaDrive state-of-the-art performance in terms of both driving accuracy and computational efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/ReaFly/AdaDrive.
Shortcut Learning in Generalist Robot Policies: The Role of Dataset Diversity and Fragmentation
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Generalist robot policies trained on large-scale datasets such as Open X-Embodiment (OXE) demonstrate strong performance across a wide range of tasks. However, they often struggle to generalize beyond the distribution of their training data. In this paper, we investigate the underlying cause of this limited generalization capability. We identify shortcut learning -- the reliance on task-irrelevant features -- as a key impediment to generalization. Through comprehensive theoretical and empirical analysis, we uncover two primary contributors to shortcut learning: (1) limited diversity within individual sub-datasets, and (2) significant distributional disparities across sub-datasets, leading to dataset fragmentation. These issues arise from the inherent structure of large-scale datasets like OXE, which are typically composed of multiple sub-datasets collected independently across varied environments and embodiments. Our findings provide critical insights into dataset collection strategies that can reduce shortcut learning and enhance the generalization ability of generalist robot policies. Moreover, in scenarios where acquiring new large-scale data is impractical, we demonstrate that carefully selected robotic data augmentation strategies can effectively reduce shortcut learning in existing offline datasets, thereby improving generalization capabilities of generalist robot policies, e.g., $\pi_0$, in both simulation and real-world environments. More information at https://lucky-light-sun.github.io/proj/shortcut-learning-in-grps/.
Policy Contrastive Decoding for Robotic Foundation Models
May 19, 2025Abstract:Robotic foundation models, or generalist robot policies, hold immense potential to enable flexible, general-purpose and dexterous robotic systems. Despite their advancements, our empirical experiments reveal that existing robot policies are prone to learning spurious correlations from pre-training trajectories, adversely affecting their generalization capabilities beyond the training data. To tackle this, we propose a novel Policy Contrastive Decoding (PCD) approach, which redirects the robot policy's focus toward object-relevant visual clues by contrasting action probability distributions derived from original and object-masked visual inputs. As a training-free method, our PCD can be used as a plugin to improve different types of robot policies without needing to finetune or access model weights. We conduct extensive experiments on top of three open-source robot policies, including the autoregressive policy OpenVLA and the diffusion-based policies Octo and $\pi_0$. The obtained results in both simulation and real-world environments prove PCD's flexibility and effectiveness, e.g., PCD enhances the state-of-the-art policy $\pi_0$ by 8% in the simulation environment and by 108% in the real-world environment. Code and demos are publicly available at: https://Koorye.github.io/proj/PCD.
H2VU-Benchmark: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Hierarchical Holistic Video Understanding
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of multimodal models, the demand for assessing video understanding capabilities has been steadily increasing. However, existing benchmarks for evaluating video understanding exhibit significant limitations in coverage, task diversity, and scene adaptability. These shortcomings hinder the accurate assessment of models' comprehensive video understanding capabilities. To tackle this challenge, we propose a hierarchical and holistic video understanding (H2VU) benchmark designed to evaluate both general video and online streaming video comprehension. This benchmark contributes three key features: Extended video duration: Spanning videos from brief 3-second clips to comprehensive 1.5-hour recordings, thereby bridging the temporal gaps found in current benchmarks. Comprehensive assessment tasks: Beyond traditional perceptual and reasoning tasks, we have introduced modules for countercommonsense comprehension and trajectory state tracking. These additions test the models' deep understanding capabilities beyond mere prior knowledge. Enriched video data: To keep pace with the rapid evolution of current AI agents, we have expanded first-person streaming video datasets. This expansion allows for the exploration of multimodal models' performance in understanding streaming videos from a first-person perspective. Extensive results from H2VU reveal that existing multimodal large language models (MLLMs) possess substantial potential for improvement in our newly proposed evaluation tasks. We expect that H2VU will facilitate advancements in video understanding research by offering a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of MLLMs.
Large Multimodal Agents: A Survey
Feb 23, 2024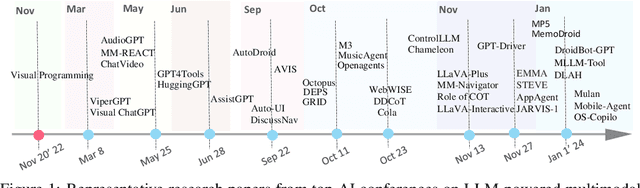
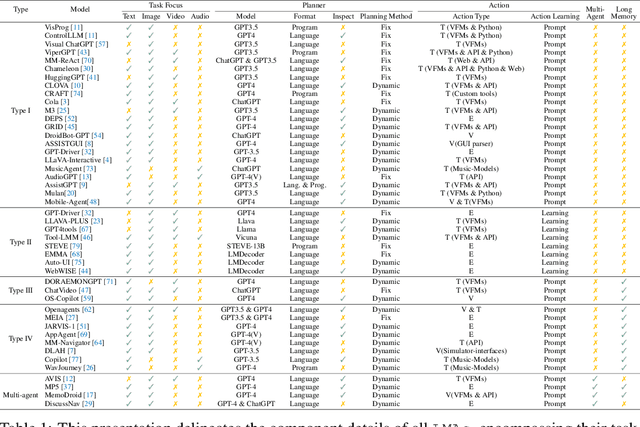
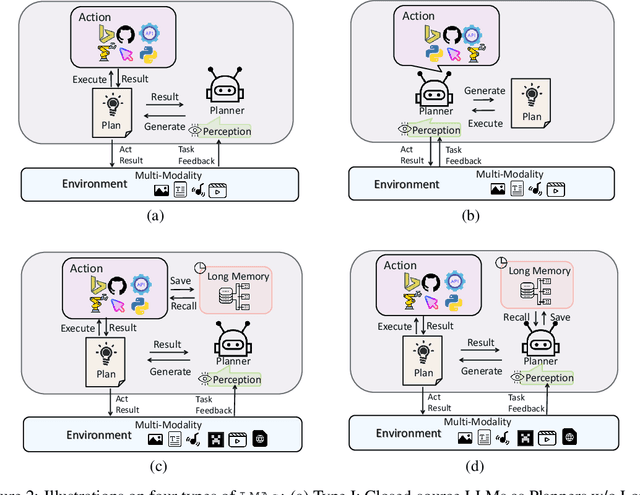
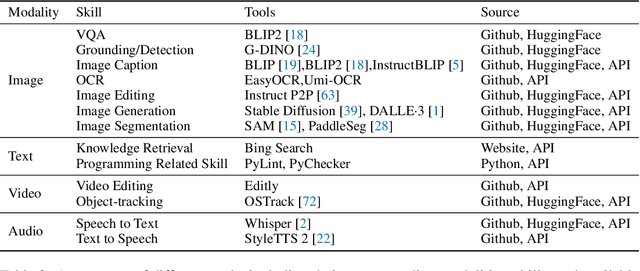
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved superior performance in powering text-based AI agents, endowing them with decision-making and reasoning abilities akin to humans. Concurrently, there is an emerging research trend focused on extending these LLM-powered AI agents into the multimodal domain. This extension enables AI agents to interpret and respond to diverse multimodal user queries, thereby handling more intricate and nuanced tasks. In this paper, we conduct a systematic review of LLM-driven multimodal agents, which we refer to as large multimodal agents ( LMAs for short). First, we introduce the essential components involved in developing LMAs and categorize the current body of research into four distinct types. Subsequently, we review the collaborative frameworks integrating multiple LMAs , enhancing collective efficacy. One of the critical challenges in this field is the diverse evaluation methods used across existing studies, hindering effective comparison among different LMAs . Therefore, we compile these evaluation methodologies and establish a comprehensive framework to bridge the gaps. This framework aims to standardize evaluations, facilitating more meaningful comparisons. Concluding our review, we highlight the extensive applications of LMAs and propose possible future research directions. Our discussion aims to provide valuable insights and guidelines for future research in this rapidly evolving field. An up-to-date resource list is available at https://github.com/jun0wanan/awesome-large-multimodal-agents.
Generalized Unbiased Scene Graph Generation
Aug 09, 2023Abstract:Existing Unbiased Scene Graph Generation (USGG) methods only focus on addressing the predicate-level imbalance that high-frequency classes dominate predictions of rare ones, while overlooking the concept-level imbalance. Actually, even if predicates themselves are balanced, there is still a significant concept-imbalance within them due to the long-tailed distribution of contexts (i.e., subject-object combinations). This concept-level imbalance poses a more pervasive and challenging issue compared to the predicate-level imbalance since subject-object pairs are inherently complex in combinations. Hence, we introduce a novel research problem: Generalized Unbiased Scene Graph Generation (G-USGG), which takes into account both predicate-level and concept-level imbalance. To the end, we propose the Multi-Concept Learning (MCL) framework, which ensures a balanced learning process across rare/ uncommon/ common concepts. MCL first quantifies the concept-level imbalance across predicates in terms of different amounts of concepts, representing as multiple concept-prototypes within the same class. It then effectively learns concept-prototypes by applying the Concept Regularization (CR) technique. Furthermore, to achieve balanced learning over different concepts, we introduce the Balanced Prototypical Memory (BPM), which guides SGG models to generate balanced representations for concept-prototypes. Extensive experiments demonstrate the remarkable efficacy of our model-agnostic strategy in enhancing the performance of benchmark models on both VG-SGG and OI-SGG datasets, leading to new state-of-the-art achievements in two key aspects: predicate-level unbiased relation recognition and concept-level compositional generability.
Dilated Context Integrated Network with Cross-Modal Consensus for Temporal Emotion Localization in Videos
Aug 03, 2022
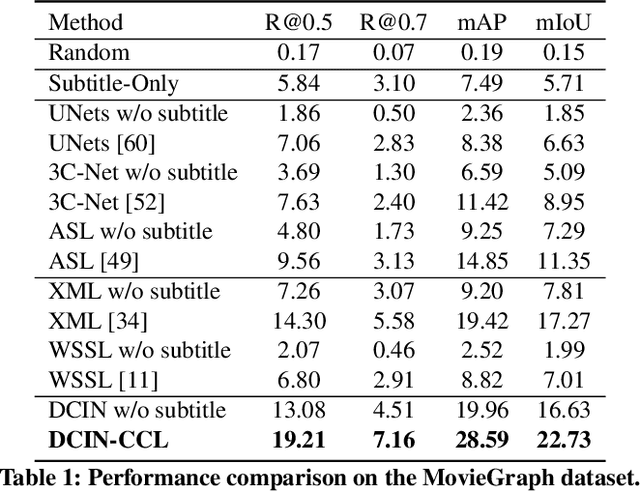
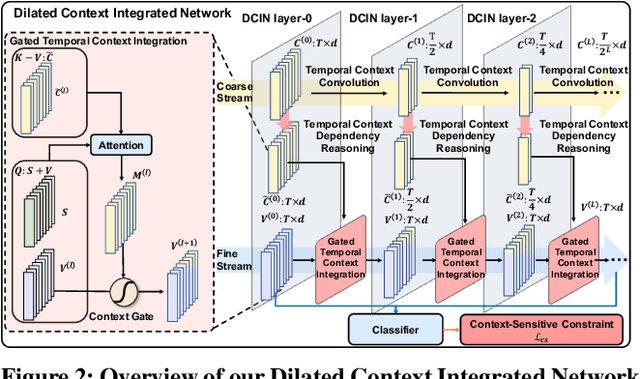
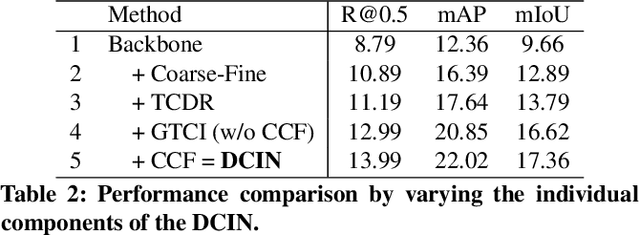
Abstract:Understanding human emotions is a crucial ability for intelligent robots to provide better human-robot interactions. The existing works are limited to trimmed video-level emotion classification, failing to locate the temporal window corresponding to the emotion. In this paper, we introduce a new task, named Temporal Emotion Localization in videos~(TEL), which aims to detect human emotions and localize their corresponding temporal boundaries in untrimmed videos with aligned subtitles. TEL presents three unique challenges compared to temporal action localization: 1) The emotions have extremely varied temporal dynamics; 2) The emotion cues are embedded in both appearances and complex plots; 3) The fine-grained temporal annotations are complicated and labor-intensive. To address the first two challenges, we propose a novel dilated context integrated network with a coarse-fine two-stream architecture. The coarse stream captures varied temporal dynamics by modeling multi-granularity temporal contexts. The fine stream achieves complex plots understanding by reasoning the dependency between the multi-granularity temporal contexts from the coarse stream and adaptively integrates them into fine-grained video segment features. To address the third challenge, we introduce a cross-modal consensus learning paradigm, which leverages the inherent semantic consensus between the aligned video and subtitle to achieve weakly-supervised learning. We contribute a new testing set with 3,000 manually-annotated temporal boundaries so that future research on the TEL problem can be quantitatively evaluated. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our approach on temporal emotion localization. The repository of this work is at https://github.com/YYJMJC/Temporal-Emotion-Localization-in-Videos.
KinD-LCE Curve Estimation And Retinex Fusion On Low-Light Image
Jul 19, 2022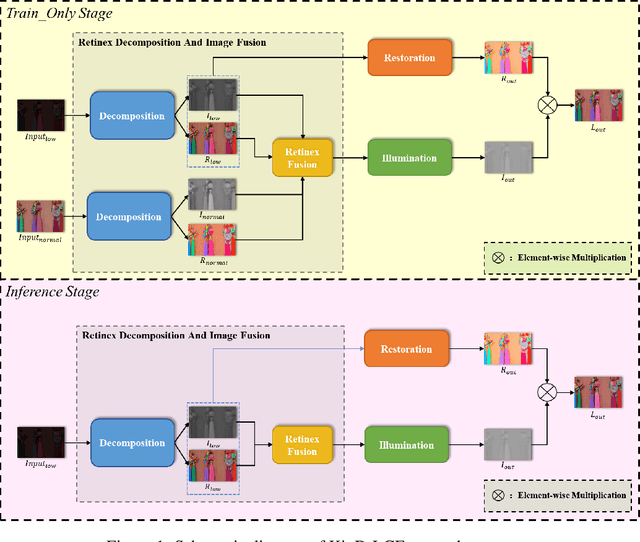
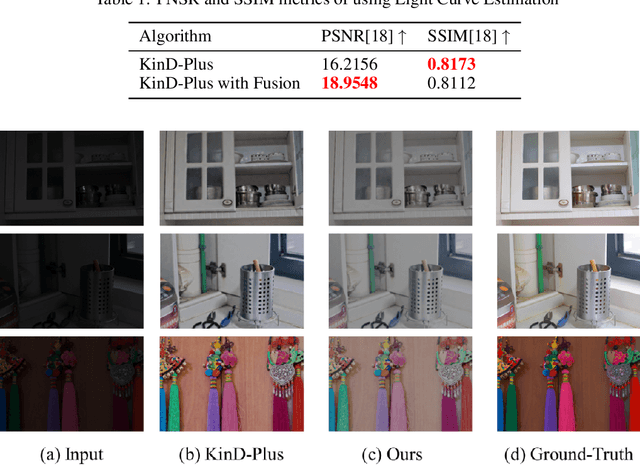

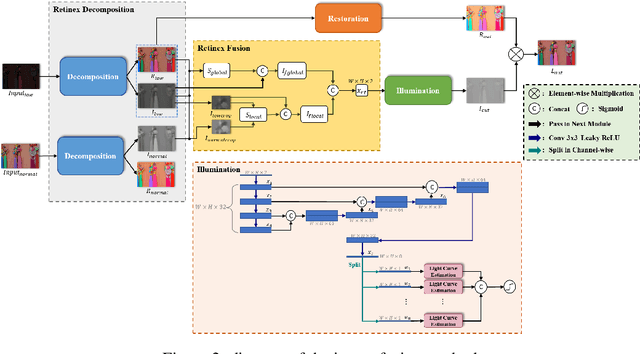
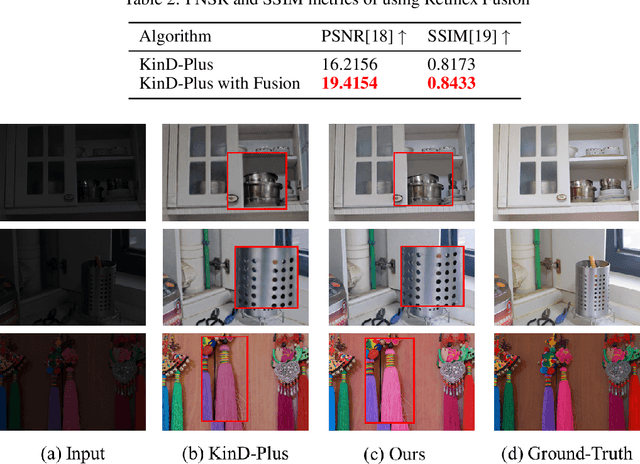
Abstract:The problems of low light image noise and chromatic aberration is a challenging problem for tasks such as object detection, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, etc. In this paper, we propose the algorithm for low illumination enhancement. KinD-LCE uses the light curve estimation module in the network structure to enhance the illumination map in the Retinex decomposed image, which improves the image brightness; we proposed the illumination map and reflection map fusion module to restore the restored image details and reduce the detail loss. Finally, we included a total variation loss function to eliminate noise. Our method uses the GladNet dataset as the training set, and the LOL dataset as the test set and is validated using ExDark as the dataset for downstream tasks. Extensive Experiments on the benchmarks demonstrate the advantages of our method and are close to the state-of-the-art results, which achieve a PSNR of 19.7216 and SSIM of 0.8213 in terms of metrics.
Compositional Temporal Grounding with Structured Variational Cross-Graph Correspondence Learning
Mar 28, 2022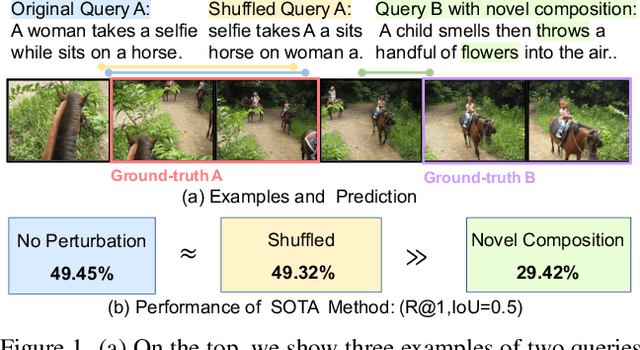
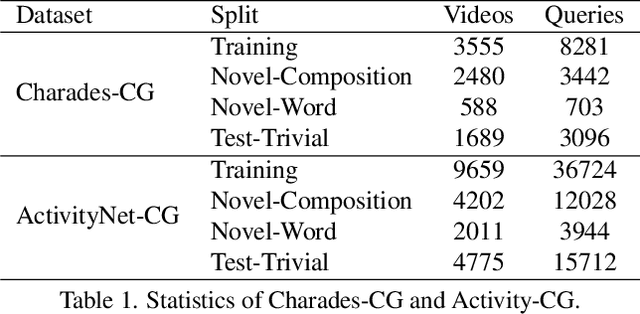
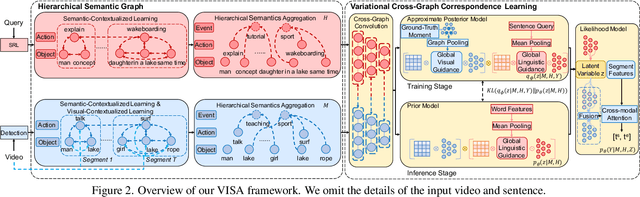
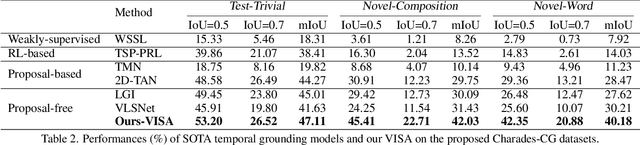
Abstract:Temporal grounding in videos aims to localize one target video segment that semantically corresponds to a given query sentence. Thanks to the semantic diversity of natural language descriptions, temporal grounding allows activity grounding beyond pre-defined classes and has received increasing attention in recent years. The semantic diversity is rooted in the principle of compositionality in linguistics, where novel semantics can be systematically described by combining known words in novel ways (compositional generalization). However, current temporal grounding datasets do not specifically test for the compositional generalizability. To systematically measure the compositional generalizability of temporal grounding models, we introduce a new Compositional Temporal Grounding task and construct two new dataset splits, i.e., Charades-CG and ActivityNet-CG. Evaluating the state-of-the-art methods on our new dataset splits, we empirically find that they fail to generalize to queries with novel combinations of seen words. To tackle this challenge, we propose a variational cross-graph reasoning framework that explicitly decomposes video and language into multiple structured hierarchies and learns fine-grained semantic correspondence among them. Experiments illustrate the superior compositional generalizability of our approach. The repository of this work is at https://github.com/YYJMJC/ Compositional-Temporal-Grounding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge