Chang Lu
Adaptive Graph Learning with Transformer for Multi-Reservoir Inflow Prediction
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Reservoir inflow prediction is crucial for water resource management, yet existing approaches mainly focus on single-reservoir models that ignore spatial dependencies among interconnected reservoirs. We introduce AdaTrip as an adaptive, time-varying graph learning framework for multi-reservoir inflow forecasting. AdaTrip constructs dynamic graphs where reservoirs are nodes with directed edges reflecting hydrological connections, employing attention mechanisms to automatically identify crucial spatial and temporal dependencies. Evaluation on thirty reservoirs in the Upper Colorado River Basin demonstrates superiority over existing baselines, with improved performance for reservoirs with limited records through parameter sharing. Additionally, AdaTrip provides interpretable attention maps at edge and time-step levels, offering insights into hydrological controls to support operational decision-making. Our code is available at https://github.com/humphreyhuu/AdaTrip.
No Black Boxes: Interpretable and Interactable Predictive Healthcare with Knowledge-Enhanced Agentic Causal Discovery
May 22, 2025Abstract:Deep learning models trained on extensive Electronic Health Records (EHR) data have achieved high accuracy in diagnosis prediction, offering the potential to assist clinicians in decision-making and treatment planning. However, these models lack two crucial features that clinicians highly value: interpretability and interactivity. The ``black-box'' nature of these models makes it difficult for clinicians to understand the reasoning behind predictions, limiting their ability to make informed decisions. Additionally, the absence of interactive mechanisms prevents clinicians from incorporating their own knowledge and experience into the decision-making process. To address these limitations, we propose II-KEA, a knowledge-enhanced agent-driven causal discovery framework that integrates personalized knowledge databases and agentic LLMs. II-KEA enhances interpretability through explicit reasoning and causal analysis, while also improving interactivity by allowing clinicians to inject their knowledge and experience through customized knowledge bases and prompts. II-KEA is evaluated on both MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV, demonstrating superior performance along with enhanced interpretability and interactivity, as evidenced by its strong results from extensive case studies.
Reflection of Episodes: Learning to Play Game from Expert and Self Experiences
Feb 19, 2025

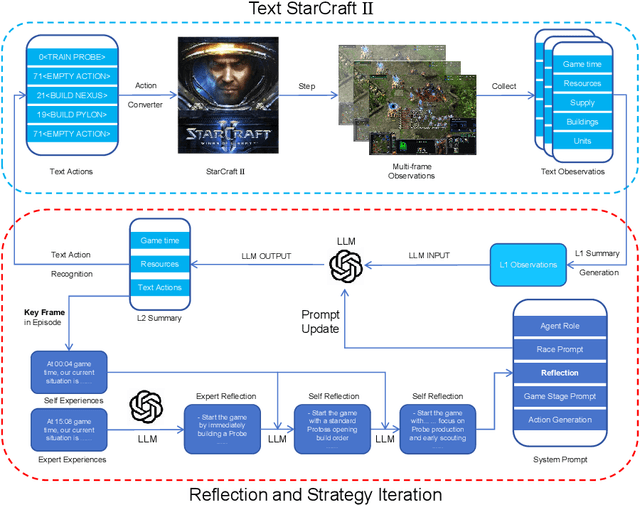

Abstract:StarCraft II is a complex and dynamic real-time strategy (RTS) game environment, which is very suitable for artificial intelligence and reinforcement learning research. To address the problem of Large Language Model(LLM) learning in complex environments through self-reflection, we propose a Reflection of Episodes(ROE) framework based on expert experience and self-experience. This framework first obtains key information in the game through a keyframe selection method, then makes decisions based on expert experience and self-experience. After a game is completed, it reflects on the previous experience to obtain new self-experience. Finally, in the experiment, our method beat the robot under the Very Hard difficulty in TextStarCraft II. We analyze the data of the LLM in the process of the game in detail, verified its effectiveness.
LLM-PySC2: Starcraft II learning environment for Large Language Models
Nov 08, 2024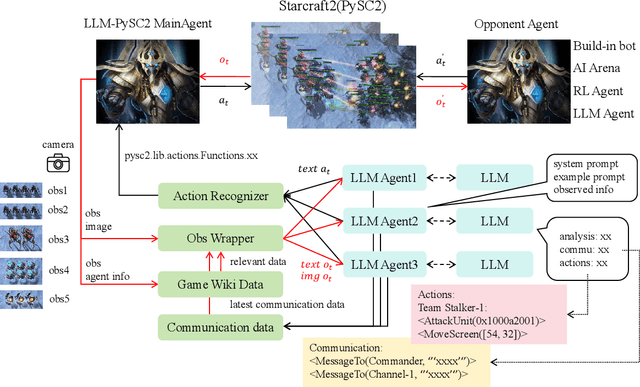
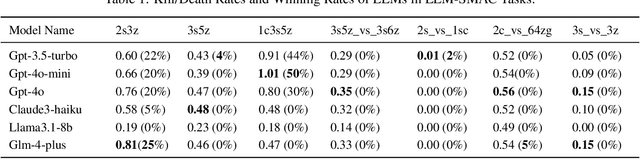
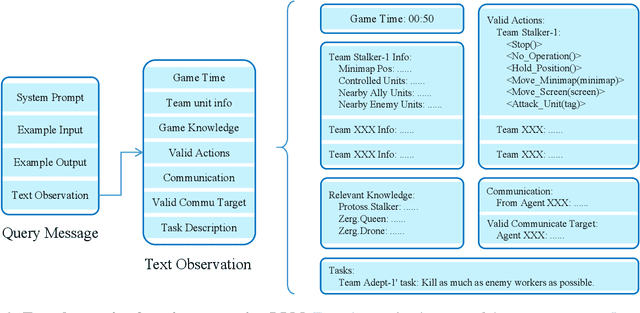
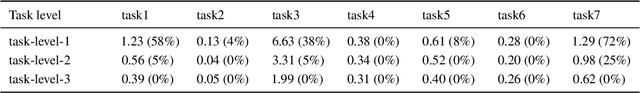
Abstract:This paper introduces a new environment LLM-PySC2 (the Large Language Model StarCraft II Learning Environment), a platform derived from DeepMind's StarCraft II Learning Environment that serves to develop Large Language Models (LLMs) based decision-making methodologies. This environment is the first to offer the complete StarCraft II action space, multi-modal observation interfaces, and a structured game knowledge database, which are seamlessly connected with various LLMs to facilitate the research of LLMs-based decision-making. To further support multi-agent research, we developed an LLM collaborative framework that supports multi-agent concurrent queries and multi-agent communication. In our experiments, the LLM-PySC2 environment is adapted to be compatible with the StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge (SMAC) task group and provided eight new scenarios focused on macro-decision abilities. We evaluated nine mainstream LLMs in the experiments, and results show that sufficient parameters are necessary for LLMs to make decisions, but improving reasoning ability does not directly lead to better decision-making outcomes. Our findings further indicate the importance of enabling large models to learn autonomously in the deployment environment through parameter training or train-free learning techniques. Ultimately, we expect that the LLM-PySC2 environment can promote research on learning methods for LLMs, helping LLM-based methods better adapt to task scenarios.
DualMAR: Medical-Augmented Representation from Dual-Expertise Perspectives
Oct 25, 2024



Abstract:Electronic Health Records (EHR) has revolutionized healthcare data management and prediction in the field of AI and machine learning. Accurate predictions of diagnosis and medications significantly mitigate health risks and provide guidance for preventive care. However, EHR driven models often have limited scope on understanding medical-domain knowledge and mostly rely on simple-and-sole ontologies. In addition, due to the missing features and incomplete disease coverage of EHR, most studies only focus on basic analysis on conditions and medication. We propose DualMAR, a framework that enhances EHR prediction tasks through both individual observation data and public knowledge bases. First, we construct a bi-hierarchical Diagnosis Knowledge Graph (KG) using verified public clinical ontologies and augment this KG via Large Language Models (LLMs); Second, we design a new proxy-task learning on lab results in EHR for pretraining, which further enhance KG representation and patient embeddings. By retrieving radial and angular coordinates upon polar space, DualMAR enables accurate predictions based on rich hierarchical and semantic embeddings from KG. Experiments also demonstrate that DualMAR outperforms state-of-the-art models, validating its effectiveness in EHR prediction and KG integration in medical domains.
Bi-Mamba4TS: Bidirectional Mamba for Time Series Forecasting
Apr 24, 2024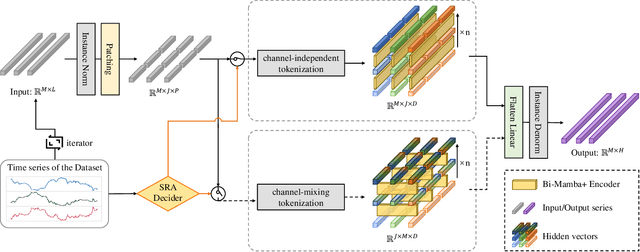
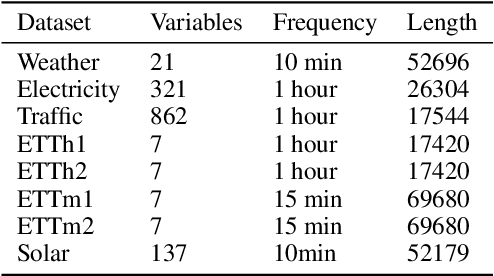
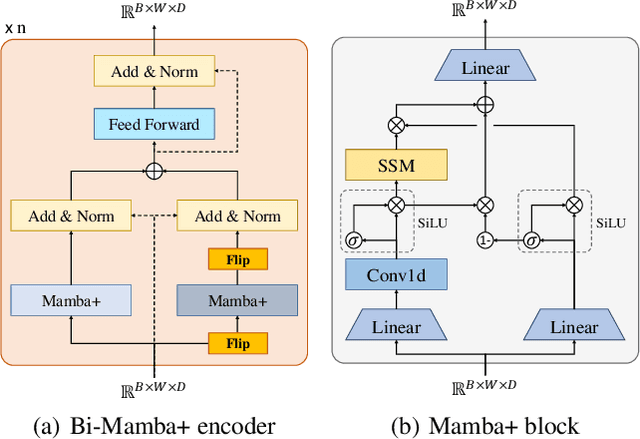
Abstract:Long-term time series forecasting (LTSF) provides longer insights into future trends and patterns. In recent years, deep learning models especially Transformers have achieved advanced performance in LTSF tasks. However, the quadratic complexity of Transformers rises the challenge of balancing computaional efficiency and predicting performance. Recently, a new state space model (SSM) named Mamba is proposed. With the selective capability on input data and the hardware-aware parallel computing algorithm, Mamba can well capture long-term dependencies while maintaining linear computational complexity. Mamba has shown great ability for long sequence modeling and is a potential competitor to Transformer-based models in LTSF. In this paper, we propose Bi-Mamba4TS, a bidirectional Mamba for time series forecasting. To address the sparsity of time series semantics, we adopt the patching technique to enrich the local information while capturing the evolutionary patterns of time series in a finer granularity. To select more appropriate modeling method based on the characteristics of the dataset, our model unifies the channel-independent and channel-mixing tokenization strategies and uses a series-relation-aware decider to control the strategy choosing process. Extensive experiments on seven real-world datasets show that our model achieves more accurate predictions compared with state-of-the-art methods.
Towards Semi-Structured Automatic ICD Coding via Tree-based Contrastive Learning
Oct 14, 2023Abstract:Automatic coding of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a multi-label text categorization task that involves extracting disease or procedure codes from clinical notes. Despite the application of state-of-the-art natural language processing (NLP) techniques, there are still challenges including limited availability of data due to privacy constraints and the high variability of clinical notes caused by different writing habits of medical professionals and various pathological features of patients. In this work, we investigate the semi-structured nature of clinical notes and propose an automatic algorithm to segment them into sections. To address the variability issues in existing ICD coding models with limited data, we introduce a contrastive pre-training approach on sections using a soft multi-label similarity metric based on tree edit distance. Additionally, we design a masked section training strategy to enable ICD coding models to locate sections related to ICD codes. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed training strategies effectively enhance the performance of existing ICD coding methods.
KinD-LCE Curve Estimation And Retinex Fusion On Low-Light Image
Jul 19, 2022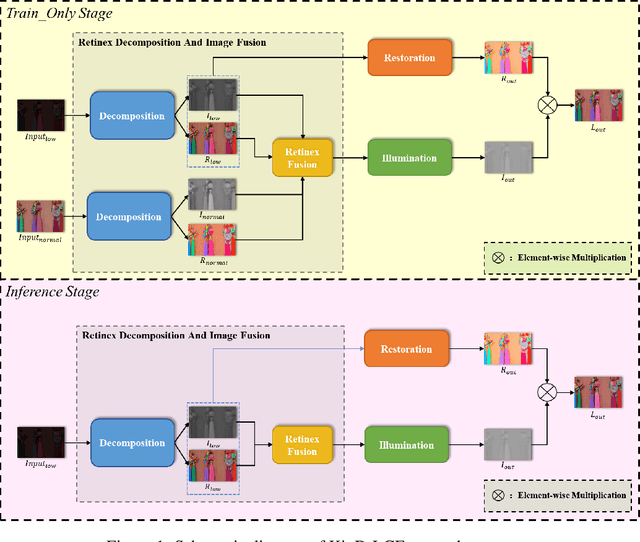
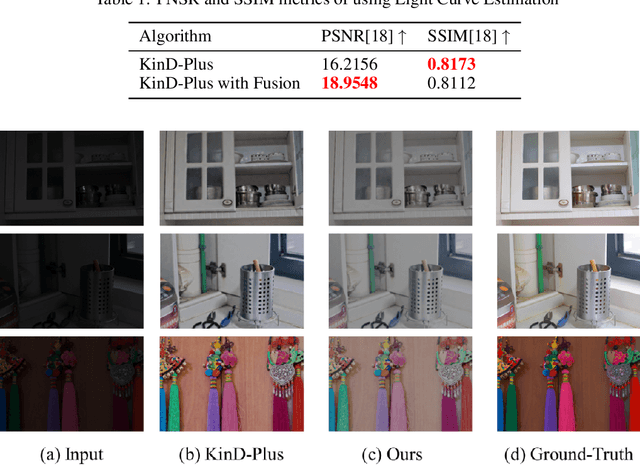

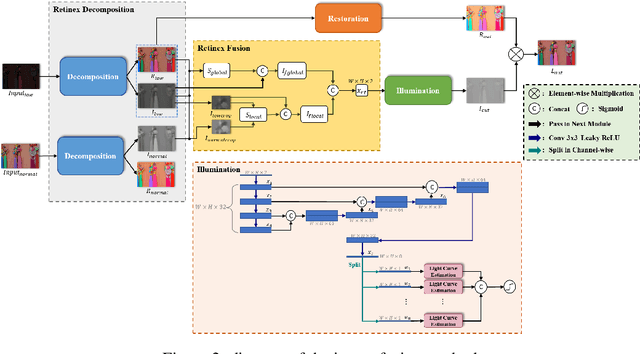
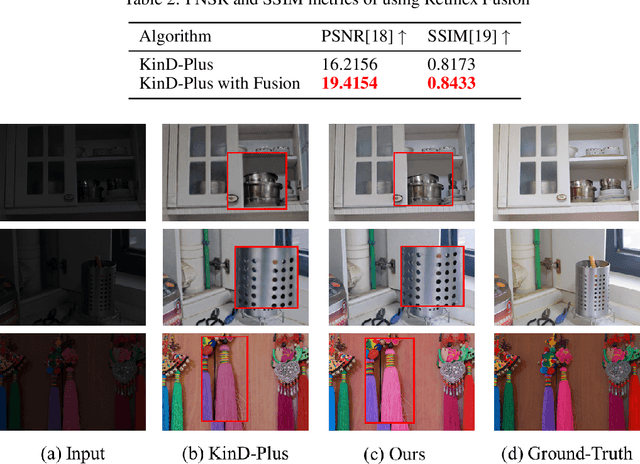
Abstract:The problems of low light image noise and chromatic aberration is a challenging problem for tasks such as object detection, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, etc. In this paper, we propose the algorithm for low illumination enhancement. KinD-LCE uses the light curve estimation module in the network structure to enhance the illumination map in the Retinex decomposed image, which improves the image brightness; we proposed the illumination map and reflection map fusion module to restore the restored image details and reduce the detail loss. Finally, we included a total variation loss function to eliminate noise. Our method uses the GladNet dataset as the training set, and the LOL dataset as the test set and is validated using ExDark as the dataset for downstream tasks. Extensive Experiments on the benchmarks demonstrate the advantages of our method and are close to the state-of-the-art results, which achieve a PSNR of 19.7216 and SSIM of 0.8213 in terms of metrics.
Using Frequency Attention to Make Adversarial Patch Powerful Against Person Detector
May 11, 2022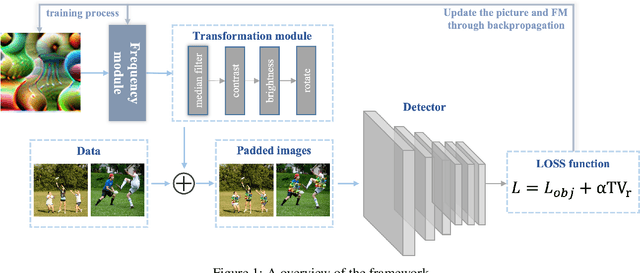
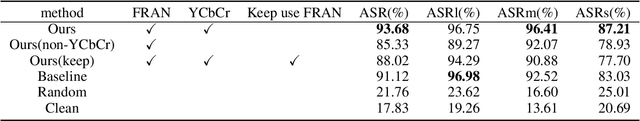
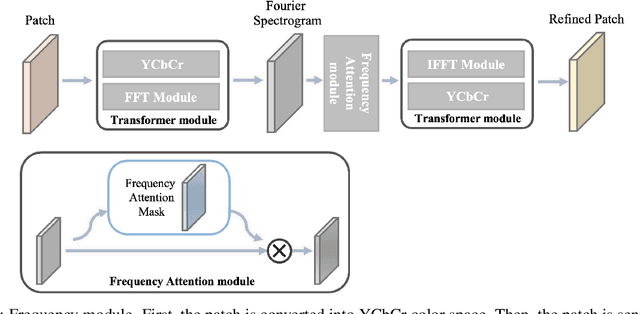
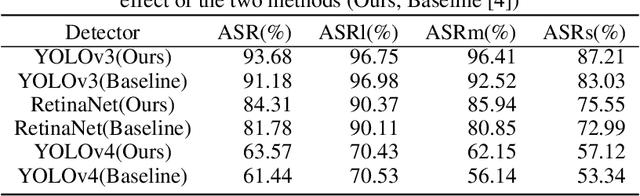
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. In particular, object detectors may be attacked by applying a particular adversarial patch to the image. However, because the patch shrinks during preprocessing, most existing approaches that employ adversarial patches to attack object detectors would diminish the attack success rate on small and medium targets. This paper proposes a Frequency Module(FRAN), a frequency-domain attention module for guiding patch generation. This is the first study to introduce frequency domain attention to optimize the attack capabilities of adversarial patches. Our method increases the attack success rates of small and medium targets by 4.18% and 3.89%, respectively, over the state-of-the-art attack method for fooling the human detector while assaulting YOLOv3 without reducing the attack success rate of big targets.
STDC-MA Network for Semantic Segmentation
May 11, 2022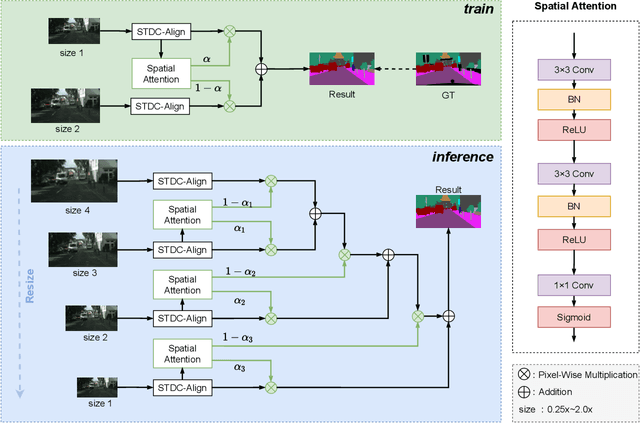

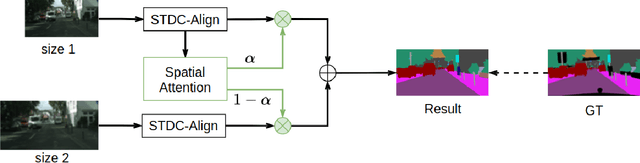
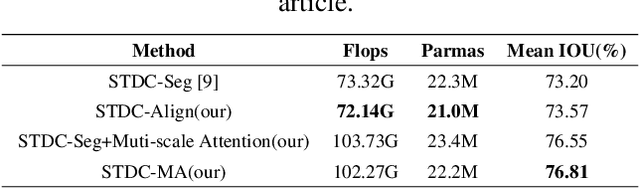
Abstract:Semantic segmentation is applied extensively in autonomous driving and intelligent transportation with methods that highly demand spatial and semantic information. Here, an STDC-MA network is proposed to meet these demands. First, the STDC-Seg structure is employed in STDC-MA to ensure a lightweight and efficient structure. Subsequently, the feature alignment module (FAM) is applied to understand the offset between high-level and low-level features, solving the problem of pixel offset related to upsampling on the high-level feature map. Our approach implements the effective fusion between high-level features and low-level features. A hierarchical multiscale attention mechanism is adopted to reveal the relationship among attention regions from two different input sizes of one image. Through this relationship, regions receiving much attention are integrated into the segmentation results, thereby reducing the unfocused regions of the input image and improving the effective utilization of multiscale features. STDC- MA maintains the segmentation speed as an STDC-Seg network while improving the segmentation accuracy of small objects. STDC-MA was verified on the verification set of Cityscapes. The segmentation result of STDC-MA attained 76.81% mIOU with the input of 0.5x scale, 3.61% higher than STDC-Seg.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge