Juan Manuel Zambrano Chaves
Tx-LLM: A Large Language Model for Therapeutics
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:Developing therapeutics is a lengthy and expensive process that requires the satisfaction of many different criteria, and AI models capable of expediting the process would be invaluable. However, the majority of current AI approaches address only a narrowly defined set of tasks, often circumscribed within a particular domain. To bridge this gap, we introduce Tx-LLM, a generalist large language model (LLM) fine-tuned from PaLM-2 which encodes knowledge about diverse therapeutic modalities. Tx-LLM is trained using a collection of 709 datasets that target 66 tasks spanning various stages of the drug discovery pipeline. Using a single set of weights, Tx-LLM simultaneously processes a wide variety of chemical or biological entities(small molecules, proteins, nucleic acids, cell lines, diseases) interleaved with free-text, allowing it to predict a broad range of associated properties, achieving competitive with state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on 43 out of 66 tasks and exceeding SOTA on 22. Among these, Tx-LLM is particularly powerful and exceeds best-in-class performance on average for tasks combining molecular SMILES representations with text such as cell line names or disease names, likely due to context learned during pretraining. We observe evidence of positive transfer between tasks with diverse drug types (e.g.,tasks involving small molecules and tasks involving proteins), and we study the impact of model size, domain finetuning, and prompting strategies on performance. We believe Tx-LLM represents an important step towards LLMs encoding biochemical knowledge and could have a future role as an end-to-end tool across the drug discovery development pipeline.
Training Small Multimodal Models to Bridge Biomedical Competency Gap: A Case Study in Radiology Imaging
Mar 20, 2024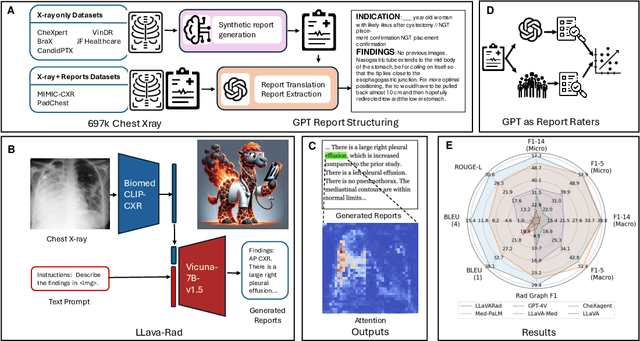
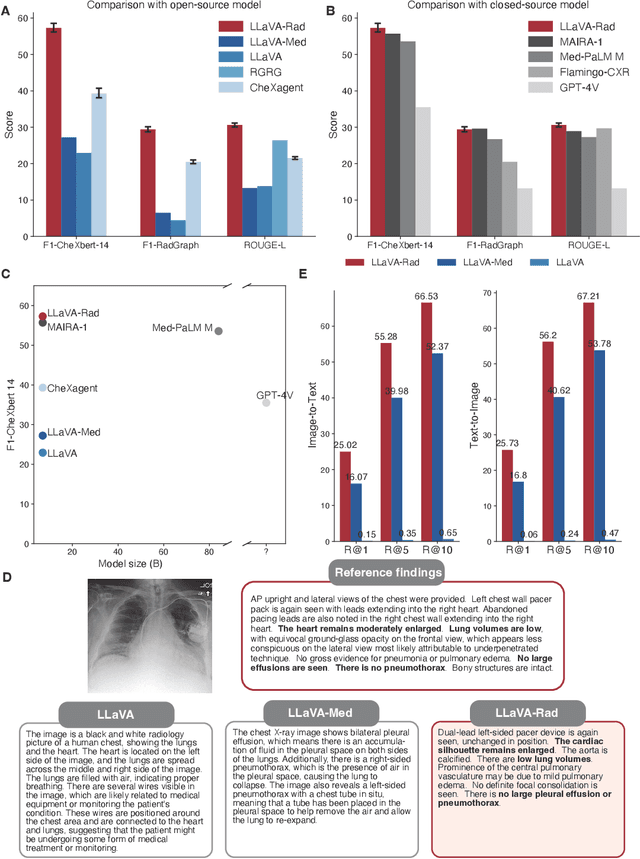
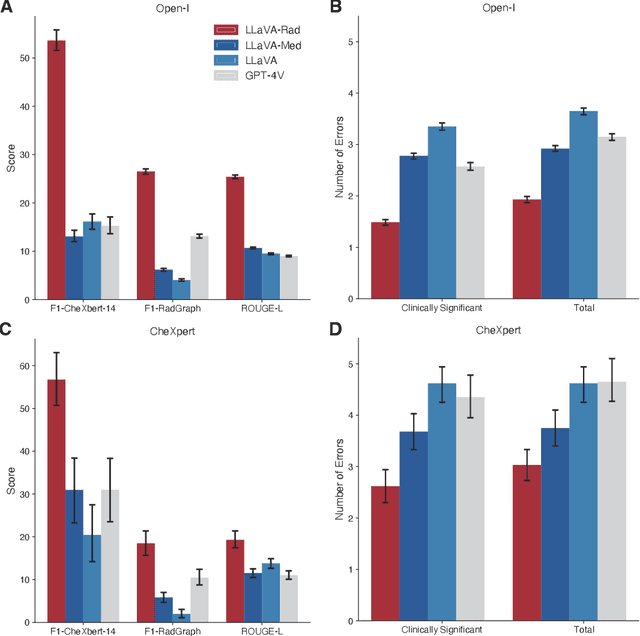
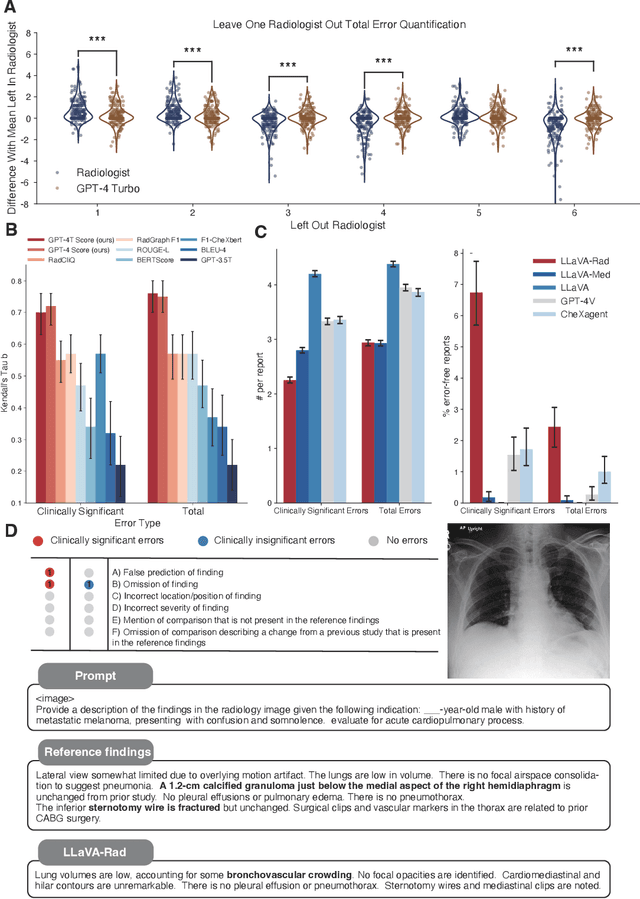
Abstract:The scaling laws and extraordinary performance of large foundation models motivate the development and utilization of such large models in biomedicine. However, despite early promising results on some biomedical benchmarks, there are still major challenges that need to be addressed before these models can be used in real-world applications. Frontier models such as GPT-4V still have major competency gaps in multimodal capabilities for biomedical applications. Moreover, pragmatic issues such as access, cost, latency, and compliance make it hard for clinicians to use privately-hosted state-of-the-art large models directly on private patient data. In this paper, we explore training open-source small multimodal models (SMMs) to bridge biomedical competency gaps for unmet clinical needs. To maximize data efficiency, we adopt a modular approach by incorporating state-of-the-art pre-trained models for image and text modalities, and focusing on training a lightweight adapter to ground each modality to the text embedding space. We conduct a comprehensive study of this approach on radiology imaging. For training, we assemble a large dataset with over 1 million image-text pairs. For evaluation, we propose a clinically driven novel approach using GPT-4 and demonstrate its parity with expert evaluation. We also study grounding qualitatively using attention. For best practice, we conduct a systematic ablation study on various choices in data engineering and multimodal training. The resulting LLaVA-Rad (7B) model attains state-of-the-art results on radiology tasks such as report generation and cross-modal retrieval, even outperforming much larger models such as GPT-4V and Med-PaLM M (84B). LLaVA-Rad is fast and can be run on a single V100 GPU in private settings, offering a promising state-of-the-art tool for real-world clinical applications.
RadAdapt: Radiology Report Summarization via Lightweight Domain Adaptation of Large Language Models
May 02, 2023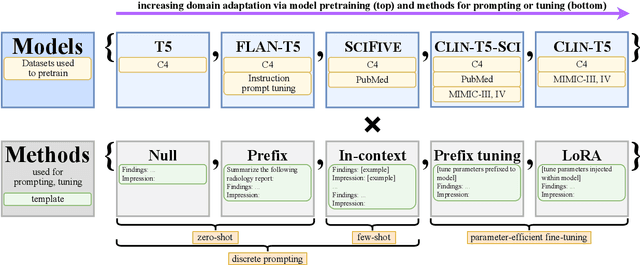
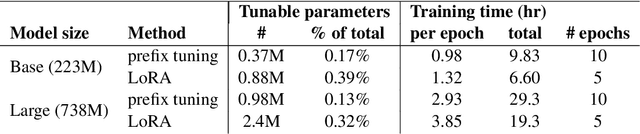
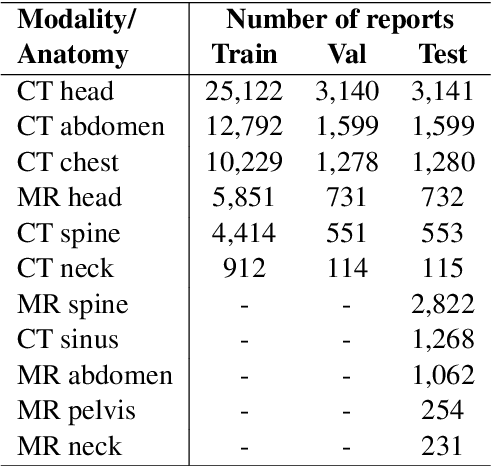

Abstract:We systematically investigate lightweight strategies to adapt large language models (LLMs) for the task of radiology report summarization (RRS). Specifically, we focus on domain adaptation via pretraining (on natural language, biomedical text, and clinical text) and via prompting (zero-shot, in-context learning) or parameter-efficient fine-tuning (prefix tuning, LoRA). Our results on the MIMIC-III dataset consistently demonstrate best performance by maximally adapting to the task via pretraining on clinical text and parameter-efficient fine-tuning on RRS examples. Importantly, this method fine-tunes a mere 0.32% of parameters throughout the model, in contrast to end-to-end fine-tuning (100% of parameters). Additionally, we study the effect of in-context examples and out-of-distribution (OOD) training before concluding with a radiologist reader study and qualitative analysis. Our findings highlight the importance of domain adaptation in RRS and provide valuable insights toward developing effective natural language processing solutions for clinical tasks.
Comp2Comp: Open-Source Body Composition Assessment on Computed Tomography
Feb 13, 2023Abstract:Computed tomography (CT) is routinely used in clinical practice to evaluate a wide variety of medical conditions. While CT scans provide diagnoses, they also offer the ability to extract quantitative body composition metrics to analyze tissue volume and quality. Extracting quantitative body composition measures manually from CT scans is a cumbersome and time-consuming task. Proprietary software has been developed recently to automate this process, but the closed-source nature impedes widespread use. There is a growing need for fully automated body composition software that is more accessible and easier to use, especially for clinicians and researchers who are not experts in medical image processing. To this end, we have built Comp2Comp, an open-source Python package for rapid and automated body composition analysis of CT scans. This package offers models, post-processing heuristics, body composition metrics, automated batching, and polychromatic visualizations. Comp2Comp currently computes body composition measures for bone, skeletal muscle, visceral adipose tissue, and subcutaneous adipose tissue on CT scans of the abdomen. We have created two pipelines for this purpose. The first pipeline computes vertebral measures, as well as muscle and adipose tissue measures, at the T12 - L5 vertebral levels from abdominal CT scans. The second pipeline computes muscle and adipose tissue measures on user-specified 2D axial slices. In this guide, we discuss the architecture of the Comp2Comp pipelines, provide usage instructions, and report internal and external validation results to measure the quality of segmentations and body composition measures. Comp2Comp can be found at https://github.com/StanfordMIMI/Comp2Comp.
RoentGen: Vision-Language Foundation Model for Chest X-ray Generation
Nov 23, 2022



Abstract:Multimodal models trained on large natural image-text pair datasets have exhibited astounding abilities in generating high-quality images. Medical imaging data is fundamentally different to natural images, and the language used to succinctly capture relevant details in medical data uses a different, narrow but semantically rich, domain-specific vocabulary. Not surprisingly, multi-modal models trained on natural image-text pairs do not tend to generalize well to the medical domain. Developing generative imaging models faithfully representing medical concepts while providing compositional diversity could mitigate the existing paucity of high-quality, annotated medical imaging datasets. In this work, we develop a strategy to overcome the large natural-medical distributional shift by adapting a pre-trained latent diffusion model on a corpus of publicly available chest x-rays (CXR) and their corresponding radiology (text) reports. We investigate the model's ability to generate high-fidelity, diverse synthetic CXR conditioned on text prompts. We assess the model outputs quantitatively using image quality metrics, and evaluate image quality and text-image alignment by human domain experts. We present evidence that the resulting model (RoentGen) is able to create visually convincing, diverse synthetic CXR images, and that the output can be controlled to a new extent by using free-form text prompts including radiology-specific language. Fine-tuning this model on a fixed training set and using it as a data augmentation method, we measure a 5% improvement of a classifier trained jointly on synthetic and real images, and a 3% improvement when trained on a larger but purely synthetic training set. Finally, we observe that this fine-tuning distills in-domain knowledge in the text-encoder and can improve its representation capabilities of certain diseases like pneumothorax by 25%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge