Joel Hestness
Power Lines: Scaling Laws for Weight Decay and Batch Size in LLM Pre-training
May 19, 2025



Abstract:Efficient LLM pre-training requires well-tuned hyperparameters (HPs), including learning rate {\eta} and weight decay {\lambda}. We study scaling laws for HPs: formulas for how to scale HPs as we scale model size N, dataset size D, and batch size B. Recent work suggests the AdamW timescale, B/({\eta}{\lambda}D), should remain constant across training settings, and we verify the implication that optimal {\lambda} scales linearly with B, for a fixed N,D. However, as N,D scale, we show the optimal timescale obeys a precise power law in the tokens-per-parameter ratio, D/N. This law thus provides a method to accurately predict {\lambda}opt in advance of large-scale training. We also study scaling laws for optimal batch size Bopt (the B enabling lowest loss at a given N,D) and critical batch size Bcrit (the B beyond which further data parallelism becomes ineffective). In contrast with prior work, we find both Bopt and Bcrit scale as power laws in D, independent of model size, N. Finally, we analyze how these findings inform the real-world selection of Pareto-optimal N and D under dual training time and compute objectives.
Don't be lazy: CompleteP enables compute-efficient deep transformers
May 02, 2025Abstract:We study compute efficiency of LLM training when using different parameterizations, i.e., rules for adjusting model and optimizer hyperparameters (HPs) as model size changes. Some parameterizations fail to transfer optimal base HPs (such as learning rate) across changes in model depth, requiring practitioners to either re-tune these HPs as they scale up (expensive), or accept sub-optimal training when re-tuning is prohibitive. Even when they achieve HP transfer, we develop theory to show parameterizations may still exist in the lazy learning regime where layers learn only features close to their linearization, preventing effective use of depth and nonlinearity. Finally, we identify and adopt the unique parameterization we call CompleteP that achieves both depth-wise HP transfer and non-lazy learning in all layers. CompleteP enables a wider range of model width/depth ratios to remain compute-efficient, unlocking shapes better suited for different hardware settings and operational contexts. Moreover, CompleteP enables 12-34\% compute efficiency improvements over the prior state-of-the-art.
Straight to Zero: Why Linearly Decaying the Learning Rate to Zero Works Best for LLMs
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:LLMs are commonly trained with a learning rate (LR) warmup, followed by cosine decay to 10% of the maximum (10x decay). In a large-scale empirical study, we show that under an optimal peak LR, a simple linear decay-to-zero (D2Z) schedule consistently outperforms other schedules when training at compute-optimal dataset sizes. D2Z is superior across a range of model sizes, batch sizes, datasets, and vocabularies. Benefits increase as dataset size increases. Leveraging a novel interpretation of AdamW as an exponential moving average of weight updates, we show how linear D2Z optimally balances the demands of early training (moving away from initial conditions) and late training (averaging over more updates in order to mitigate gradient noise). In experiments, a 610M-parameter model trained for 80 tokens-per-parameter (TPP) using D2Z achieves lower loss than when trained for 200 TPP using 10x decay, corresponding to an astonishing 60% compute savings. Models such as Llama2-7B, trained for 286 TPP with 10x decay, could likely have saved a majority of compute by training with D2Z.
Crystal: Illuminating LLM Abilities on Language and Code
Nov 06, 2024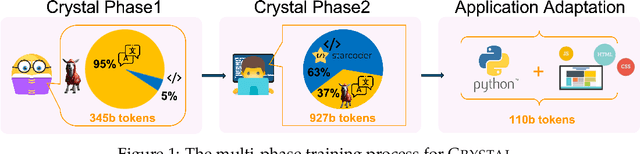
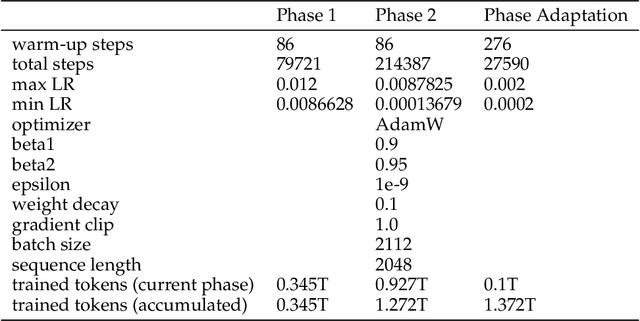
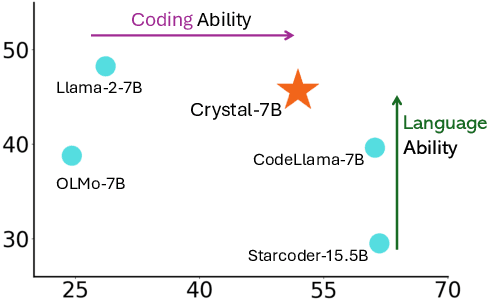
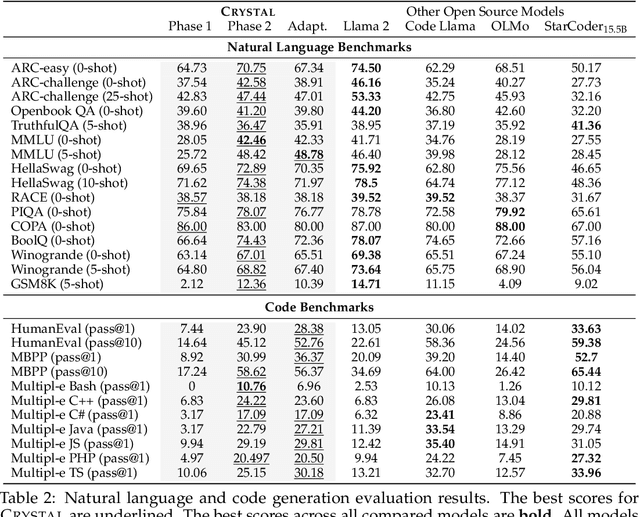
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) specializing in code generation (which are also often referred to as code LLMs), e.g., StarCoder and Code Llama, play increasingly critical roles in various software development scenarios. It is also crucial for code LLMs to possess both code generation and natural language abilities for many specific applications, such as code snippet retrieval using natural language or code explanations. The intricate interaction between acquiring language and coding skills complicates the development of strong code LLMs. Furthermore, there is a lack of thorough prior studies on the LLM pretraining strategy that mixes code and natural language. In this work, we propose a pretraining strategy to enhance the integration of natural language and coding capabilities within a single LLM. Specifically, it includes two phases of training with appropriately adjusted code/language ratios. The resulting model, Crystal, demonstrates remarkable capabilities in both domains. Specifically, it has natural language and coding performance comparable to that of Llama 2 and Code Llama, respectively. Crystal exhibits better data efficiency, using 1.4 trillion tokens compared to the more than 2 trillion tokens used by Llama 2 and Code Llama. We verify our pretraining strategy by analyzing the training process and observe consistent improvements in most benchmarks. We also adopted a typical application adaptation phase with a code-centric data mixture, only to find that it did not lead to enhanced performance or training efficiency, underlining the importance of a carefully designed data recipe. To foster research within the community, we commit to open-sourcing every detail of the pretraining, including our training datasets, code, loggings and 136 checkpoints throughout the training.
Normalization Layer Per-Example Gradients are Sufficient to Predict Gradient Noise Scale in Transformers
Nov 01, 2024Abstract:Per-example gradient norms are a vital ingredient for estimating gradient noise scale (GNS) with minimal variance. Observing the tensor contractions required to compute them, we propose a method with minimal FLOPs in 3D or greater tensor regimes by simultaneously computing the norms while computing the parameter gradients. Using this method we are able to observe the GNS of different layers at higher accuracy than previously possible. We find that the total GNS of contemporary transformer models is predicted well by the GNS of only the normalization layers. As a result, focusing only on the normalization layer, we develop a custom kernel to compute the per-example gradient norms while performing the LayerNorm backward pass with zero throughput overhead. Tracking GNS on only those layers, we are able to guide a practical batch size schedule that reduces training time by 18% on a Chinchilla-optimal language model.
Bilingual Adaptation of Monolingual Foundation Models
Jul 13, 2024
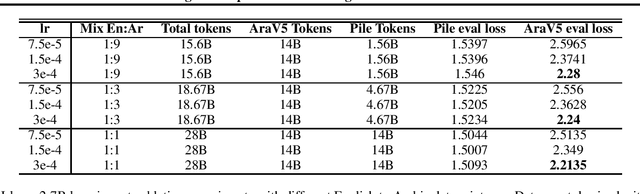


Abstract:We present an efficient method for adapting a monolingual Large Language Model (LLM) to another language, addressing challenges of catastrophic forgetting and tokenizer limitations. We focus this study on adapting Llama 2 to Arabic. Our two-stage approach begins with expanding the vocabulary and training only the embeddings matrix, followed by full model continual pretraining on a bilingual corpus. By continually pretraining on a mix of Arabic and English corpora, the model retains its proficiency in English while acquiring capabilities in Arabic. Our approach results in significant improvements in Arabic and slight enhancements in English, demonstrating cost-effective cross-lingual transfer. We also perform extensive ablations on embedding initialization techniques, data mix ratios, and learning rates and release a detailed training recipe.
Sparse maximal update parameterization: A holistic approach to sparse training dynamics
May 24, 2024



Abstract:Several challenges make it difficult for sparse neural networks to compete with dense models. First, setting a large fraction of weights to zero impairs forward and gradient signal propagation. Second, sparse studies often need to test multiple sparsity levels, while also introducing new hyperparameters (HPs), leading to prohibitive tuning costs. Indeed, the standard practice is to re-use the learning HPs originally crafted for dense models. Unfortunately, we show sparse and dense networks do not share the same optimal HPs. Without stable dynamics and effective training recipes, it is costly to test sparsity at scale, which is key to surpassing dense networks and making the business case for sparsity acceleration in hardware. A holistic approach is needed to tackle these challenges and we propose S$\mu$Par as one such approach. S$\mu$Par ensures activations, gradients, and weight updates all scale independently of sparsity level. Further, by reparameterizing the HPs, S$\mu$Par enables the same HP values to be optimal as we vary both sparsity level and model width. HPs can be tuned on small dense networks and transferred to large sparse models, greatly reducing tuning costs. On large-scale language modeling, S$\mu$Par training improves loss by up to 8.2% over the common approach of using the dense model standard parameterization.
MediSwift: Efficient Sparse Pre-trained Biomedical Language Models
Mar 01, 2024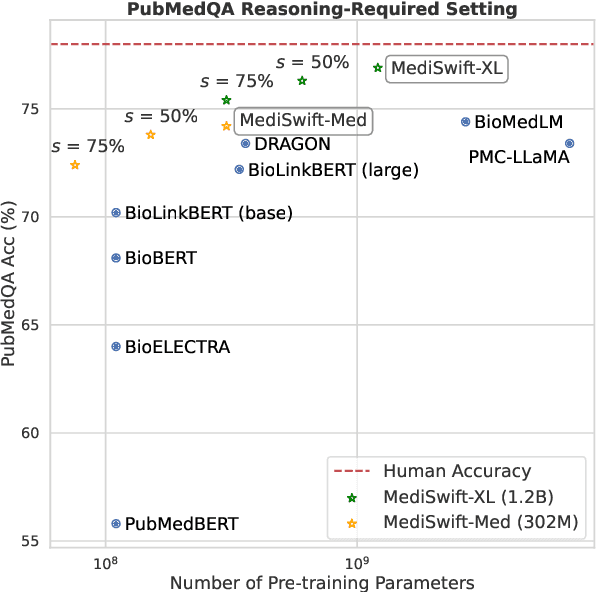
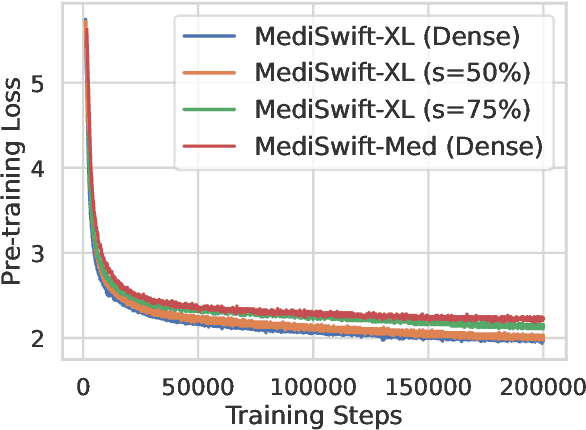
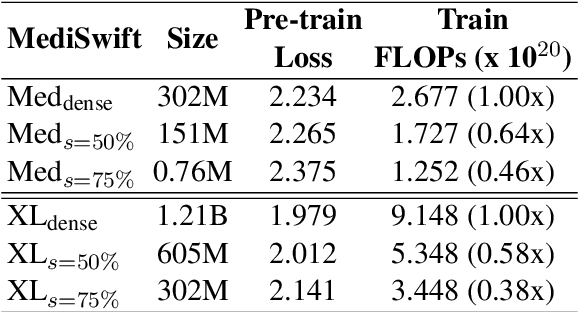
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are typically trained on general source data for various domains, but a recent surge in domain-specific LLMs has shown their potential to outperform general-purpose models in domain-specific tasks (e.g., biomedicine). Although domain-specific pre-training enhances efficiency and leads to smaller models, the computational costs of training these LLMs remain high, posing budgeting challenges. We introduce MediSwift, a suite of biomedical LMs that leverage sparse pre-training on domain-specific biomedical text data. By inducing up to 75% weight sparsity during the pre-training phase, MediSwift achieves a 2-2.5x reduction in training FLOPs. Notably, all sparse pre-training was performed on the Cerebras CS-2 system, which is specifically designed to realize the acceleration benefits from unstructured weight sparsity, thereby significantly enhancing the efficiency of the MediSwift models. Through subsequent dense fine-tuning and strategic soft prompting, MediSwift models outperform existing LLMs up to 7B parameters on biomedical tasks, setting new benchmarks w.r.t efficiency-accuracy on tasks such as PubMedQA. Our results show that sparse pre-training, along with dense fine-tuning and soft prompting, offers an effective method for creating high-performing, computationally efficient models in specialized domains.
Position Interpolation Improves ALiBi Extrapolation
Oct 18, 2023Abstract:Linear position interpolation helps pre-trained models using rotary position embeddings (RoPE) to extrapolate to longer sequence lengths. We propose using linear position interpolation to extend the extrapolation range of models using Attention with Linear Biases (ALiBi). We find position interpolation significantly improves extrapolation capability on upstream language modelling and downstream summarization and retrieval tasks.
BTLM-3B-8K: 7B Parameter Performance in a 3B Parameter Model
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:We introduce the Bittensor Language Model, called "BTLM-3B-8K", a new state-of-the-art 3 billion parameter open-source language model. BTLM-3B-8K was trained on 627B tokens from the SlimPajama dataset with a mixture of 2,048 and 8,192 context lengths. BTLM-3B-8K outperforms all existing 3B parameter models by 2-5.5% across downstream tasks. BTLM-3B-8K is even competitive with some 7B parameter models. Additionally, BTLM-3B-8K provides excellent long context performance, outperforming MPT-7B-8K and XGen-7B-8K on tasks up to 8,192 context length. We trained the model on a cleaned and deduplicated SlimPajama dataset; aggressively tuned the \textmu P hyperparameters and schedule; used ALiBi position embeddings; and adopted the SwiGLU nonlinearity. On Hugging Face, the most popular models have 7B parameters, indicating that users prefer the quality-size ratio of 7B models. Compacting the 7B parameter model to one with 3B parameters, with little performance impact, is an important milestone. BTLM-3B-8K needs only 3GB of memory with 4-bit precision and takes 2.5x less inference compute than 7B models, helping to open up access to a powerful language model on mobile and edge devices. BTLM-3B-8K is available under an Apache 2.0 license on Hugging Face: https://huggingface.co/cerebras/btlm-3b-8k-base.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge