Jinlu Zhang
OpenDance: Multimodal Controllable 3D Dance Generation Using Large-scale Internet Data
Jun 09, 2025



Abstract:Music-driven dance generation offers significant creative potential yet faces considerable challenges. The absence of fine-grained multimodal data and the difficulty of flexible multi-conditional generation limit previous works on generation controllability and diversity in practice. In this paper, we build OpenDance5D, an extensive human dance dataset comprising over 101 hours across 14 distinct genres. Each sample has five modalities to facilitate robust cross-modal learning: RGB video, audio, 2D keypoints, 3D motion, and fine-grained textual descriptions from human arts. Furthermore, we propose OpenDanceNet, a unified masked modeling framework for controllable dance generation conditioned on music and arbitrary combinations of text prompts, keypoints, or character positioning. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that OpenDanceNet achieves high-fidelity and flexible controllability.
InteractAnything: Zero-shot Human Object Interaction Synthesis via LLM Feedback and Object Affordance Parsing
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in 3D human-aware generation have made significant progress. However, existing methods still struggle with generating novel Human Object Interaction (HOI) from text, particularly for open-set objects. We identify three main challenges of this task: precise human-object relation reasoning, affordance parsing for any object, and detailed human interaction pose synthesis aligning description and object geometry. In this work, we propose a novel zero-shot 3D HOI generation framework without training on specific datasets, leveraging the knowledge from large-scale pre-trained models. Specifically, the human-object relations are inferred from large language models (LLMs) to initialize object properties and guide the optimization process. Then we utilize a pre-trained 2D image diffusion model to parse unseen objects and extract contact points, avoiding the limitations imposed by existing 3D asset knowledge. The initial human pose is generated by sampling multiple hypotheses through multi-view SDS based on the input text and object geometry. Finally, we introduce a detailed optimization to generate fine-grained, precise, and natural interaction, enforcing realistic 3D contact between the 3D object and the involved body parts, including hands in grasping. This is achieved by distilling human-level feedback from LLMs to capture detailed human-object relations from the text instruction. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach compared to prior works, particularly in terms of the fine-grained nature of interactions and the ability to handle open-set 3D objects.
EMO-X: Efficient Multi-Person Pose and Shape Estimation in One-Stage
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Expressive Human Pose and Shape Estimation (EHPS) aims to jointly estimate human pose, hand gesture, and facial expression from monocular images. Existing methods predominantly rely on Transformer-based architectures, which suffer from quadratic complexity in self-attention, leading to substantial computational overhead, especially in multi-person scenarios. Recently, Mamba has emerged as a promising alternative to Transformers due to its efficient global modeling capability. However, it remains limited in capturing fine-grained local dependencies, which are essential for precise EHPS. To address these issues, we propose EMO-X, the Efficient Multi-person One-stage model for multi-person EHPS. Specifically, we explore a Scan-based Global-Local Decoder (SGLD) that integrates global context with skeleton-aware local features to iteratively enhance human tokens. Our EMO-X leverages the superior global modeling capability of Mamba and designs a local bidirectional scan mechanism for skeleton-aware local refinement. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that EMO-X strikes an excellent balance between efficiency and accuracy. Notably, it achieves a significant reduction in computational complexity, requiring 69.8% less inference time compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, while outperforming most of them in accuracy.
OwlSight: A Robust Illumination Adaptation Framework for Dark Video Human Action Recognition
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Human action recognition in low-light environments is crucial for various real-world applications. However, the existing approaches overlook the full utilization of brightness information throughout the training phase, leading to suboptimal performance. To address this limitation, we propose OwlSight, a biomimetic-inspired framework with whole-stage illumination enhancement to interact with action classification for accurate dark video human action recognition. Specifically, OwlSight incorporates a Time-Consistency Module (TCM) to capture shallow spatiotemporal features meanwhile maintaining temporal coherence, which are then processed by a Luminance Adaptation Module (LAM) to dynamically adjust the brightness based on the input luminance distribution. Furthermore, a Reflect Augmentation Module (RAM) is presented to maximize illumination utilization and simultaneously enhance action recognition via two interactive paths. Additionally, we build Dark-101, a large-scale dataset comprising 18,310 dark videos across 101 action categories, significantly surpassing existing datasets (e.g., ARID1.5 and Dark-48) in scale and diversity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed OwlSight achieves state-of-the-art performance across four low-light action recognition benchmarks. Notably, it outperforms previous best approaches by 5.36% on ARID1.5 and 1.72% on Dark-101, highlighting its effectiveness in challenging dark environments.
StoryWeaver: A Unified World Model for Knowledge-Enhanced Story Character Customization
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Story visualization has gained increasing attention in artificial intelligence. However, existing methods still struggle with maintaining a balance between character identity preservation and text-semantics alignment, largely due to a lack of detailed semantic modeling of the story scene. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel knowledge graph, namely Character Graph (\textbf{CG}), which comprehensively represents various story-related knowledge, including the characters, the attributes related to characters, and the relationship between characters. We then introduce StoryWeaver, an image generator that achieve Customization via Character Graph (\textbf{C-CG}), capable of consistent story visualization with rich text semantics. To further improve the multi-character generation performance, we incorporate knowledge-enhanced spatial guidance (\textbf{KE-SG}) into StoryWeaver to precisely inject character semantics into generation. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, extensive experiments are conducted using a new benchmark called TBC-Bench. The experiments confirm that our StoryWeaver excels not only in creating vivid visual story plots but also in accurately conveying character identities across various scenarios with considerable storage efficiency, \emph{e.g.}, achieving an average increase of +9.03\% DINO-I and +13.44\% CLIP-T. Furthermore, ablation experiments are conducted to verify the superiority of the proposed module. Codes and datasets are released at https://github.com/Aria-Zhangjl/StoryWeaver.
Expressive Keypoints for Skeleton-based Action Recognition via Skeleton Transformation
Jun 26, 2024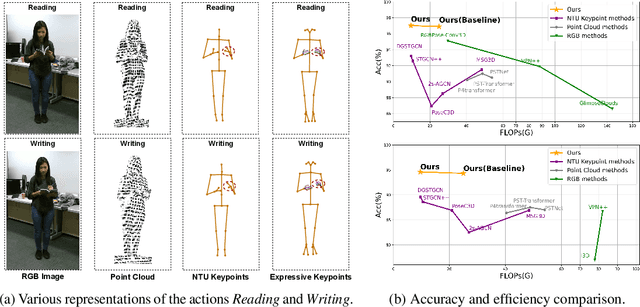
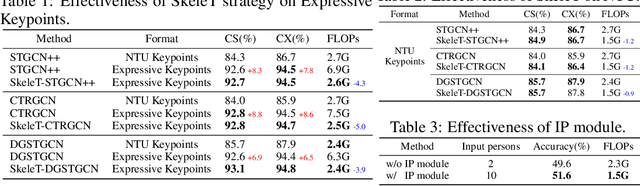
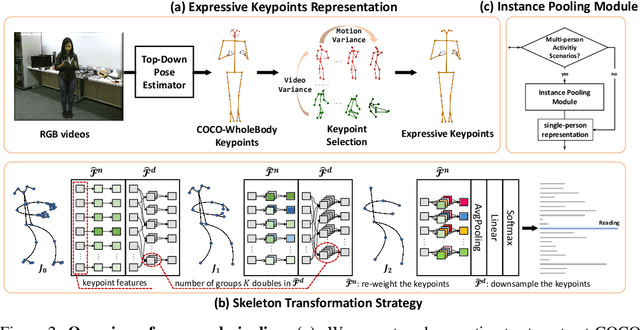
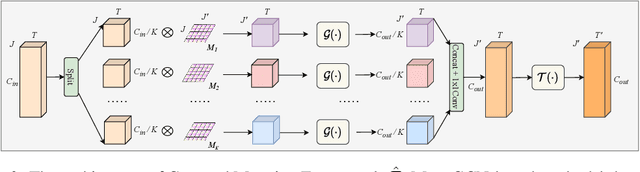
Abstract:In the realm of skeleton-based action recognition, the traditional methods which rely on coarse body keypoints fall short of capturing subtle human actions. In this work, we propose Expressive Keypoints that incorporates hand and foot details to form a fine-grained skeletal representation, improving the discriminative ability for existing models in discerning intricate actions. To efficiently model Expressive Keypoints, the Skeleton Transformation strategy is presented to gradually downsample the keypoints and prioritize prominent joints by allocating the importance weights. Additionally, a plug-and-play Instance Pooling module is exploited to extend our approach to multi-person scenarios without surging computation costs. Extensive experimental results over seven datasets present the superiority of our method compared to the state-of-the-art for skeleton-based human action recognition. Code is available at https://github.com/YijieYang23/SkeleT-GCN.
A Progressive Framework of Vision-language Knowledge Distillation and Alignment for Multilingual Scene
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Pre-trained vision-language (V-L) models such as CLIP have shown excellent performance in many downstream cross-modal tasks. However, most of them are only applicable to the English context. Subsequent research has focused on this problem and proposed improved models, such as CN-CLIP and AltCLIP, to facilitate their applicability to Chinese and even other languages. Nevertheless, these models suffer from high latency and a large memory footprint in inference, which limits their further deployment on resource-constrained edge devices. In this work, we propose a conceptually simple yet effective multilingual CLIP Compression framework and train a lightweight multilingual vision-language model, called DC-CLIP, for both Chinese and English context. In this framework, we collect high-quality Chinese and English text-image pairs and design two training stages, including multilingual vision-language feature distillation and alignment. During the first stage, lightweight image/text student models are designed to learn robust visual/multilingual textual feature representation ability from corresponding teacher models, respectively. Subsequently, the multilingual vision-language alignment stage enables effective alignment of visual and multilingual textual features to further improve the model's multilingual performance. Comprehensive experiments in zero-shot image classification, conducted based on the ELEVATER benchmark, showcase that DC-CLIP achieves superior performance in the English context and competitive performance in the Chinese context, even with less training data, when compared to existing models of similar parameter magnitude. The evaluation demonstrates the effectiveness of our designed training mechanism.
Move as You Say, Interact as You Can: Language-guided Human Motion Generation with Scene Affordance
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Despite significant advancements in text-to-motion synthesis, generating language-guided human motion within 3D environments poses substantial challenges. These challenges stem primarily from (i) the absence of powerful generative models capable of jointly modeling natural language, 3D scenes, and human motion, and (ii) the generative models' intensive data requirements contrasted with the scarcity of comprehensive, high-quality, language-scene-motion datasets. To tackle these issues, we introduce a novel two-stage framework that employs scene affordance as an intermediate representation, effectively linking 3D scene grounding and conditional motion generation. Our framework comprises an Affordance Diffusion Model (ADM) for predicting explicit affordance map and an Affordance-to-Motion Diffusion Model (AMDM) for generating plausible human motions. By leveraging scene affordance maps, our method overcomes the difficulty in generating human motion under multimodal condition signals, especially when training with limited data lacking extensive language-scene-motion pairs. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms all baselines on established benchmarks, including HumanML3D and HUMANISE. Additionally, we validate our model's exceptional generalization capabilities on a specially curated evaluation set featuring previously unseen descriptions and scenes.
Fast Text-to-3D-Aware Face Generation and Manipulation via Direct Cross-modal Mapping and Geometric Regularization
Mar 11, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-3D-aware face (T3D Face) generation and manipulation is an emerging research hot spot in machine learning, which still suffers from low efficiency and poor quality. In this paper, we propose an End-to-End Efficient and Effective network for fast and accurate T3D face generation and manipulation, termed $E^3$-FaceNet. Different from existing complex generation paradigms, $E^3$-FaceNet resorts to a direct mapping from text instructions to 3D-aware visual space. We introduce a novel Style Code Enhancer to enhance cross-modal semantic alignment, alongside an innovative Geometric Regularization objective to maintain consistency across multi-view generations. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that $E^3$-FaceNet can not only achieve picture-like 3D face generation and manipulation, but also improve inference speed by orders of magnitudes. For instance, compared with Latent3D, $E^3$-FaceNet speeds up the five-view generations by almost 470 times, while still exceeding in generation quality. Our code are released at https://github.com/Aria-Zhangjl/E3-FaceNet.
Scientific Large Language Models: A Survey on Biological & Chemical Domains
Jan 26, 2024
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a transformative power in enhancing natural language comprehension, representing a significant stride toward artificial general intelligence. The application of LLMs extends beyond conventional linguistic boundaries, encompassing specialized linguistic systems developed within various scientific disciplines. This growing interest has led to the advent of scientific LLMs, a novel subclass specifically engineered for facilitating scientific discovery. As a burgeoning area in the community of AI for Science, scientific LLMs warrant comprehensive exploration. However, a systematic and up-to-date survey introducing them is currently lacking. In this paper, we endeavor to methodically delineate the concept of "scientific language", whilst providing a thorough review of the latest advancements in scientific LLMs. Given the expansive realm of scientific disciplines, our analysis adopts a focused lens, concentrating on the biological and chemical domains. This includes an in-depth examination of LLMs for textual knowledge, small molecules, macromolecular proteins, genomic sequences, and their combinations, analyzing them in terms of model architectures, capabilities, datasets, and evaluation. Finally, we critically examine the prevailing challenges and point out promising research directions along with the advances of LLMs. By offering a comprehensive overview of technical developments in this field, this survey aspires to be an invaluable resource for researchers navigating the intricate landscape of scientific LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge