Jiayao Zhang
Reliable and Private Utility Signaling for Data Markets
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:The explosive growth of data has highlighted its critical role in driving economic growth through data marketplaces, which enable extensive data sharing and access to high-quality datasets. To support effective trading, signaling mechanisms provide participants with information about data products before transactions, enabling informed decisions and facilitating trading. However, due to the inherent free-duplication nature of data, commonly practiced signaling methods face a dilemma between privacy and reliability, undermining the effectiveness of signals in guiding decision-making. To address this, this paper explores the benefits and develops a non-TCP-based construction for a desirable signaling mechanism that simultaneously ensures privacy and reliability. We begin by formally defining the desirable utility signaling mechanism and proving its ability to prevent suboptimal decisions for both participants and facilitate informed data trading. To design a protocol to realize its functionality, we propose leveraging maliciously secure multi-party computation (MPC) to ensure the privacy and robustness of signal computation and introduce an MPC-based hash verification scheme to ensure input reliability. In multi-seller scenarios requiring fair data valuation, we further explore the design and optimization of the MPC-based KNN-Shapley method with improved efficiency. Rigorous experiments demonstrate the efficiency and practicality of our approach.
CoKV: Optimizing KV Cache Allocation via Cooperative Game
Feb 21, 2025
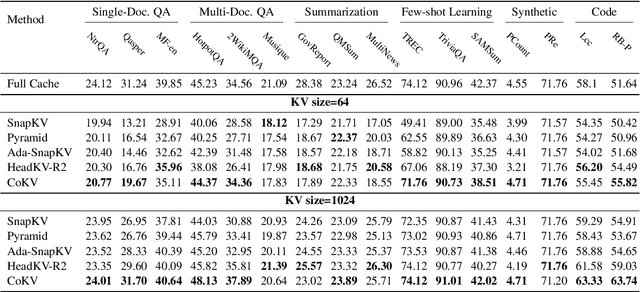
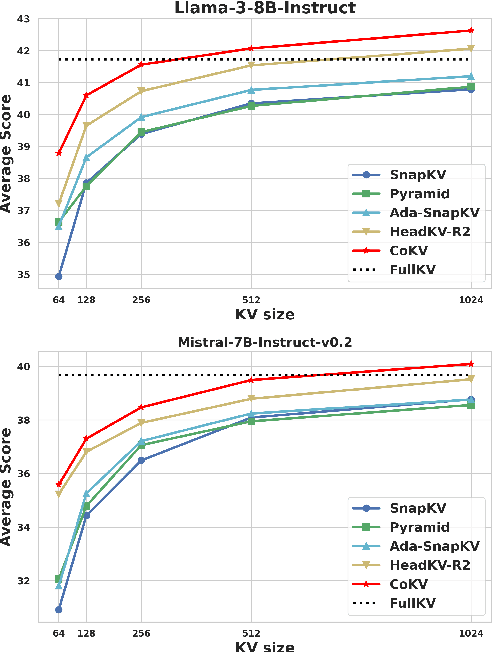

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success on various aspects of human life. However, one of the major challenges in deploying these models is the substantial memory consumption required to store key-value pairs (KV), which imposes significant resource demands. Recent research has focused on KV cache budget allocation, with several approaches proposing head-level budget distribution by evaluating the importance of individual attention heads. These methods, however, assess the importance of heads independently, overlooking their cooperative contributions within the model, which may result in a deviation from their true impact on model performance. In light of this limitation, we propose CoKV, a novel method that models the cooperation between heads in model inference as a cooperative game. By evaluating the contribution of each head within the cooperative game, CoKV can allocate the cache budget more effectively. Extensive experiments show that CoKV achieves state-of-the-art performance on the LongBench benchmark using LLama-3-8B-Instruct and Mistral-7B models.
A Survey on Data Markets
Nov 09, 2024



Abstract:Data is the new oil of the 21st century. The growing trend of trading data for greater welfare has led to the emergence of data markets. A data market is any mechanism whereby the exchange of data products including datasets and data derivatives takes place as a result of data buyers and data sellers being in contact with one another, either directly or through mediating agents. It serves as a coordinating mechanism by which several functions, including the pricing and the distribution of data as the most important ones, interact to make the value of data fully exploited and enhanced. In this article, we present a comprehensive survey of this important and emerging direction from the aspects of data search, data productization, data transaction, data pricing, revenue allocation as well as privacy, security, and trust issues. We also investigate the government policies and industry status of data markets across different countries and different domains. Finally, we identify the unresolved challenges and discuss possible future directions for the development of data markets.
Analysis of the ICML 2023 Ranking Data: Can Authors' Opinions of Their Own Papers Assist Peer Review in Machine Learning?
Aug 24, 2024Abstract:We conducted an experiment during the review process of the 2023 International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) that requested authors with multiple submissions to rank their own papers based on perceived quality. We received 1,342 rankings, each from a distinct author, pertaining to 2,592 submissions. In this paper, we present an empirical analysis of how author-provided rankings could be leveraged to improve peer review processes at machine learning conferences. We focus on the Isotonic Mechanism, which calibrates raw review scores using author-provided rankings. Our analysis demonstrates that the ranking-calibrated scores outperform raw scores in estimating the ground truth ``expected review scores'' in both squared and absolute error metrics. Moreover, we propose several cautious, low-risk approaches to using the Isotonic Mechanism and author-provided rankings in peer review processes, including assisting senior area chairs' oversight of area chairs' recommendations, supporting the selection of paper awards, and guiding the recruitment of emergency reviewers. We conclude the paper by addressing the study's limitations and proposing future research directions.
Estimating the Causal Effect of Early ArXiving on Paper Acceptance
Jun 24, 2023Abstract:What is the effect of releasing a preprint of a paper before it is submitted for peer review? No randomized controlled trial has been conducted, so we turn to observational data to answer this question. We use data from the ICLR conference (2018--2022) and apply methods from causal inference to estimate the effect of arXiving a paper before the reviewing period (early arXiving) on its acceptance to the conference. Adjusting for 18 confounders such as topic, authors, and quality, we may estimate the causal effect. However, since quality is a challenging construct to estimate, we use the negative outcome control method, using paper citation count as a control variable to debias the quality confounding effect. Our results suggest that early arXiving may have a small effect on a paper's chances of acceptance. However, this effect (when existing) does not differ significantly across different groups of authors, as grouped by author citation count and institute rank. This suggests that early arXiving does not provide an advantage to any particular group.
COLA: Contextualized Commonsense Causal Reasoning from the Causal Inference Perspective
May 09, 2023Abstract:Detecting commonsense causal relations (causation) between events has long been an essential yet challenging task. Given that events are complicated, an event may have different causes under various contexts. Thus, exploiting context plays an essential role in detecting causal relations. Meanwhile, previous works about commonsense causation only consider two events and ignore their context, simplifying the task formulation. This paper proposes a new task to detect commonsense causation between two events in an event sequence (i.e., context), called contextualized commonsense causal reasoning. We also design a zero-shot framework: COLA (Contextualized Commonsense Causality Reasoner) to solve the task from the causal inference perspective. This framework obtains rich incidental supervision from temporality and balances covariates from multiple timestamps to remove confounding effects. Our extensive experiments show that COLA can detect commonsense causality more accurately than baselines.
Investigating Fairness Disparities in Peer Review: A Language Model Enhanced Approach
Nov 07, 2022Abstract:Double-blind peer review mechanism has become the skeleton of academic research across multiple disciplines including computer science, yet several studies have questioned the quality of peer reviews and raised concerns on potential biases in the process. In this paper, we conduct a thorough and rigorous study on fairness disparities in peer review with the help of large language models (LMs). We collect, assemble, and maintain a comprehensive relational database for the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) conference from 2017 to date by aggregating data from OpenReview, Google Scholar, arXiv, and CSRanking, and extracting high-level features using language models. We postulate and study fairness disparities on multiple protective attributes of interest, including author gender, geography, author, and institutional prestige. We observe that the level of disparity differs and textual features are essential in reducing biases in the predictive modeling. We distill several insights from our analysis on study the peer review process with the help of large LMs. Our database also provides avenues for studying new natural language processing (NLP) methods that facilitate the understanding of the peer review mechanism. We study a concrete example towards automatic machine review systems and provide baseline models for the review generation and scoring tasks such that the database can be used as a benchmark.
High-Resolution Depth Estimation for 360-degree Panoramas through Perspective and Panoramic Depth Images Registration
Oct 20, 2022
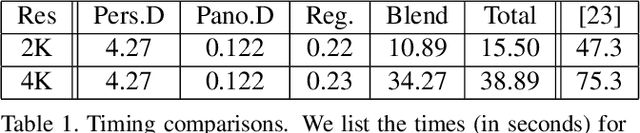
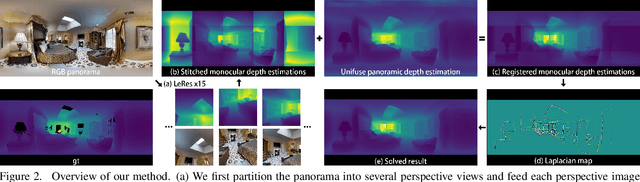
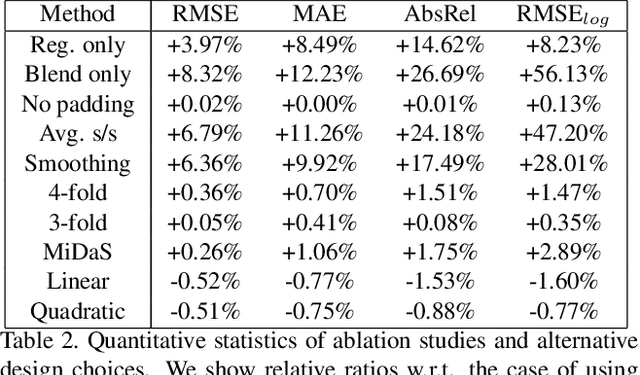
Abstract:We propose a novel approach to compute high-resolution (2048x1024 and higher) depths for panoramas that is significantly faster and qualitatively and qualitatively more accurate than the current state-of-the-art method (360MonoDepth). As traditional neural network-based methods have limitations in the output image sizes (up to 1024x512) due to GPU memory constraints, both 360MonoDepth and our method rely on stitching multiple perspective disparity or depth images to come out a unified panoramic depth map. However, to achieve globally consistent stitching, 360MonoDepth relied on solving extensive disparity map alignment and Poisson-based blending problems, leading to high computation time. Instead, we propose to use an existing panoramic depth map (computed in real-time by any panorama-based method) as the common target for the individual perspective depth maps to register to. This key idea made producing globally consistent stitching results from a straightforward task. Our experiments show that our method generates qualitatively better results than existing panorama-based methods, and further outperforms them quantitatively on datasets unseen by these methods.
FIFA: Making Fairness More Generalizable in Classifiers Trained on Imbalanced Data
Jun 06, 2022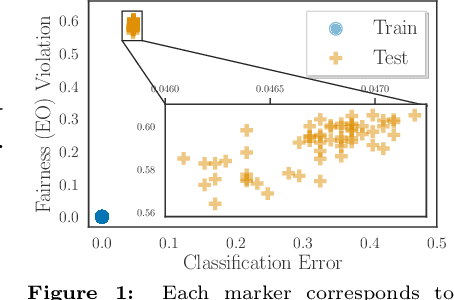
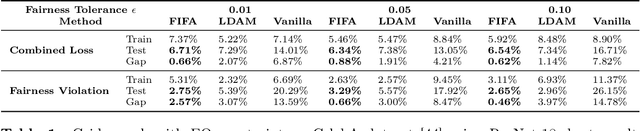
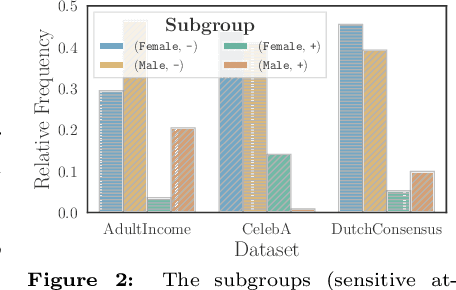
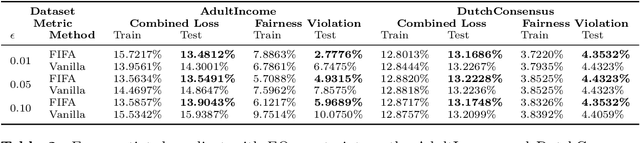
Abstract:Algorithmic fairness plays an important role in machine learning and imposing fairness constraints during learning is a common approach. However, many datasets are imbalanced in certain label classes (e.g. "healthy") and sensitive subgroups (e.g. "older patients"). Empirically, this imbalance leads to a lack of generalizability not only of classification, but also of fairness properties, especially in over-parameterized models. For example, fairness-aware training may ensure equalized odds (EO) on the training data, but EO is far from being satisfied on new users. In this paper, we propose a theoretically-principled, yet Flexible approach that is Imbalance-Fairness-Aware (FIFA). Specifically, FIFA encourages both classification and fairness generalization and can be flexibly combined with many existing fair learning methods with logits-based losses. While our main focus is on EO, FIFA can be directly applied to achieve equalized opportunity (EqOpt); and under certain conditions, it can also be applied to other fairness notions. We demonstrate the power of FIFA by combining it with a popular fair classification algorithm, and the resulting algorithm achieves significantly better fairness generalization on several real-world datasets.
Some Reflections on Drawing Causal Inference using Textual Data: Parallels Between Human Subjects and Organized Texts
Feb 02, 2022Abstract:We examine the role of textual data as study units when conducting causal inference by drawing parallels between human subjects and organized texts. %in human population research. We elaborate on key causal concepts and principles, and expose some ambiguity and sometimes fallacies. To facilitate better framing a causal query, we discuss two strategies: (i) shifting from immutable traits to perceptions of them, and (ii) shifting from some abstract concept/property to its constituent parts, i.e., adopting a constructivist perspective of an abstract concept. We hope this article would raise the awareness of the importance of articulating and clarifying fundamental concepts before delving into developing methodologies when drawing causal inference using textual data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge