Jey Han Lau
Context Volume Drives Performance: Tackling Domain Shift in Extremely Low-Resource Translation via RAG
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models for low-resource languages suffer significant performance degradation under domain shift. We quantify this challenge using Dhao, an indigenous language of Eastern Indonesia with no digital footprint beyond the New Testament (NT). When applied to the unseen Old Testament (OT), a standard NMT model fine-tuned on the NT drops from an in-domain score of 36.17 chrF++ to 27.11 chrF++. To recover this loss, we introduce a hybrid framework where a fine-tuned NMT model generates an initial draft, which is then refined by a Large Language Model (LLM) using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). The final system achieves 35.21 chrF++ (+8.10 recovery), effectively matching the original in-domain quality. Our analysis reveals that this performance is driven primarily by the number of retrieved examples rather than the choice of retrieval algorithm. Qualitative analysis confirms the LLM acts as a robust "safety net," repairing severe failures in zero-shot domains.
Investigating The Functional Roles of Attention Heads in Vision Language Models: Evidence for Reasoning Modules
Dec 11, 2025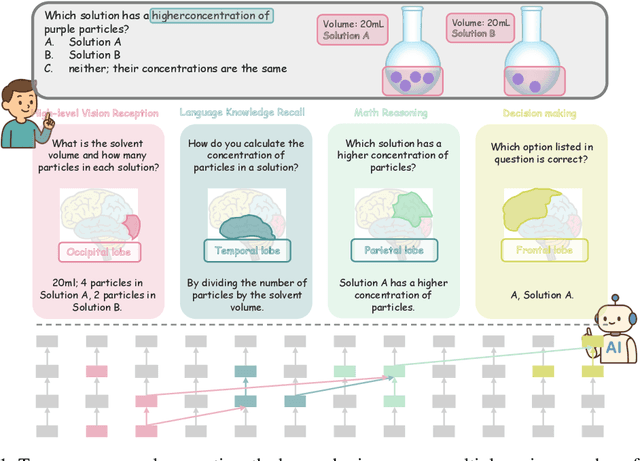
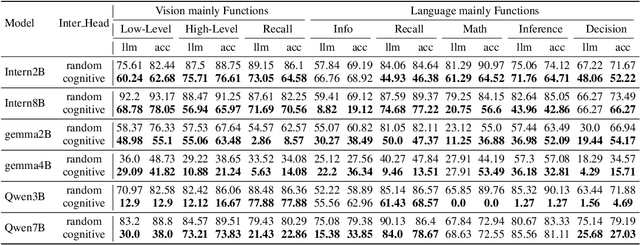
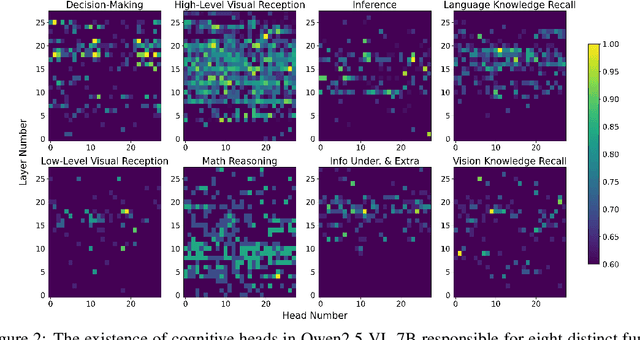
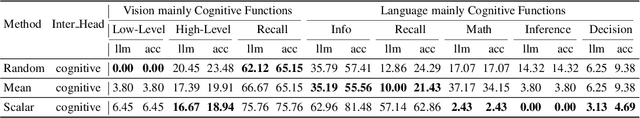
Abstract:Despite excelling on multimodal benchmarks, vision-language models (VLMs) largely remain a black box. In this paper, we propose a novel interpretability framework to systematically analyze the internal mechanisms of VLMs, focusing on the functional roles of attention heads in multimodal reasoning. To this end, we introduce CogVision, a dataset that decomposes complex multimodal questions into step-by-step subquestions designed to simulate human reasoning through a chain-of-thought paradigm, with each subquestion associated with specific receptive or cognitive functions such as high-level visual reception and inference. Using a probing-based methodology, we identify attention heads that specialize in these functions and characterize them as functional heads. Our analysis across diverse VLM families reveals that these functional heads are universally sparse, vary in number and distribution across functions, and mediate interactions and hierarchical organization. Furthermore, intervention experiments demonstrate their critical role in multimodal reasoning: removing functional heads leads to performance degradation, while emphasizing them enhances accuracy. These findings provide new insights into the cognitive organization of VLMs and suggest promising directions for designing models with more human-aligned perceptual and reasoning abilities.
PROPA: Toward Process-level Optimization in Visual Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Despite significant progress, Vision-Language Models (VLMs) still struggle with complex visual reasoning, where multi-step dependencies cause early errors to cascade through the reasoning chain. Existing post-training paradigms are limited: Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) relies on costly step-level annotations, while Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) methods like GRPO provide only sparse, outcome-level feedback, hindering stable optimization. We introduce PROPA (Process-level Reasoning Optimization with interleaved Policy Alignment), a novel framework that integrates Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) with GRPO to generate dense, process-level rewards and optimize reasoning at each intermediate step without human annotations. To overcome the cold-start problem, PROPA interleaves GRPO updates with SFT, enabling the model to learn from both successful and failed reasoning trajectories. A Process Reward Model (PRM) is further trained to guide inference-time search, aligning the test-time search with the training signal. Across seven benchmarks and four VLM backbones, PROPA consistently outperforms both SFT- and RLVR-based baselines. It achieves up to 17.0% gains on in-domain tasks and 21.0% gains on out-of-domain tasks compared to existing state-of-the-art, establishing a strong reasoning and generalization capability for visual reasoning tasks. The code isavailable at: https://github.com/YanbeiJiang/PROPA.
Understanding the Geospatial Reasoning Capabilities of LLMs: A Trajectory Recovery Perspective
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:We explore the geospatial reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), specifically, whether LLMs can read road network maps and perform navigation. We frame trajectory recovery as a proxy task, which requires models to reconstruct masked GPS traces, and introduce GLOBALTRACE, a dataset with over 4,000 real-world trajectories across diverse regions and transportation modes. Using road network as context, our prompting framework enables LLMs to generate valid paths without accessing any external navigation tools. Experiments show that LLMs outperform off-the-shelf baselines and specialized trajectory recovery models, with strong zero-shot generalization. Fine-grained analysis shows that LLMs have strong comprehension of the road network and coordinate systems, but also pose systematic biases with respect to regions and transportation modes. Finally, we demonstrate how LLMs can enhance navigation experiences by reasoning over maps in flexible ways to incorporate user preferences.
Beyond Perception: Evaluating Abstract Visual Reasoning through Multi-Stage Task
May 28, 2025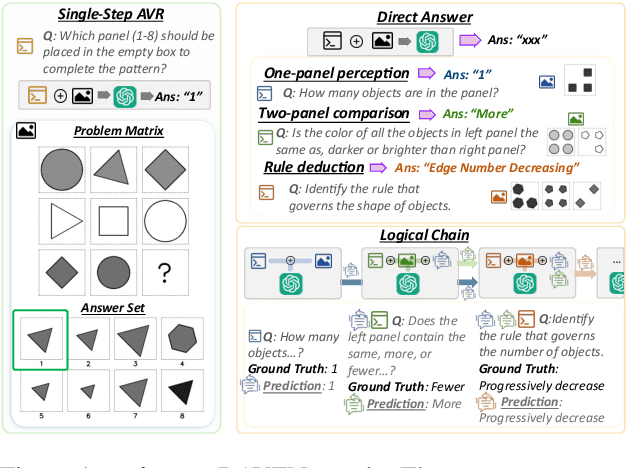
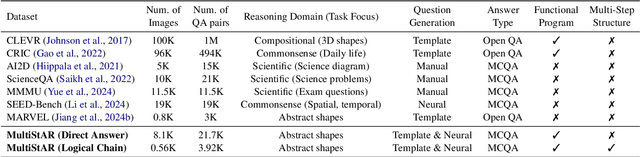
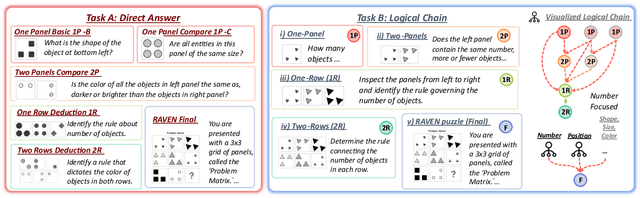
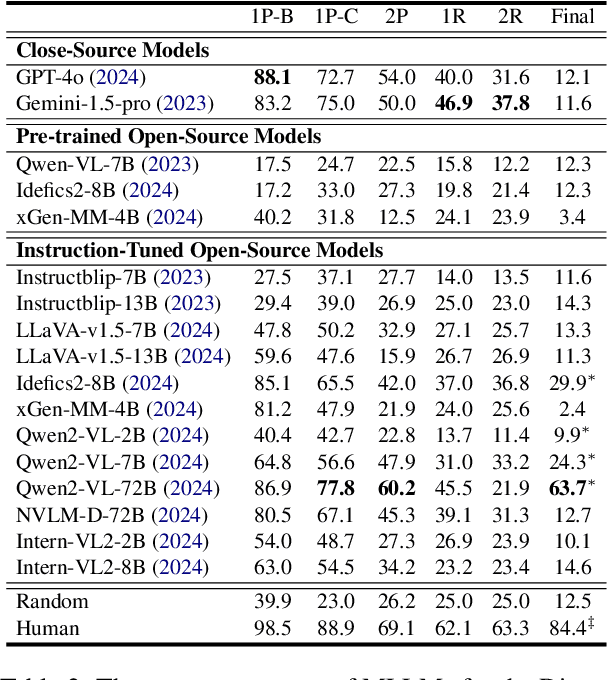
Abstract:Current Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel in general visual reasoning but remain underexplored in Abstract Visual Reasoning (AVR), which demands higher-order reasoning to identify abstract rules beyond simple perception. Existing AVR benchmarks focus on single-step reasoning, emphasizing the end result but neglecting the multi-stage nature of reasoning process. Past studies found MLLMs struggle with these benchmarks, but it doesn't explain how they fail. To address this gap, we introduce MultiStAR, a Multi-Stage AVR benchmark, based on RAVEN, designed to assess reasoning across varying levels of complexity. Additionally, existing metrics like accuracy only focus on the final outcomes while do not account for the correctness of intermediate steps. Therefore, we propose a novel metric, MSEval, which considers the correctness of intermediate steps in addition to the final outcomes. We conduct comprehensive experiments on MultiStAR using 17 representative close-source and open-source MLLMs. The results reveal that while existing MLLMs perform adequately on basic perception tasks, they continue to face challenges in more complex rule detection stages.
FLUKE: A Linguistically-Driven and Task-Agnostic Framework for Robustness Evaluation
Apr 24, 2025



Abstract:We present FLUKE (Framework for LingUistically-driven and tasK-agnostic robustness Evaluation), a task-agnostic framework for assessing model robustness through systematic minimal variations of test data. FLUKE introduces controlled variations across linguistic levels - from orthography to dialect and style varieties - and leverages large language models (LLMs) with human validation to generate modifications. We demonstrate FLUKE's utility by evaluating both fine-tuned models and LLMs across four diverse NLP tasks, and reveal that (1) the impact of linguistic variations is highly task-dependent, with some tests being critical for certain tasks but irrelevant for others; (2) while LLMs have better overall robustness compared to fine-tuned models, they still exhibit significant brittleness to certain linguistic variations; (3) all models show substantial vulnerability to negation modifications across most tasks. These findings highlight the importance of systematic robustness testing for understanding model behaviors.
Moderation Matters:Measuring Conversational Moderation Impact in English as a Second Language Group Discussion
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:English as a Second Language (ESL) speakers often struggle to engage in group discussions due to language barriers. While moderators can facilitate participation, few studies assess conversational engagement and evaluate moderation effectiveness. To address this gap, we develop a dataset comprising 17 sessions from an online ESL conversation club, which includes both moderated and non-moderated discussions. We then introduce an approach that integrates automatic ESL dialogue assessment and a framework that categorizes moderation strategies. Our findings indicate that moderators help improve the flow of topics and start/end a conversation. Interestingly, we find active acknowledgement and encouragement to be the most effective moderation strategy, while excessive information and opinion sharing by moderators has a negative impact. Ultimately, our study paves the way for analyzing ESL group discussions and the role of moderators in non-native conversation settings.
Analysis of Emotion in Rumour Threads on Social Media
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Rumours in online social media pose significant risks to modern society, motivating the need for better understanding of how they develop. We focus specifically on the interface between emotion and rumours in threaded discourses, building on the surprisingly sparse literature on the topic which has largely focused on emotions within the original rumour posts themselves, and largely overlooked the comparative differences between rumours and non-rumours. In this work, we provide a comprehensive analytical emotion framework, contrasting rumour and non-rumour cases using existing NLP datasets to further understand the emotion dynamics within rumours. Our framework reveals several findings: rumours exhibit more negative sentiment and emotions, including anger, fear and pessimism, while non-rumours evoke more positive emotions; emotions are contagious in online interactions, with rumours facilitate negative emotions and non-rumours foster positive emotions; and based on causal analysis, surprise acts as a bridge between rumours and other emotions, pessimism is driven by sadness and fear, optimism by joy and love.
Can LLMs Simulate L2-English Dialogue? An Information-Theoretic Analysis of L1-Dependent Biases
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:This study evaluates Large Language Models' (LLMs) ability to simulate non-native-like English use observed in human second language (L2) learners interfered with by their native first language (L1). In dialogue-based interviews, we prompt LLMs to mimic L2 English learners with specific L1s (e.g., Japanese, Thai, Urdu) across seven languages, comparing their outputs to real L2 learner data. Our analysis examines L1-driven linguistic biases, such as reference word usage and avoidance behaviors, using information-theoretic and distributional density measures. Results show that modern LLMs (e.g., Qwen2.5, LLAMA3.3, DeepseekV3, GPT-4o) replicate L1-dependent patterns observed in human L2 data, with distinct influences from various languages (e.g., Japanese, Korean, and Mandarin significantly affect tense agreement, and Urdu influences noun-verb collocations). Our results reveal the potential of LLMs for L2 dialogue generation and evaluation for future educational applications.
Beyond Seen Data: Improving KBQA Generalization Through Schema-Guided Logical Form Generation
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Knowledge base question answering (KBQA) aims to answer user questions in natural language using rich human knowledge stored in large KBs. As current KBQA methods struggle with unseen knowledge base elements at test time,we introduce SG-KBQA: a novel model that injects schema contexts into entity retrieval and logical form generation to tackle this issue. It uses the richer semantics and awareness of the knowledge base structure provided by schema contexts to enhance generalizability. We show that SG-KBQA achieves strong generalizability, outperforming state-of-the-art models on two commonly used benchmark datasets across a variety of test settings. Our source code is available at https://github.com/gaosx2000/SG_KBQA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge