Enze Shi
Non-Asymptotic Analysis of Online Local Private Learning with SGD
Jul 09, 2025



Abstract:Differentially Private Stochastic Gradient Descent (DP-SGD) has been widely used for solving optimization problems with privacy guarantees in machine learning and statistics. Despite this, a systematic non-asymptotic convergence analysis for DP-SGD, particularly in the context of online problems and local differential privacy (LDP) models, remains largely elusive. Existing non-asymptotic analyses have focused on non-private optimization methods, and hence are not applicable to privacy-preserving optimization problems. This work initiates the analysis to bridge this gap and opens the door to non-asymptotic convergence analysis of private optimization problems. A general framework is investigated for the online LDP model in stochastic optimization problems. We assume that sensitive information from individuals is collected sequentially and aim to estimate, in real-time, a static parameter that pertains to the population of interest. Most importantly, we conduct a comprehensive non-asymptotic convergence analysis of the proposed estimators in finite-sample situations, which gives their users practical guidelines regarding the effect of various hyperparameters, such as step size, parameter dimensions, and privacy budgets, on convergence rates. Our proposed estimators are validated in the theoretical and practical realms by rigorous mathematical derivations and carefully constructed numerical experiments.
Deep Fair Learning: A Unified Framework for Fine-tuning Representations with Sufficient Networks
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Ensuring fairness in machine learning is a critical and challenging task, as biased data representations often lead to unfair predictions. To address this, we propose Deep Fair Learning, a framework that integrates nonlinear sufficient dimension reduction with deep learning to construct fair and informative representations. By introducing a novel penalty term during fine-tuning, our method enforces conditional independence between sensitive attributes and learned representations, addressing bias at its source while preserving predictive performance. Unlike prior methods, it supports diverse sensitive attributes, including continuous, discrete, binary, or multi-group types. Experiments on various types of data structure show that our approach achieves a superior balance between fairness and utility, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art baselines.
HARP: Human-Assisted Regrouping with Permutation Invariant Critic for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:Human-in-the-loop reinforcement learning integrates human expertise to accelerate agent learning and provide critical guidance and feedback in complex fields. However, many existing approaches focus on single-agent tasks and require continuous human involvement during the training process, significantly increasing the human workload and limiting scalability. In this paper, we propose HARP (Human-Assisted Regrouping with Permutation Invariant Critic), a multi-agent reinforcement learning framework designed for group-oriented tasks. HARP integrates automatic agent regrouping with strategic human assistance during deployment, enabling and allowing non-experts to offer effective guidance with minimal intervention. During training, agents dynamically adjust their groupings to optimize collaborative task completion. When deployed, they actively seek human assistance and utilize the Permutation Invariant Group Critic to evaluate and refine human-proposed groupings, allowing non-expert users to contribute valuable suggestions. In multiple collaboration scenarios, our approach is able to leverage limited guidance from non-experts and enhance performance. The project can be found at https://github.com/huawen-hu/HARP.
Identifying Influential nodes in Brain Networks via Self-Supervised Graph-Transformer
Sep 17, 2024


Abstract:Studying influential nodes (I-nodes) in brain networks is of great significance in the field of brain imaging. Most existing studies consider brain connectivity hubs as I-nodes. However, this approach relies heavily on prior knowledge from graph theory, which may overlook the intrinsic characteristics of the brain network, especially when its architecture is not fully understood. In contrast, self-supervised deep learning can learn meaningful representations directly from the data. This approach enables the exploration of I-nodes for brain networks, which is also lacking in current studies. This paper proposes a Self-Supervised Graph Reconstruction framework based on Graph-Transformer (SSGR-GT) to identify I-nodes, which has three main characteristics. First, as a self-supervised model, SSGR-GT extracts the importance of brain nodes to the reconstruction. Second, SSGR-GT uses Graph-Transformer, which is well-suited for extracting features from brain graphs, combining both local and global characteristics. Third, multimodal analysis of I-nodes uses graph-based fusion technology, combining functional and structural brain information. The I-nodes we obtained are distributed in critical areas such as the superior frontal lobe, lateral parietal lobe, and lateral occipital lobe, with a total of 56 identified across different experiments. These I-nodes are involved in more brain networks than other regions, have longer fiber connections, and occupy more central positions in structural connectivity. They also exhibit strong connectivity and high node efficiency in both functional and structural networks. Furthermore, there is a significant overlap between the I-nodes and both the structural and functional rich-club. These findings enhance our understanding of the I-nodes within the brain network, and provide new insights for future research in further understanding the brain working mechanisms.
Large Language Models for Robotics: Opportunities, Challenges, and Perspectives
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have undergone significant expansion and have been increasingly integrated across various domains. Notably, in the realm of robot task planning, LLMs harness their advanced reasoning and language comprehension capabilities to formulate precise and efficient action plans based on natural language instructions. However, for embodied tasks, where robots interact with complex environments, text-only LLMs often face challenges due to a lack of compatibility with robotic visual perception. This study provides a comprehensive overview of the emerging integration of LLMs and multimodal LLMs into various robotic tasks. Additionally, we propose a framework that utilizes multimodal GPT-4V to enhance embodied task planning through the combination of natural language instructions and robot visual perceptions. Our results, based on diverse datasets, indicate that GPT-4V effectively enhances robot performance in embodied tasks. This extensive survey and evaluation of LLMs and multimodal LLMs across a variety of robotic tasks enriches the understanding of LLM-centric embodied intelligence and provides forward-looking insights toward bridging the gap in Human-Robot-Environment interaction.
Review of Large Vision Models and Visual Prompt Engineering
Jul 03, 2023
Abstract:Visual prompt engineering is a fundamental technology in the field of visual and image Artificial General Intelligence, serving as a key component for achieving zero-shot capabilities. As the development of large vision models progresses, the importance of prompt engineering becomes increasingly evident. Designing suitable prompts for specific visual tasks has emerged as a meaningful research direction. This review aims to summarize the methods employed in the computer vision domain for large vision models and visual prompt engineering, exploring the latest advancements in visual prompt engineering. We present influential large models in the visual domain and a range of prompt engineering methods employed on these models. It is our hope that this review provides a comprehensive and systematic description of prompt engineering methods based on large visual models, offering valuable insights for future researchers in their exploration of this field.
Prompt Engineering for Healthcare: Methodologies and Applications
Apr 28, 2023Abstract:This review will introduce the latest advances in prompt engineering in the field of natural language processing (NLP) for the medical domain. First, we will provide a brief overview of the development of prompt engineering and emphasize its significant contributions to healthcare NLP applications such as question-answering systems, text summarization, and machine translation. With the continuous improvement of general large language models, the importance of prompt engineering in the healthcare domain is becoming increasingly prominent. The aim of this article is to provide useful resources and bridges for healthcare NLP researchers to better explore the application of prompt engineering in this field. We hope that this review can provide new ideas and inspire ample possibilities for research and application in medical NLP.
Towards Understanding Distributional Reinforcement Learning: Regularization, Optimization, Acceleration and Sinkhorn Algorithm
Oct 07, 2021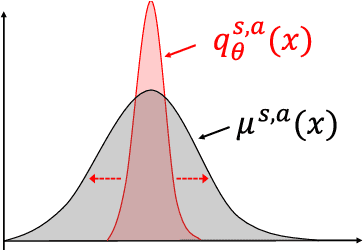
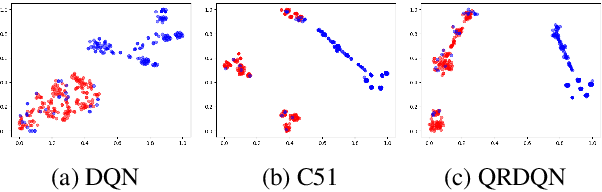
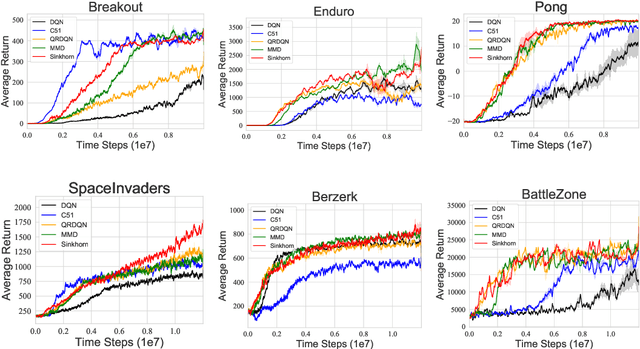
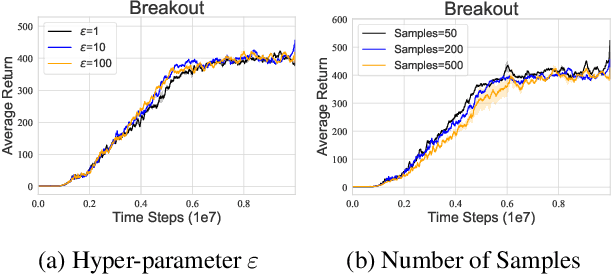
Abstract:Distributional reinforcement learning~(RL) is a class of state-of-the-art algorithms that estimate the whole distribution of the total return rather than only its expectation. Despite the remarkable performance of distributional RL, a theoretical understanding of its advantages over expectation-based RL remains elusive. In this paper, we interpret distributional RL as entropy-regularized maximum likelihood estimation in the \textit{neural Z-fitted iteration} framework, and establish the connection of the resulting risk-aware regularization with maximum entropy RL. In addition, We shed light on the stability-promoting distributional loss with desirable smoothness properties in distributional RL, which can yield stable optimization and guaranteed generalization. We also analyze the acceleration behavior while optimizing distributional RL algorithms and show that an appropriate approximation to the true target distribution can speed up the convergence. From the perspective of representation, we find that distributional RL encourages state representation from the same action class classified by the policy in tighter clusters. Finally, we propose a class of \textit{Sinkhorn distributional RL} algorithm that interpolates between the Wasserstein distance and maximum mean discrepancy~(MMD). Experiments on a suite of Atari games reveal the competitive performance of our algorithm relative to existing state-of-the-art distributional RL algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge