Di Qiu
SkyReels-V2: Infinite-length Film Generative Model
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in video generation have been driven by diffusion models and autoregressive frameworks, yet critical challenges persist in harmonizing prompt adherence, visual quality, motion dynamics, and duration: compromises in motion dynamics to enhance temporal visual quality, constrained video duration (5-10 seconds) to prioritize resolution, and inadequate shot-aware generation stemming from general-purpose MLLMs' inability to interpret cinematic grammar, such as shot composition, actor expressions, and camera motions. These intertwined limitations hinder realistic long-form synthesis and professional film-style generation. To address these limitations, we propose SkyReels-V2, an Infinite-length Film Generative Model, that synergizes Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM), Multi-stage Pretraining, Reinforcement Learning, and Diffusion Forcing Framework. Firstly, we design a comprehensive structural representation of video that combines the general descriptions by the Multi-modal LLM and the detailed shot language by sub-expert models. Aided with human annotation, we then train a unified Video Captioner, named SkyCaptioner-V1, to efficiently label the video data. Secondly, we establish progressive-resolution pretraining for the fundamental video generation, followed by a four-stage post-training enhancement: Initial concept-balanced Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) improves baseline quality; Motion-specific Reinforcement Learning (RL) training with human-annotated and synthetic distortion data addresses dynamic artifacts; Our diffusion forcing framework with non-decreasing noise schedules enables long-video synthesis in an efficient search space; Final high-quality SFT refines visual fidelity. All the code and models are available at https://github.com/SkyworkAI/SkyReels-V2.
SkyReels-A2: Compose Anything in Video Diffusion Transformers
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents SkyReels-A2, a controllable video generation framework capable of assembling arbitrary visual elements (e.g., characters, objects, backgrounds) into synthesized videos based on textual prompts while maintaining strict consistency with reference images for each element. We term this task elements-to-video (E2V), whose primary challenges lie in preserving the fidelity of each reference element, ensuring coherent composition of the scene, and achieving natural outputs. To address these, we first design a comprehensive data pipeline to construct prompt-reference-video triplets for model training. Next, we propose a novel image-text joint embedding model to inject multi-element representations into the generative process, balancing element-specific consistency with global coherence and text alignment. We also optimize the inference pipeline for both speed and output stability. Moreover, we introduce a carefully curated benchmark for systematic evaluation, i.e, A2 Bench. Experiments demonstrate that our framework can generate diverse, high-quality videos with precise element control. SkyReels-A2 is the first open-source commercial grade model for the generation of E2V, performing favorably against advanced closed-source commercial models. We anticipate SkyReels-A2 will advance creative applications such as drama and virtual e-commerce, pushing the boundaries of controllable video generation.
Ingredients: Blending Custom Photos with Video Diffusion Transformers
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a powerful framework to customize video creations by incorporating multiple specific identity (ID) photos, with video diffusion Transformers, referred to as \texttt{Ingredients}. Generally, our method consists of three primary modules: (\textbf{i}) a facial extractor that captures versatile and precise facial features for each human ID from both global and local perspectives; (\textbf{ii}) a multi-scale projector that maps face embeddings into the contextual space of image query in video diffusion transformers; (\textbf{iii}) an ID router that dynamically combines and allocates multiple ID embedding to the corresponding space-time regions. Leveraging a meticulously curated text-video dataset and a multi-stage training protocol, \texttt{Ingredients} demonstrates superior performance in turning custom photos into dynamic and personalized video content. Qualitative evaluations highlight the advantages of proposed method, positioning it as a significant advancement toward more effective generative video control tools in Transformer-based architecture, compared to existing methods. The data, code, and model weights are publicly available at: \url{https://github.com/feizc/Ingredients}.
Video Diffusion Transformers are In-Context Learners
Dec 14, 2024


Abstract:This paper investigates a solution for enabling in-context capabilities of video diffusion transformers, with minimal tuning required for activation. Specifically, we propose a simple pipeline to leverage in-context generation: ($\textbf{i}$) concatenate videos along spacial or time dimension, ($\textbf{ii}$) jointly caption multi-scene video clips from one source, and ($\textbf{iii}$) apply task-specific fine-tuning using carefully curated small datasets. Through a series of diverse controllable tasks, we demonstrate qualitatively that existing advanced text-to-video models can effectively perform in-context generation. Notably, it allows for the creation of consistent multi-scene videos exceeding 30 seconds in duration, without additional computational overhead. Importantly, this method requires no modifications to the original models, results in high-fidelity video outputs that better align with prompt specifications and maintain role consistency. Our framework presents a valuable tool for the research community and offers critical insights for advancing product-level controllable video generation systems. The data, code, and model weights are publicly available at: \url{https://github.com/feizc/Video-In-Context}.
MotionCharacter: Identity-Preserving and Motion Controllable Human Video Generation
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in personalized Text-to-Video (T2V) generation highlight the importance of integrating character-specific identities and actions. However, previous T2V models struggle with identity consistency and controllable motion dynamics, mainly due to limited fine-grained facial and action-based textual prompts, and datasets that overlook key human attributes and actions. To address these challenges, we propose MotionCharacter, an efficient and high-fidelity human video generation framework designed for identity preservation and fine-grained motion control. We introduce an ID-preserving module to maintain identity fidelity while allowing flexible attribute modifications, and further integrate ID-consistency and region-aware loss mechanisms, significantly enhancing identity consistency and detail fidelity. Additionally, our approach incorporates a motion control module that prioritizes action-related text while maintaining subject consistency, along with a dataset, Human-Motion, which utilizes large language models to generate detailed motion descriptions. For simplify user control during inference, we parameterize motion intensity through a single coefficient, allowing for easy adjustments. Extensive experiments highlight the effectiveness of MotionCharacter, demonstrating significant improvements in ID-preserving, high-quality video generation.
MovieCharacter: A Tuning-Free Framework for Controllable Character Video Synthesis
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in character video synthesis still depend on extensive fine-tuning or complex 3D modeling processes, which can restrict accessibility and hinder real-time applicability. To address these challenges, we propose a simple yet effective tuning-free framework for character video synthesis, named MovieCharacter, designed to streamline the synthesis process while ensuring high-quality outcomes. Our framework decomposes the synthesis task into distinct, manageable modules: character segmentation and tracking, video object removal, character motion imitation, and video composition. This modular design not only facilitates flexible customization but also ensures that each component operates collaboratively to effectively meet user needs. By leveraging existing open-source models and integrating well-established techniques, MovieCharacter achieves impressive synthesis results without necessitating substantial resources or proprietary datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework enhances the efficiency, accessibility, and adaptability of character video synthesis, paving the way for broader creative and interactive applications.
A deep neural network framework for dynamic multi-valued mapping estimation and its applications
Jun 29, 2024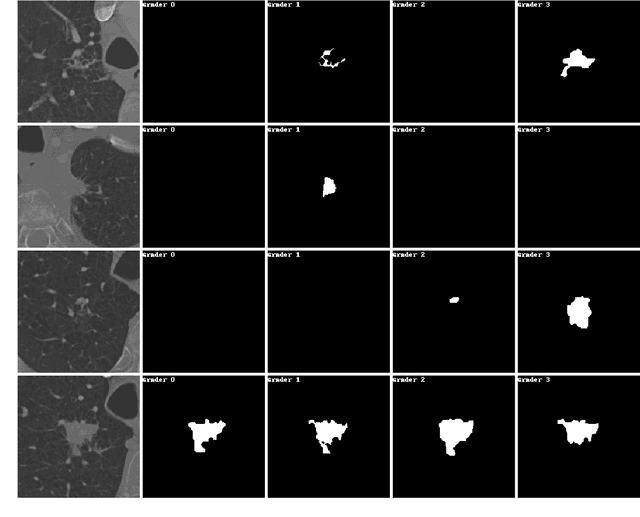
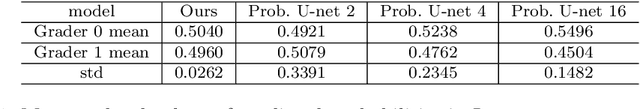
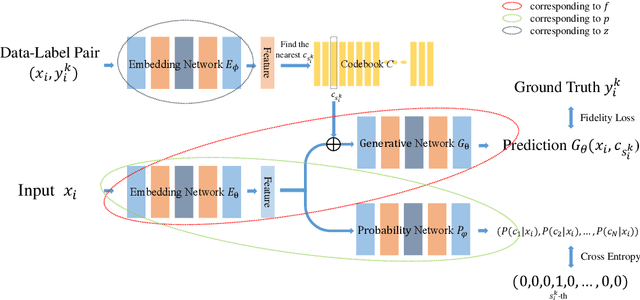
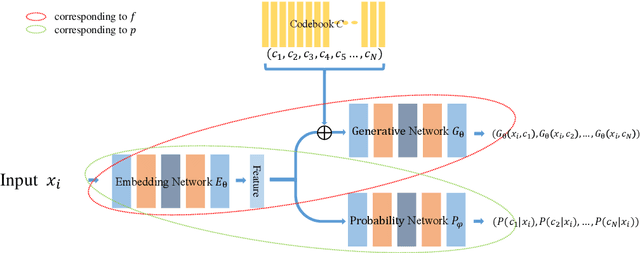
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of modeling and estimating dynamic multi-valued mappings. While most mathematical models provide a unique solution for a given input, real-world applications often lack deterministic solutions. In such scenarios, estimating dynamic multi-valued mappings is necessary to suggest different reasonable solutions for each input. This paper introduces a deep neural network framework incorporating a generative network and a classification component. The objective is to model the dynamic multi-valued mapping between the input and output by providing a reliable uncertainty measurement. Generating multiple solutions for a given input involves utilizing a discrete codebook comprising finite variables. These variables are fed into a generative network along with the input, producing various output possibilities. The discreteness of the codebook enables efficient estimation of the output's conditional probability distribution for any given input using a classifier. By jointly optimizing the discrete codebook and its uncertainty estimation during training using a specially designed loss function, a highly accurate approximation is achieved. The effectiveness of our proposed framework is demonstrated through its application to various imaging problems, using both synthetic and real imaging data. Experimental results show that our framework accurately estimates the dynamic multi-valued mapping with uncertainty estimation.
AdaFedFR: Federated Face Recognition with Adaptive Inter-Class Representation Learning
May 22, 2024



Abstract:With the growing attention on data privacy and communication security in face recognition applications, federated learning has been introduced to learn a face recognition model with decentralized datasets in a privacy-preserving manner. However, existing works still face challenges such as unsatisfying performance and additional communication costs, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective federated face recognition framework called AdaFedFR, by devising an adaptive inter-class representation learning algorithm to enhance the generalization of the generic face model and the efficiency of federated training under strict privacy-preservation. In particular, our work delicately utilizes feature representations of public identities as learnable negative knowledge to optimize the local objective within the feature space, which further encourages the local model to learn powerful representations and optimize personalized models for clients. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms previous approaches on several prevalent face recognition benchmarks within less than 3 communication rounds, which shows communication-friendly and great efficiency.
CHOSEN: Contrastive Hypothesis Selection for Multi-View Depth Refinement
Apr 02, 2024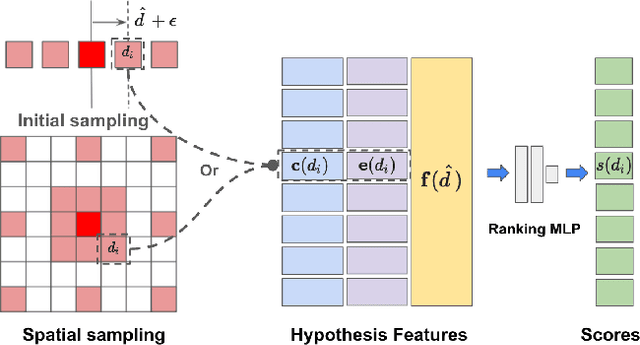
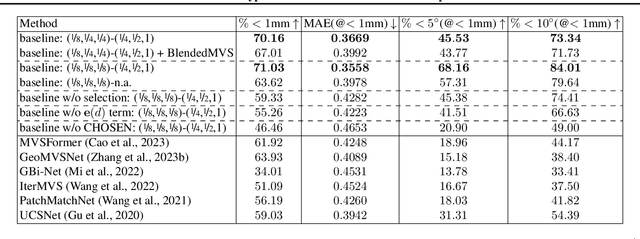
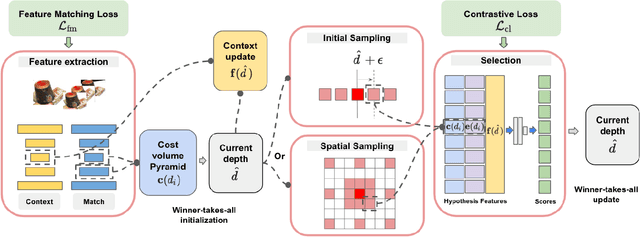

Abstract:We propose CHOSEN, a simple yet flexible, robust and effective multi-view depth refinement framework. It can be employed in any existing multi-view stereo pipeline, with straightforward generalization capability for different multi-view capture systems such as camera relative positioning and lenses. Given an initial depth estimation, CHOSEN iteratively re-samples and selects the best hypotheses, and automatically adapts to different metric or intrinsic scales determined by the capture system. The key to our approach is the application of contrastive learning in an appropriate solution space and a carefully designed hypothesis feature, based on which positive and negative hypotheses can be effectively distinguished. Integrated in a simple baseline multi-view stereo pipeline, CHOSEN delivers impressive quality in terms of depth and normal accuracy compared to many current deep learning based multi-view stereo pipelines.
MagicMirror: Fast and High-Quality Avatar Generation with a Constrained Search Space
Apr 01, 2024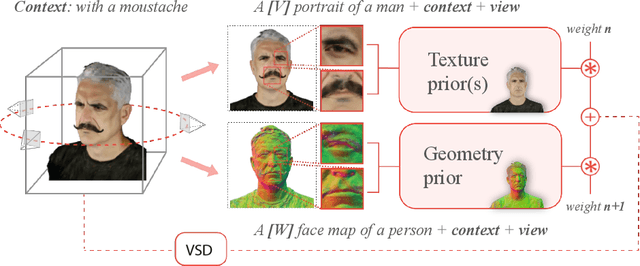
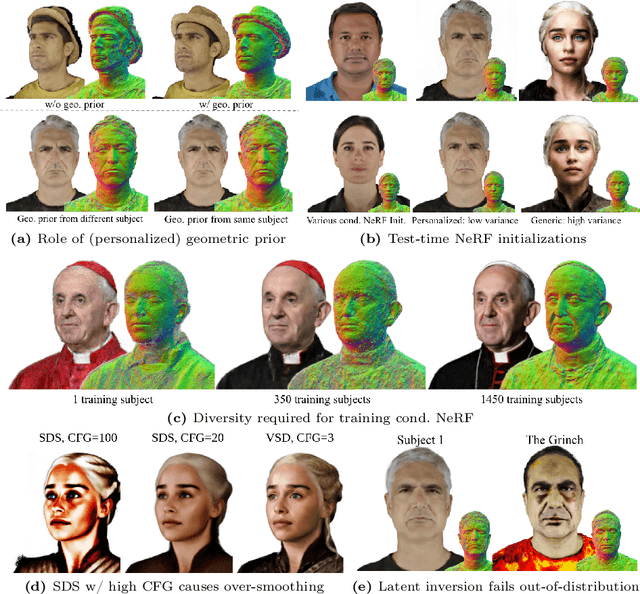



Abstract:We introduce a novel framework for 3D human avatar generation and personalization, leveraging text prompts to enhance user engagement and customization. Central to our approach are key innovations aimed at overcoming the challenges in photo-realistic avatar synthesis. Firstly, we utilize a conditional Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) model, trained on a large-scale unannotated multi-view dataset, to create a versatile initial solution space that accelerates and diversifies avatar generation. Secondly, we develop a geometric prior, leveraging the capabilities of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models, to ensure superior view invariance and enable direct optimization of avatar geometry. These foundational ideas are complemented by our optimization pipeline built on Variational Score Distillation (VSD), which mitigates texture loss and over-saturation issues. As supported by our extensive experiments, these strategies collectively enable the creation of custom avatars with unparalleled visual quality and better adherence to input text prompts. You can find more results and videos in our website: https://syntec-research.github.io/MagicMirror
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge