Xinyang Lin
AdaFedFR: Federated Face Recognition with Adaptive Inter-Class Representation Learning
May 22, 2024



Abstract:With the growing attention on data privacy and communication security in face recognition applications, federated learning has been introduced to learn a face recognition model with decentralized datasets in a privacy-preserving manner. However, existing works still face challenges such as unsatisfying performance and additional communication costs, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective federated face recognition framework called AdaFedFR, by devising an adaptive inter-class representation learning algorithm to enhance the generalization of the generic face model and the efficiency of federated training under strict privacy-preservation. In particular, our work delicately utilizes feature representations of public identities as learnable negative knowledge to optimize the local objective within the feature space, which further encourages the local model to learn powerful representations and optimize personalized models for clients. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms previous approaches on several prevalent face recognition benchmarks within less than 3 communication rounds, which shows communication-friendly and great efficiency.
MobileVLM V2: Faster and Stronger Baseline for Vision Language Model
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:We introduce MobileVLM V2, a family of significantly improved vision language models upon MobileVLM, which proves that a delicate orchestration of novel architectural design, an improved training scheme tailored for mobile VLMs, and rich high-quality dataset curation can substantially benefit VLMs' performance. Specifically, MobileVLM V2 1.7B achieves better or on-par performance on standard VLM benchmarks compared with much larger VLMs at the 3B scale. Notably, our 3B model outperforms a large variety of VLMs at the 7B+ scale. Our models will be released at https://github.com/Meituan-AutoML/MobileVLM .
MobileVLM : A Fast, Strong and Open Vision Language Assistant for Mobile Devices
Dec 30, 2023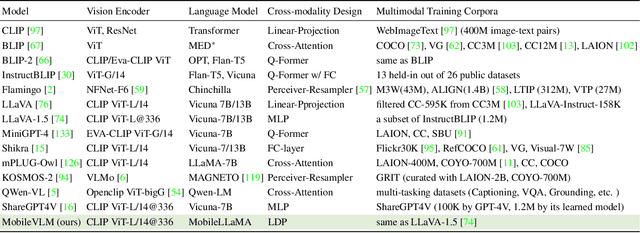
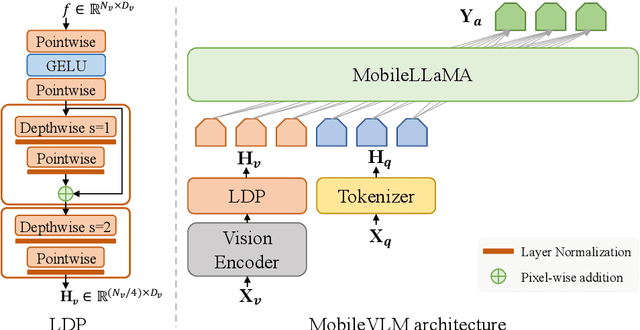
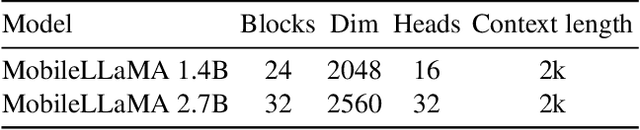
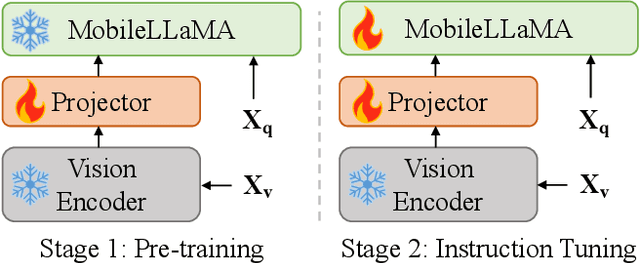
Abstract:We present MobileVLM, a competent multimodal vision language model (MMVLM) targeted to run on mobile devices. It is an amalgamation of a myriad of architectural designs and techniques that are mobile-oriented, which comprises a set of language models at the scale of 1.4B and 2.7B parameters, trained from scratch, a multimodal vision model that is pre-trained in the CLIP fashion, cross-modality interaction via an efficient projector. We evaluate MobileVLM on several typical VLM benchmarks. Our models demonstrate on par performance compared with a few much larger models. More importantly, we measure the inference speed on both a Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 CPU and an NVIDIA Jeston Orin GPU, and we obtain state-of-the-art performance of 21.5 tokens and 65.3 tokens per second, respectively. Our code will be made available at: https://github.com/Meituan-AutoML/MobileVLM.
Federated Learning with Positive and Unlabeled Data
Jun 21, 2021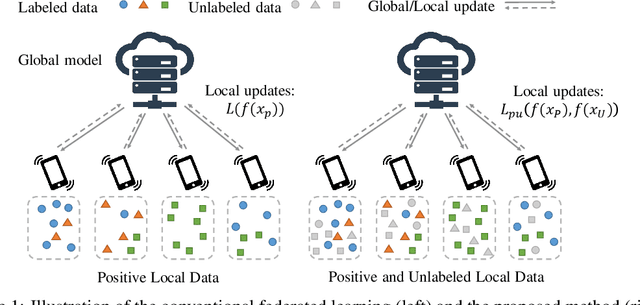
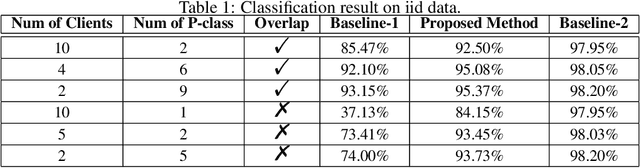
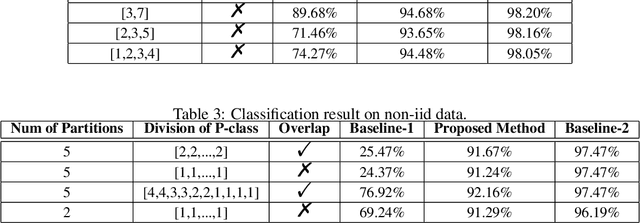
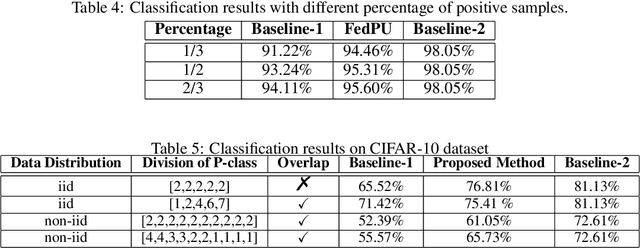
Abstract:We study the problem of learning from positive and unlabeled (PU) data in the federated setting, where each client only labels a little part of their dataset due to the limitation of resources and time. Different from the settings in traditional PU learning where the negative class consists of a single class, the negative samples which cannot be identified by a client in the federated setting may come from multiple classes which are unknown to the client. Therefore, existing PU learning methods can be hardly applied in this situation. To address this problem, we propose a novel framework, namely Federated learning with Positive and Unlabeled data (FedPU), to minimize the expected risk of multiple negative classes by leveraging the labeled data in other clients. We theoretically prove that the proposed FedPU can achieve a generalization bound which is no worse than $C\sqrt{C}$ times (where $C$ denotes the number of classes) of the fully-supervised model. Empirical experiments show that the FedPU can achieve much better performance than conventional learning methods which can only use positive data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge