Demin Song
Eric
Explicit Multi-head Attention for Inter-head Interaction in Large Language Models
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:In large language models built upon the Transformer architecture, recent studies have shown that inter-head interaction can enhance attention performance. Motivated by this, we propose Multi-head Explicit Attention (MEA), a simple yet effective attention variant that explicitly models cross-head interaction. MEA consists of two key components: a Head-level Linear Composition (HLC) module that separately applies learnable linear combinations to the key and value vectors across heads, thereby enabling rich inter-head communication; and a head-level Group Normalization layer that aligns the statistical properties of the recombined heads. MEA shows strong robustness in pretraining, which allows the use of larger learning rates that lead to faster convergence, ultimately resulting in lower validation loss and improved performance across a range of tasks. Furthermore, we explore the parameter efficiency of MEA by reducing the number of attention heads and leveraging HLC to reconstruct them using low-rank "virtual heads". This enables a practical key-value cache compression strategy that reduces KV-cache memory usage by 50% with negligible performance loss on knowledge-intensive and scientific reasoning tasks, and only a 3.59% accuracy drop for Olympiad-level mathematical benchmarks.
CritiQ: Mining Data Quality Criteria from Human Preferences
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Language model heavily depends on high-quality data for optimal performance. Existing approaches rely on manually designed heuristics, the perplexity of existing models, training classifiers, or careful prompt engineering, which require significant expert experience and human annotation effort while introduce biases. We introduce CritiQ, a novel data selection method that automatically mines criteria from human preferences for data quality with only $\sim$30 human-annotated pairs and performs efficient data selection. The main component, CritiQ Flow, employs a manager agent to evolve quality criteria and worker agents to make pairwise judgments. We build a knowledge base that extracts quality criteria from previous work to boost CritiQ Flow. Compared to perplexity- and classifier- based methods, verbal criteria are more interpretable and possess reusable value. After deriving the criteria, we train the CritiQ Scorer to give quality scores and perform efficient data selection. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in the code, math, and logic domains, achieving high accuracy on human-annotated test sets. To validate the quality of the selected data, we continually train Llama 3.1 models and observe improved performance on downstream tasks compared to uniform sampling. Ablation studies validate the benefits of the knowledge base and the reflection process. We analyze how criteria evolve and the effectiveness of majority voting.
UnitCoder: Scalable Iterative Code Synthesis with Unit Test Guidance
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in various tasks, yet code generation remains a major challenge. Current approaches for obtaining high-quality code data primarily focus on (i) collecting large-scale pre-training data and (ii) synthesizing instruction data through prompt engineering with powerful models. While pre-training data faces quality consistency issues, instruction-based synthesis suffers from limited instruction diversity and inherent biases of LLMs. To address this gap, we introduce UnitCoder, a systematic pipeline leveraging model-generated unit tests to both guide and validate the code generation process. Combined with large-scale package-based retrieval from pre-training corpus, we generate a dataset of 500K+ verifiable programs containing diverse API calls. Evaluations on multiple Python benchmarks (BigCodeBench, HumanEval, MBPP) demonstrate that models fine-tuned on our synthetic data exhibit consistent performance improvements. Notably, Llama3.1-8B and InternLM2.5-7B improve from 31\% and 28\% to 40\% and 39\% success rates on BigCodeBench, respectively. Our work presents a scalable approach that leverages model-generated unit tests to guide the synthesis of high-quality code data from pre-training corpora, demonstrating the potential for producing diverse and high-quality post-training data at scale. All code and data will be released (https://github.com).
OriGen:Enhancing RTL Code Generation with Code-to-Code Augmentation and Self-Reflection
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:Recent studies have illuminated that Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit substantial potential in the realm of RTL (Register Transfer Level) code generation, with notable advancements evidenced by commercial models such as GPT-4 and Claude3-Opus. Despite their proficiency, these commercial LLMs often raise concerns regarding privacy and security. Conversely, open-source LLMs, which offer solutions to these concerns, have inferior performance in RTL code generation tasks to commercial models due to the lack of highquality open-source RTL datasets. To address this issue, we introduce OriGen, a fully open-source framework featuring self-reflection capabilities and a dataset augmentation methodology for generating high-quality, large-scale RTL code. We propose a novel code-to-code augmentation methodology that leverages knowledge distillation to enhance the quality of the open-source RTL code datasets. Additionally, OriGen is capable of correcting syntactic errors by leveraging a self-reflection process based on feedback from the compiler. The self-reflection ability of the model is facilitated by a carefully constructed dataset, which comprises a comprehensive collection of samples. Experimental results demonstrate that OriGen remarkably outperforms other open-source alternatives in RTL code generation, surpassing the previous best-performing LLM by 9.8% on the VerilogEval-Human benchmark. Furthermore, OriGen exhibits superior capabilities in self-reflection and error rectification, surpassing GPT-4 by 18.1% on the benchmark designed to evaluate the capability of self-reflection.
Case2Code: Learning Inductive Reasoning with Synthetic Data
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:Complex reasoning is an impressive ability shown by large language models (LLMs). Most LLMs are skilled in deductive reasoning, such as chain-of-thought prompting or iterative tool-using to solve challenging tasks step-by-step. In this paper, we hope to focus on evaluating and teaching LLMs to conduct inductive reasoning, that is, LLMs are supposed to infer underlying rules by observing examples or sequential transformations. However, collecting large-scale and diverse human-generated inductive data is challenging. We focus on data synthesis in the code domain and propose a \textbf{Case2Code} task by exploiting the expressiveness and correctness of programs. Specifically, we collect a diverse set of executable programs, synthesize input-output transformations for each program, and force LLMs to infer the underlying code implementations based on the synthetic I/O cases. We first evaluate representative LLMs on the synthesized Case2Code task and demonstrate that the Case-to-code induction is challenging for LLMs. Then, we synthesize large-scale Case2Code training samples to train LLMs to perform inductive reasoning. Experimental results show that such induction training benefits not only in distribution Case2Code performance but also enhances various coding abilities of trained LLMs, demonstrating the great potential of learning inductive reasoning via synthetic data.
AlchemistCoder: Harmonizing and Eliciting Code Capability by Hindsight Tuning on Multi-source Data
May 29, 2024Abstract:Open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) and their specialized variants, particularly Code LLMs, have recently delivered impressive performance. However, previous Code LLMs are typically fine-tuned on single-source data with limited quality and diversity, which may insufficiently elicit the potential of pre-trained Code LLMs. In this paper, we present AlchemistCoder, a series of Code LLMs with enhanced code generation and generalization capabilities fine-tuned on multi-source data. To achieve this, we pioneer to unveil inherent conflicts among the various styles and qualities in multi-source code corpora and introduce data-specific prompts with hindsight relabeling, termed AlchemistPrompts, to harmonize different data sources and instruction-response pairs. Additionally, we propose incorporating the data construction process into the fine-tuning data as code comprehension tasks, including instruction evolution, data filtering, and code review. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AlchemistCoder holds a clear lead among all models of the same size (6.7B/7B) and rivals or even surpasses larger models (15B/33B/70B), showcasing the efficacy of our method in refining instruction-following capabilities and advancing the boundaries of code intelligence.
InternLM2 Technical Report
Mar 26, 2024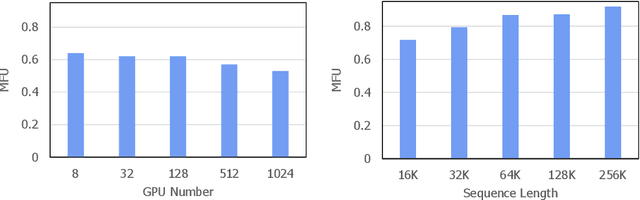
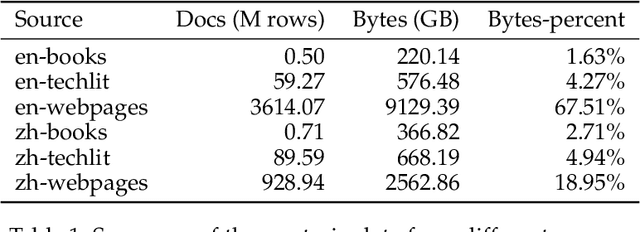

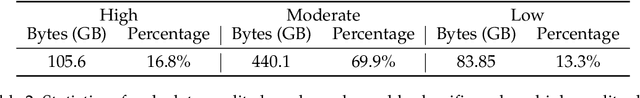
Abstract:The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and GPT-4 has sparked discussions on the advent of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). However, replicating such advancements in open-source models has been challenging. This paper introduces InternLM2, an open-source LLM that outperforms its predecessors in comprehensive evaluations across 6 dimensions and 30 benchmarks, long-context modeling, and open-ended subjective evaluations through innovative pre-training and optimization techniques. The pre-training process of InternLM2 is meticulously detailed, highlighting the preparation of diverse data types including text, code, and long-context data. InternLM2 efficiently captures long-term dependencies, initially trained on 4k tokens before advancing to 32k tokens in pre-training and fine-tuning stages, exhibiting remarkable performance on the 200k ``Needle-in-a-Haystack" test. InternLM2 is further aligned using Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and a novel Conditional Online Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (COOL RLHF) strategy that addresses conflicting human preferences and reward hacking. By releasing InternLM2 models in different training stages and model sizes, we provide the community with insights into the model's evolution.
Code Needs Comments: Enhancing Code LLMs with Comment Augmentation
Feb 20, 2024



Abstract:The programming skill is one crucial ability for Large Language Models (LLMs), necessitating a deep understanding of programming languages (PLs) and their correlation with natural languages (NLs). We examine the impact of pre-training data on code-focused LLMs' performance by assessing the comment density as a measure of PL-NL alignment. Given the scarcity of code-comment aligned data in pre-training corpora, we introduce a novel data augmentation method that generates comments for existing code, coupled with a data filtering strategy that filters out code data poorly correlated with natural language. We conducted experiments on three code-focused LLMs and observed consistent improvements in performance on two widely-used programming skill benchmarks. Notably, the model trained on the augmented data outperformed both the model used for generating comments and the model further trained on the data without augmentation.
Rebuild and Ensemble: Exploring Defense Against Text Adversaries
Mar 27, 2022



Abstract:Adversarial attacks can mislead strong neural models; as such, in NLP tasks, substitution-based attacks are difficult to defend. Current defense methods usually assume that the substitution candidates are accessible, which cannot be widely applied against adversarial attacks unless knowing the mechanism of the attacks. In this paper, we propose a \textbf{Rebuild and Ensemble} Framework to defend against adversarial attacks in texts without knowing the candidates. We propose a rebuild mechanism to train a robust model and ensemble the rebuilt texts during inference to achieve good adversarial defense results. Experiments show that our method can improve accuracy under the current strong attack methods.
KNN-BERT: Fine-Tuning Pre-Trained Models with KNN Classifier
Oct 06, 2021



Abstract:Pre-trained models are widely used in fine-tuning downstream tasks with linear classifiers optimized by the cross-entropy loss, which might face robustness and stability problems. These problems can be improved by learning representations that focus on similarities in the same class and contradictions in different classes when making predictions. In this paper, we utilize the K-Nearest Neighbors Classifier in pre-trained model fine-tuning. For this KNN classifier, we introduce a supervised momentum contrastive learning framework to learn the clustered representations of the supervised downstream tasks. Extensive experiments on text classification tasks and robustness tests show that by incorporating KNNs with the traditional fine-tuning process, we can obtain significant improvements on the clean accuracy in both rich-source and few-shot settings and can improve the robustness against adversarial attacks. \footnote{all codes is available at https://github.com/LinyangLee/KNN-BERT}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge