Chaoqun Yang
Watermarking Large Language Model-based Time Series Forecasting
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Large Language Model-based Time Series Forecasting (LLMTS) has shown remarkable promise in handling complex and diverse temporal data, representing a significant step toward foundation models for time series analysis. However, this emerging paradigm introduces two critical challenges. First, the substantial commercial potential and resource-intensive development raise urgent concerns about intellectual property (IP) protection. Second, their powerful time series forecasting capabilities may be misused to produce misleading or fabricated deepfake time series data. To address these concerns, we explore watermarking the outputs of LLMTS models, that is, embedding imperceptible signals into the generated time series data that remain detectable by specialized algorithms. We propose a novel post-hoc watermarking framework, Waltz, which is broadly compatible with existing LLMTS models. Waltz is inspired by the empirical observation that time series patch embeddings are rarely aligned with a specific set of LLM tokens, which we term ``cold tokens''. Leveraging this insight, Waltz embeds watermarks by rewiring the similarity statistics between patch embeddings and cold token embeddings, and detects watermarks using similarity z-scores. To minimize potential side effects, we introduce a similarity-based embedding position identification strategy and employ projected gradient descent to constrain the watermark noise within a defined boundary. Extensive experiments using two popular LLMTS models across seven benchmark datasets demonstrate that Waltz achieves high watermark detection accuracy with minimal impact on the quality of the generated time series.
UniCTokens: Boosting Personalized Understanding and Generation via Unified Concept Tokens
May 20, 2025Abstract:Personalized models have demonstrated remarkable success in understanding and generating concepts provided by users. However, existing methods use separate concept tokens for understanding and generation, treating these tasks in isolation. This may result in limitations for generating images with complex prompts. For example, given the concept $\langle bo\rangle$, generating "$\langle bo\rangle$ wearing its hat" without additional textual descriptions of its hat. We call this kind of generation personalized knowledge-driven generation. To address the limitation, we present UniCTokens, a novel framework that effectively integrates personalized information into a unified vision language model (VLM) for understanding and generation. UniCTokens trains a set of unified concept tokens to leverage complementary semantics, boosting two personalized tasks. Moreover, we propose a progressive training strategy with three stages: understanding warm-up, bootstrapping generation from understanding, and deepening understanding from generation to enhance mutual benefits between both tasks. To quantitatively evaluate the unified VLM personalization, we present UnifyBench, the first benchmark for assessing concept understanding, concept generation, and knowledge-driven generation. Experimental results on UnifyBench indicate that UniCTokens shows competitive performance compared to leading methods in concept understanding, concept generation, and achieving state-of-the-art results in personalized knowledge-driven generation. Our research demonstrates that enhanced understanding improves generation, and the generation process can yield valuable insights into understanding. Our code and dataset will be released at: \href{https://github.com/arctanxarc/UniCTokens}{https://github.com/arctanxarc/UniCTokens}.
MCTS-Judge: Test-Time Scaling in LLM-as-a-Judge for Code Correctness Evaluation
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:The LLM-as-a-Judge paradigm shows promise for evaluating generative content but lacks reliability in reasoning-intensive scenarios, such as programming. Inspired by recent advances in reasoning models and shifts in scaling laws, we pioneer bringing test-time computation into LLM-as-a-Judge, proposing MCTS-Judge, a resource-efficient, System-2 thinking framework for code correctness evaluation. MCTS-Judge leverages Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to decompose problems into simpler, multi-perspective evaluations. Through a node-selection strategy that combines self-assessment based on historical actions in the current trajectory and the Upper Confidence Bound for Trees based on prior rollouts, MCTS-Judge balances global optimization and refinement of the current trajectory. We further designed a high-precision, unit-test-level reward mechanism to encourage the Large Language Model (LLM) to perform line-by-line analysis. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks and five LLMs demonstrate the effectiveness of MCTS-Judge, which improves the base model's accuracy from 41% to 80%, surpassing the o1-series models with 3x fewer tokens. Further evaluations validate the superiority of its reasoning trajectory in logic, analytics, thoroughness, and overall quality, while revealing the test-time scaling law of the LLM-as-a-Judge paradigm.
FELLAS: Enhancing Federated Sequential Recommendation with LLM as External Services
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Federated sequential recommendation (FedSeqRec) has gained growing attention due to its ability to protect user privacy. Unfortunately, the performance of FedSeqRec is still unsatisfactory because the models used in FedSeqRec have to be lightweight to accommodate communication bandwidth and clients' on-device computational resource constraints. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have exhibited strong transferable and generalized language understanding abilities and therefore, in the NLP area, many downstream tasks now utilize LLMs as a service to achieve superior performance without constructing complex models. Inspired by this successful practice, we propose a generic FedSeqRec framework, FELLAS, which aims to enhance FedSeqRec by utilizing LLMs as an external service. Specifically, FELLAS employs an LLM server to provide both item-level and sequence-level representation assistance. The item-level representation service is queried by the central server to enrich the original ID-based item embedding with textual information, while the sequence-level representation service is accessed by each client. However, invoking the sequence-level representation service requires clients to send sequences to the external LLM server. To safeguard privacy, we implement dx-privacy satisfied sequence perturbation, which protects clients' sensitive data with guarantees. Additionally, a contrastive learning-based method is designed to transfer knowledge from the noisy sequence representation to clients' sequential recommendation models. Furthermore, to empirically validate the privacy protection capability of FELLAS, we propose two interacted item inference attacks. Extensive experiments conducted on three datasets with two widely used sequential recommendation models demonstrate the effectiveness and privacy-preserving capability of FELLAS.
Efficient Inference for Large Language Model-based Generative Recommendation
Oct 07, 2024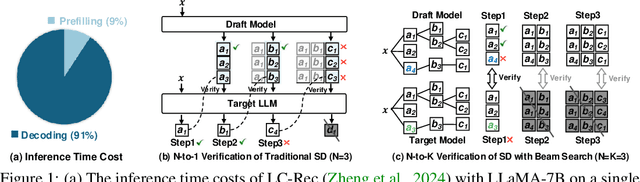

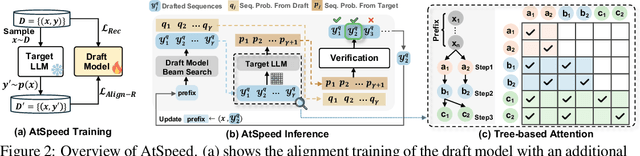

Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based generative recommendation has achieved notable success, yet its practical deployment is costly particularly due to excessive inference latency caused by autoregressive decoding. For lossless LLM decoding acceleration, Speculative Decoding (SD) has emerged as a promising solution. However, applying SD to generative recommendation presents unique challenges due to the requirement of generating top-K items (i.e., K distinct token sequences) as a recommendation list by beam search. This leads to more stringent verification in SD, where all the top-K sequences from the target LLM must be successfully drafted by the draft model at each decoding step. To alleviate this, we consider 1) boosting top-K sequence alignment between the draft model and the target LLM, and 2) relaxing the verification strategy to reduce trivial LLM calls. To this end, we propose an alignment framework named AtSpeed, which presents the AtSpeed-S optimization objective for top-K alignment under the strict top-K verification. Moreover, we introduce a relaxed sampling verification strategy that allows high-probability non-top-K drafted sequences to be accepted, significantly reducing LLM calls. Correspondingly, we propose AtSpeed-R for top-K alignment under this relaxed sampling verification. Empirical results on two real-world datasets demonstrate that AtSpeed significantly accelerates LLM-based generative recommendation, e.g., near 2x speedup under strict top-K verification and up to 2.5 speedup under relaxed sampling verification. The codes and datasets will be released in the near future.
PDC-FRS: Privacy-preserving Data Contribution for Federated Recommender System
Sep 12, 2024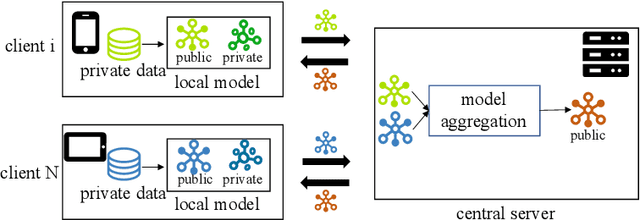
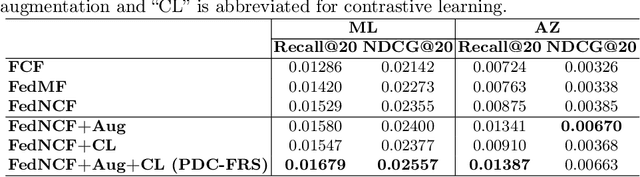
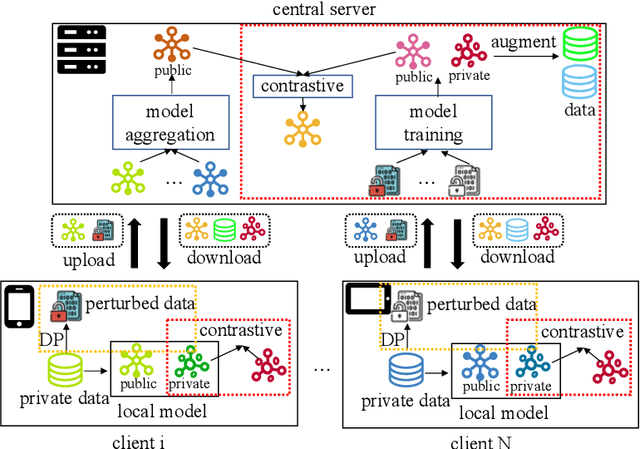
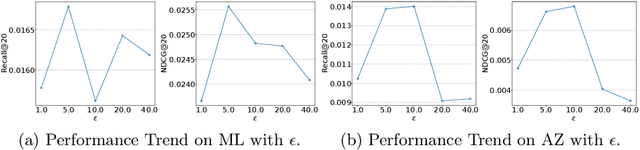
Abstract:Federated recommender systems (FedRecs) have emerged as a popular research direction for protecting users' privacy in on-device recommendations. In FedRecs, users keep their data locally and only contribute their local collaborative information by uploading model parameters to a central server. While this rigid framework protects users' raw data during training, it severely compromises the recommendation model's performance due to the following reasons: (1) Due to the power law distribution nature of user behavior data, individual users have few data points to train a recommendation model, resulting in uploaded model updates that may be far from optimal; (2) As each user's uploaded parameters are learned from local data, which lacks global collaborative information, relying solely on parameter aggregation methods such as FedAvg to fuse global collaborative information may be suboptimal. To bridge this performance gap, we propose a novel federated recommendation framework, PDC-FRS. Specifically, we design a privacy-preserving data contribution mechanism that allows users to share their data with a differential privacy guarantee. Based on the shared but perturbed data, an auxiliary model is trained in parallel with the original federated recommendation process. This auxiliary model enhances FedRec by augmenting each user's local dataset and integrating global collaborative information. To demonstrate the effectiveness of PDC-FRS, we conduct extensive experiments on two widely used recommendation datasets. The empirical results showcase the superiority of PDC-FRS compared to baseline methods.
PTF-FSR: A Parameter Transmission-Free Federated Sequential Recommender System
Jun 08, 2024Abstract:Sequential recommender systems have made significant progress. Recently, due to increasing concerns about user data privacy, some researchers have implemented federated learning for sequential recommendation, a.k.a., Federated Sequential Recommender Systems (FedSeqRecs), in which a public sequential recommender model is shared and frequently transmitted between a central server and clients to achieve collaborative learning. Although these solutions mitigate user privacy to some extent, they present two significant limitations that affect their practical usability: (1) They require a globally shared sequential recommendation model. However, in real-world scenarios, the recommendation model constitutes a critical intellectual property for platform and service providers. Therefore, service providers may be reluctant to disclose their meticulously developed models. (2) The communication costs are high as they correlate with the number of model parameters. This becomes particularly problematic as the current FedSeqRec will be inapplicable when sequential recommendation marches into a large language model era. To overcome the above challenges, this paper proposes a parameter transmission-free federated sequential recommendation framework (PTF-FSR), which ensures both model and data privacy protection to meet the privacy needs of service providers and system users alike. Furthermore, since PTF-FSR only transmits prediction results under privacy protection, which are independent of model sizes, this new federated learning architecture can accommodate more complex and larger sequential recommendation models. Extensive experiments conducted on three widely used recommendation datasets, employing various sequential recommendation models from both ID-based and ID-free paradigms, demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization capability of our proposed framework.
Robust Federated Contrastive Recommender System against Model Poisoning Attack
Mar 29, 2024



Abstract:Federated Recommender Systems (FedRecs) have garnered increasing attention recently, thanks to their privacy-preserving benefits. However, the decentralized and open characteristics of current FedRecs present two dilemmas. First, the performance of FedRecs is compromised due to highly sparse on-device data for each client. Second, the system's robustness is undermined by the vulnerability to model poisoning attacks launched by malicious users. In this paper, we introduce a novel contrastive learning framework designed to fully leverage the client's sparse data through embedding augmentation, referred to as CL4FedRec. Unlike previous contrastive learning approaches in FedRecs that necessitate clients to share their private parameters, our CL4FedRec aligns with the basic FedRec learning protocol, ensuring compatibility with most existing FedRec implementations. We then evaluate the robustness of FedRecs equipped with CL4FedRec by subjecting it to several state-of-the-art model poisoning attacks. Surprisingly, our observations reveal that contrastive learning tends to exacerbate the vulnerability of FedRecs to these attacks. This is attributed to the enhanced embedding uniformity, making the polluted target item embedding easily proximate to popular items. Based on this insight, we propose an enhanced and robust version of CL4FedRec (rCL4FedRec) by introducing a regularizer to maintain the distance among item embeddings with different popularity levels. Extensive experiments conducted on four commonly used recommendation datasets demonstrate that CL4FedRec significantly enhances both the model's performance and the robustness of FedRecs.
Hide Your Model: A Parameter Transmission-free Federated Recommender System
Nov 28, 2023Abstract:With the growing concerns regarding user data privacy, Federated Recommender System (FedRec) has garnered significant attention recently due to its privacy-preserving capabilities. Existing FedRecs generally adhere to a learning protocol in which a central server shares a global recommendation model with clients, and participants achieve collaborative learning by frequently communicating the model's public parameters. Nevertheless, this learning framework has two drawbacks that limit its practical usability: (1) It necessitates a global-sharing recommendation model; however, in real-world scenarios, information related to the recommender model, including its algorithm and parameters, constitutes the platforms' intellectual property. Hence, service providers are unlikely to release such information actively. (2) The communication costs of model parameter transmission are expensive since the model parameters are usually high-dimensional matrices. With the model size increasing, the communication burden will be the bottleneck for such traditional FedRecs. Given the above limitations, this paper introduces a novel parameter transmission-free federated recommendation framework that balances the protection between users' data privacy and platforms' model privacy, namely PTF-FedRec. Specifically, participants in PTF-FedRec collaboratively exchange knowledge by sharing their predictions within a privacy-preserving mechanism. Through this way, the central server can learn a recommender model without disclosing its model parameters or accessing clients' raw data, preserving both the server's model privacy and users' data privacy. Besides, since clients and the central server only need to communicate prediction scores which are just a few real numbers, the overhead is significantly reduced compared to traditional FedRecs.
Motif-Based Prompt Learning for Universal Cross-Domain Recommendation
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Cross-Domain Recommendation (CDR) stands as a pivotal technology addressing issues of data sparsity and cold start by transferring general knowledge from the source to the target domain. However, existing CDR models suffer limitations in adaptability across various scenarios due to their inherent complexity. To tackle this challenge, recent advancements introduce universal CDR models that leverage shared embeddings to capture general knowledge across domains and transfer it through "Multi-task Learning" or "Pre-train, Fine-tune" paradigms. However, these models often overlook the broader structural topology that spans domains and fail to align training objectives, potentially leading to negative transfer. To address these issues, we propose a motif-based prompt learning framework, MOP, which introduces motif-based shared embeddings to encapsulate generalized domain knowledge, catering to both intra-domain and inter-domain CDR tasks. Specifically, we devise three typical motifs: butterfly, triangle, and random walk, and encode them through a Motif-based Encoder to obtain motif-based shared embeddings. Moreover, we train MOP under the "Pre-training \& Prompt Tuning" paradigm. By unifying pre-training and recommendation tasks as a common motif-based similarity learning task and integrating adaptable prompt parameters to guide the model in downstream recommendation tasks, MOP excels in transferring domain knowledge effectively. Experimental results on four distinct CDR tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of MOP than the state-of-the-art models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge