Jiaoyang Li
Analyzing Planner Design Trade-offs for MAPF under Realistic Simulation
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) algorithms are increasingly deployed in industrial warehouses and automated manufacturing facilities, where robots must operate reliably under real-world physical constraints. However, existing MAPF evaluation frameworks typically rely on simplified robot models, leaving a substantial gap between algorithmic benchmarks and practical performance. Recent frameworks such as SMART, incorporate kinodynamic modeling and offer the MAPF community a platform for large-scale, realistic evaluation. Building on this capability, this work investigates how key planner design choices influence performance under realistic execution settings. We systematically study three fundamental factors: (1) the relationship between solution optimality and execution performance, (2) the sensitivity of system performance to inaccuracies in kinodynamic modeling, and (3) the interaction between model accuracy and plan optimality. Empirically, we examine these factors to understand how these design choices affect performance in realistic scenarios. We highlight open challenges and research directions to steer the community toward practical, real-world deployment.
Collaborative Multi-Robot Non-Prehensile Manipulation via Flow-Matching Co-Generation
Nov 14, 2025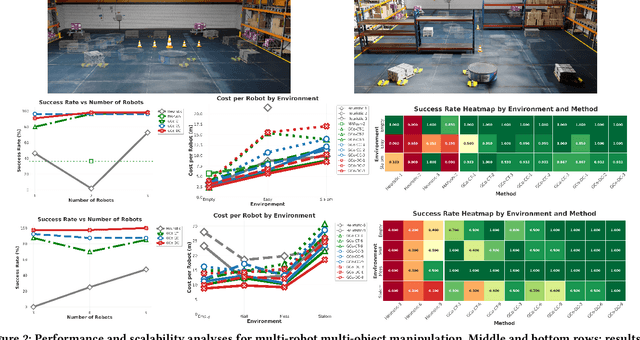
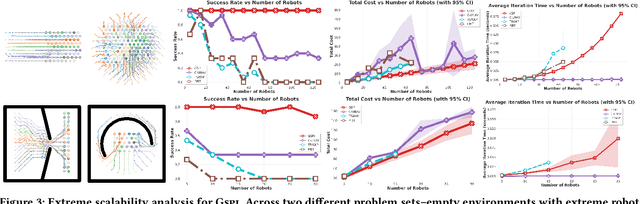

Abstract:Coordinating a team of robots to reposition multiple objects in cluttered environments requires reasoning jointly about where robots should establish contact, how to manipulate objects once contact is made, and how to navigate safely and efficiently at scale. Prior approaches typically fall into two extremes -- either learning the entire task or relying on privileged information and hand-designed planners -- both of which struggle to handle diverse objects in long-horizon tasks. To address these challenges, we present a unified framework for collaborative multi-robot, multi-object non-prehensile manipulation that integrates flow-matching co-generation with anonymous multi-robot motion planning. Within this framework, a generative model co-generates contact formations and manipulation trajectories from visual observations, while a novel motion planner conveys robots at scale. Crucially, the same planner also supports coordination at the object level, assigning manipulated objects to larger target structures and thereby unifying robot- and object-level reasoning within a single algorithmic framework. Experiments in challenging simulated environments demonstrate that our approach outperforms baselines in both motion planning and manipulation tasks, highlighting the benefits of generative co-design and integrated planning for scaling collaborative manipulation to complex multi-agent, multi-object settings. Visit gco-paper.github.io for code and demonstrations.
SUBQRAG: sub-question driven dynamic graph rag
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Graph RAG) effectively builds a knowledge graph (KG) to connect disparate facts across a large document corpus. However, this broad-view approach often lacks the deep structured reasoning needed for complex multi-hop question answering (QA), leading to incomplete evidence and error accumulation. To address these limitations, we propose SubQRAG, a sub-question-driven framework that enhances reasoning depth. SubQRAG decomposes a complex question into an ordered chain of verifiable sub-questions. For each sub-question, it retrieves relevant triples from the graph. When the existing graph is insufficient, the system dynamically expands it by extracting new triples from source documents in real time. All triples used in the reasoning process are aggregated into a "graph memory," forming a structured and traceable evidence path for final answer generation. Experiments on three multi-hop QA benchmarks demonstrate that SubQRAG achieves consistent and significant improvements, especially in Exact Match scores.
Prompt-to-Product: Generative Assembly via Bimanual Manipulation
Aug 28, 2025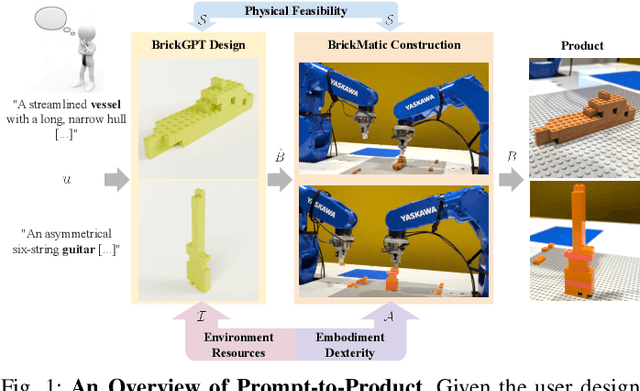
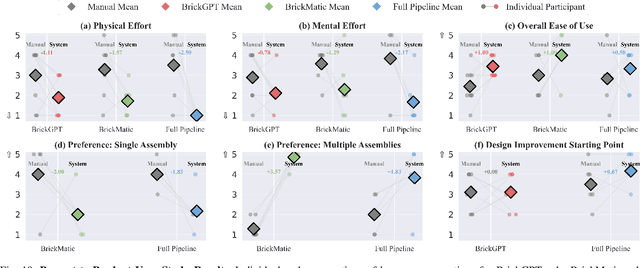
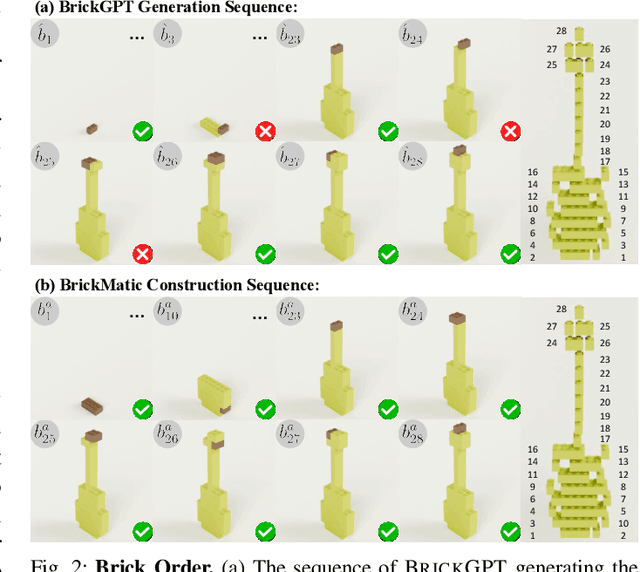
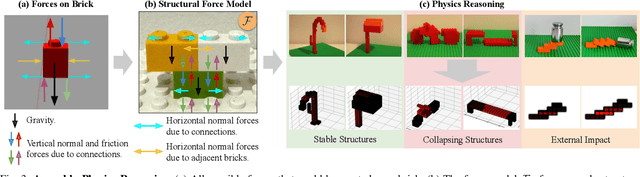
Abstract:Creating assembly products demands significant manual effort and expert knowledge in 1) designing the assembly and 2) constructing the product. This paper introduces Prompt-to-Product, an automated pipeline that generates real-world assembly products from natural language prompts. Specifically, we leverage LEGO bricks as the assembly platform and automate the process of creating brick assembly structures. Given the user design requirements, Prompt-to-Product generates physically buildable brick designs, and then leverages a bimanual robotic system to construct the real assembly products, bringing user imaginations into the real world. We conduct a comprehensive user study, and the results demonstrate that Prompt-to-Product significantly lowers the barrier and reduces manual effort in creating assembly products from imaginative ideas.
Benchmarking Shortcutting Techniques for Multi-Robot-Arm Motion Planning
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Generating high-quality motion plans for multiple robot arms is challenging due to the high dimensionality of the system and the potential for inter-arm collisions. Traditional motion planning methods often produce motions that are suboptimal in terms of smoothness and execution time for multi-arm systems. Post-processing via shortcutting is a common approach to improve motion quality for efficient and smooth execution. However, in multi-arm scenarios, optimizing one arm's motion must not introduce collisions with other arms. Although existing multi-arm planning works often use some form of shortcutting techniques, their exact methodology and impact on performance are often vaguely described. In this work, we present a comprehensive study quantitatively comparing existing shortcutting methods for multi-arm trajectories across diverse simulated scenarios. We carefully analyze the pros and cons of each shortcutting method and propose two simple strategies for combining these methods to achieve the best performance-runtime tradeoff. Video, code, and dataset are available at https://philip-huang.github.io/mr-shortcut/.
BTPG-max: Achieving Local Maximal Bidirectional Pairs for Bidirectional Temporal Plan Graphs
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) requires computing collision-free paths for multiple agents in shared environment. Most MAPF planners assume that each agent reaches a specific location at a specific timestep, but this is infeasible to directly follow on real systems where delays often occur. To address collisions caused by agents deviating due to delays, the Temporal Plan Graph (TPG) was proposed, which converts a MAPF time dependent solution into a time independent set of inter-agent dependencies. Recently, a Bidirectional TPG (BTPG) was proposed which relaxed some dependencies into ``bidirectional pairs" and improved efficiency of agents executing their MAPF solution with delays. Our work improves upon this prior work by designing an algorithm, BPTG-max, that finds more bidirectional pairs. Our main theoretical contribution is in designing the BTPG-max algorithm is locally optimal, i.e. which constructs a BTPG where no additional bidirectional pairs can be added. We also show how in practice BTPG-max leads to BTPGs with significantly more bidirectional edges, superior anytime behavior, and improves robustness to delays.
New Mechanisms in Flex Distribution for Bounded Suboptimal Multi-Agent Path Finding
Jul 22, 2025



Abstract:Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) is the problem of finding a set of collision-free paths, one for each agent in a shared environment. Its objective is to minimize the sum of path costs (SOC), where the path cost of each agent is defined as the travel time from its start location to its target location. Explicit Estimation Conflict-Based Search (EECBS) is the leading algorithm for bounded-suboptimal MAPF, with the SOC of the solution being at most a user-specified factor $w$ away from optimal. EECBS maintains sets of paths and a lower bound $LB$ on the optimal SOC. Then, it iteratively selects a set of paths whose SOC is at most $w \cdot LB$ and introduces constraints to resolve collisions. For each path in a set, EECBS maintains a lower bound on its optimal path that satisfies constraints. By finding an individually bounded-suboptimal path with cost at most a threshold of $w$ times its lower bound, EECBS guarantees to find a bounded-suboptimal solution. To speed up EECBS, previous work uses flex distribution to increase the threshold. Though EECBS with flex distribution guarantees to find a bounded-suboptimal solution, increasing the thresholds may push the SOC beyond $w \cdot LB$, forcing EECBS to switch among different sets of paths instead of resolving collisions on a particular set of paths, and thus reducing efficiency. To address this issue, we propose Conflict-Based Flex Distribution that distributes flex in proportion to the number of collisions. We also estimate the delays needed to satisfy constraints and propose Delay-Based Flex Distribution. On top of that, we propose Mixed-Strategy Flex Distribution, combining both in a hierarchical framework. We prove that EECBS with our new flex distribution mechanisms is complete and bounded-suboptimal. Our experiments show that our approaches outperform the original (greedy) flex distribution.
Anytime Single-Step MAPF Planning with Anytime PIBT
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:PIBT is a popular Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) method at the core of many state-of-the-art MAPF methods including LaCAM, CS-PIBT, and WPPL. The main utility of PIBT is that it is a very fast and effective single-step MAPF solver and can return a collision-free single-step solution for hundreds of agents in less than a millisecond. However, the main drawback of PIBT is that it is extremely greedy in respect to its priorities and thus leads to poor solution quality. Additionally, PIBT cannot use all the planning time that might be available to it and returns the first solution it finds. We thus develop Anytime PIBT, which quickly finds a one-step solution identically to PIBT but then continuously improves the solution in an anytime manner. We prove that Anytime PIBT converges to the optimal solution given sufficient time. We experimentally validate that Anytime PIBT can rapidly improve single-step solution quality within milliseconds and even find the optimal single-step action. However, we interestingly find that improving the single-step solution quality does not have a significant effect on full-horizon solution costs.
Real-Time LaCAM
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:The vast majority of Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) methods with completeness guarantees require planning full horizon paths. However, planning full horizon paths can take too long and be impractical in real-world applications. Instead, real-time planning and execution, which only allows the planner a finite amount of time before executing and replanning, is more practical for real world multi-agent systems. Several methods utilize real-time planning schemes but none are provably complete, which leads to livelock or deadlock. Our main contribution is to show the first Real-Time MAPF method with provable completeness guarantees. We do this by leveraging LaCAM (Okumura 2023) in an incremental fashion. Our results show how we can iteratively plan for congested environments with a cutoff time of milliseconds while still maintaining the same success rate as full horizon LaCAM. We also show how it can be used with a single-step learned MAPF policy. The proposed Real-Time LaCAM also provides us with a general mechanism for using iterative constraints for completeness in future real-time MAPF algorithms.
APEX-MR: Multi-Robot Asynchronous Planning and Execution for Cooperative Assembly
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Compared to a single-robot workstation, a multi-robot system offers several advantages: 1) it expands the system's workspace, 2) improves task efficiency, and more importantly, 3) enables robots to achieve significantly more complex and dexterous tasks, such as cooperative assembly. However, coordinating the tasks and motions of multiple robots is challenging due to issues, e.g. system uncertainty, task efficiency, algorithm scalability, and safety concerns. To address these challenges, this paper studies multi-robot coordination and proposes APEX-MR, an asynchronous planning and execution framework designed to safely and efficiently coordinate multiple robots to achieve cooperative assembly, e.g. LEGO assembly. In particular, APEX-MR provides a systematic approach to post-process multi-robot tasks and motion plans to enable robust asynchronous execution under uncertainty. Experimental results demonstrate that APEX-MR can significantly speed up the execution time of many long-horizon LEGO assembly tasks by 48% compared to sequential planning and 36% compared to synchronous planning on average. To further demonstrate the performance, we deploy APEX-MR to a dual-arm system to perform physical LEGO assembly. To our knowledge, this is the first robotic system capable of performing customized LEGO assembly using commercial LEGO bricks. The experiment results demonstrate that the dual-arm system, with APEX-MR, can safely coordinate robot motions, efficiently collaborate, and construct complex LEGO structures. Our project website is available at https://intelligent-control-lab.github.io/APEX-MR/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge