Xiao Xiong
From Atoms to Chains: Divergence-Guided Reasoning Curriculum for Unlabeled LLM Domain Adaptation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) to specialized domains without human-annotated data is a crucial yet formidable challenge. Widely adopted knowledge distillation methods often devolve into coarse-grained mimicry, where the student model inefficiently targets its own weaknesses and risks inheriting the teacher's reasoning flaws. This exposes a critical pedagogical dilemma: how to devise a reliable curriculum when the teacher itself is not an infallible expert. Our work resolves this by capitalizing on a key insight: while LLMs may exhibit fallibility in complex, holistic reasoning, they often exhibit high fidelity on focused, atomic sub-problems. Based on this, we propose Divergence-Guided Reasoning Curriculum (DGRC), which constructs a learning path from atomic knowledge to reasoning chains by dynamically deriving two complementary curricula from disagreements in reasoning pathways. When a student and teacher produce conflicting results, DGRC directs the teacher to perform a diagnostic analysis: it analyzes both reasoning paths to formulate atomic queries that target the specific points of divergence, and then self-answers these queries to create high-confidence atomic question-answer pairs. These pairs then serve a dual purpose: (1) providing an atomic curriculum to rectify the student's knowledge gaps, and (2) serving as factual criteria to filter the teacher's original reasoning chains, yielding a verified CoT curriculum that teaches the student how to integrate atomic knowledge into complete reasoning paths. Experiments across the medical and legal domains on student models of various sizes demonstrate the effectiveness of our DGRC framework. Notably, our method achieves a 7.76% relative improvement for the 1.5B student model in the medical domain over strong unlabeled baseline.
RAILGUN: A Unified Convolutional Policy for Multi-Agent Path Finding Across Different Environments and Tasks
Mar 04, 2025



Abstract:Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF), which focuses on finding collision-free paths for multiple robots, is crucial for applications ranging from aerial swarms to warehouse automation. Solving MAPF is NP-hard so learning-based approaches for MAPF have gained attention, particularly those leveraging deep neural networks. Nonetheless, despite the community's continued efforts, all learning-based MAPF planners still rely on decentralized planning due to variability in the number of agents and map sizes. We have developed the first centralized learning-based policy for MAPF problem called RAILGUN. RAILGUN is not an agent-based policy but a map-based policy. By leveraging a CNN-based architecture, RAILGUN can generalize across different maps and handle any number of agents. We collect trajectories from rule-based methods to train our model in a supervised way. In experiments, RAILGUN outperforms most baseline methods and demonstrates great zero-shot generalization capabilities on various tasks, maps and agent numbers that were not seen in the training dataset.
AdvSwap: Covert Adversarial Perturbation with High Frequency Info-swapping for Autonomous Driving Perception
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Perception module of Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are increasingly susceptible to be attacked, which exploit vulnerabilities in neural networks through adversarial inputs, thereby compromising the AI safety. Some researches focus on creating covert adversarial samples, but existing global noise techniques are detectable and difficult to deceive the human visual system. This paper introduces a novel adversarial attack method, AdvSwap, which creatively utilizes wavelet-based high-frequency information swapping to generate covert adversarial samples and fool the camera. AdvSwap employs invertible neural network for selective high-frequency information swapping, preserving both forward propagation and data integrity. The scheme effectively removes the original label data and incorporates the guidance image data, producing concealed and robust adversarial samples. Experimental evaluations and comparisons on the GTSRB and nuScenes datasets demonstrate that AdvSwap can make concealed attacks on common traffic targets. The generates adversarial samples are also difficult to perceive by humans and algorithms. Meanwhile, the method has strong attacking robustness and attacking transferability.
Bionic Collapsible Wings in Aquatic-aerial Robot
Apr 09, 2023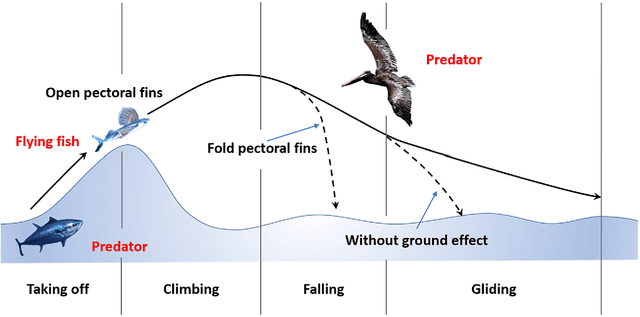
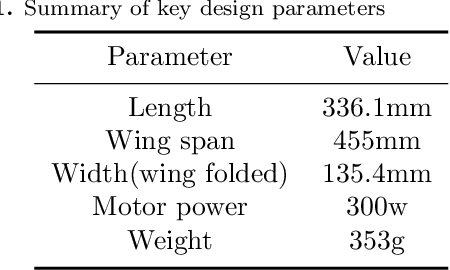
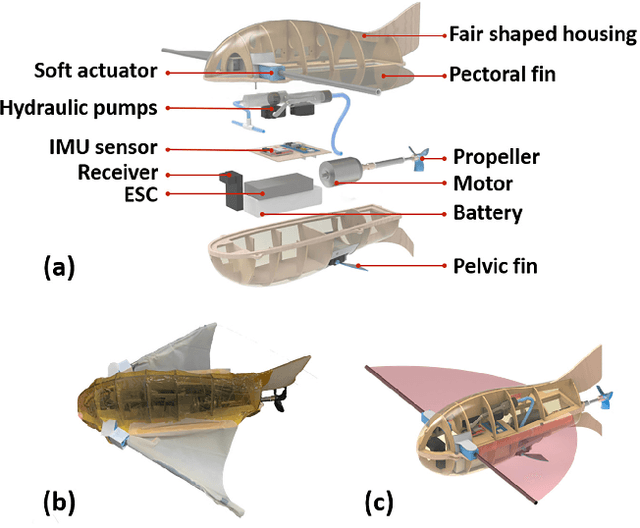
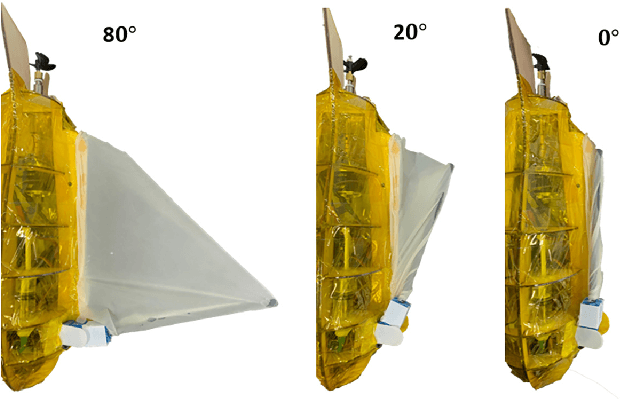
Abstract:The concept of aerial-aquatic robots has emerged as an innovative solution that can operate both in the air and underwater. Previous research on the design of such robots has been mainly focused on mature technologies such as fixed-wing and multi-rotor aircraft. Flying fish, a unique aerial-aquatic animal that can both swim in water and glide over the sea surface, has not been fully explored as a bionic robot model, especially regarding its motion patterns with the collapsible pectoral fins. To verify the contribution of the collapsible wings to the flying fish motion pattern, we have designed a novel bio-robot with collapsible wings inspired by the flying fish. The bionic prototype has been successfully designed and fabricated, incorporating collapsible wings with soft hydraulic actuators, an innovative application of soft actuators to a micro aquatic-aerial robot. We have analyzed and built a precise model of dynamics for control, and tested both the soft hydraulic actuators and detailed aerodynamic coefficients. To further verify the feasibility of collapsible wings, we conducted simulations in different situations such as discharge angles, the area of collapsible wings, and the advantages of using ground effect. The results confirm the control of the collapsible wings and demonstrate the unique multi-modal motion pattern between water and air. Overall, our research represents the study of the collapsible wings in aquatic-aerial robots and significant contributes to the development of aquatic-aerial robots. The using of the collapsible wings must a contribution to the future aquatic-aerial robot.
A Bayesian Robust Regression Method for Corrupted Data Reconstruction
Jan 08, 2023



Abstract:Because of the widespread existence of noise and data corruption, recovering the true regression parameters with a certain proportion of corrupted response variables is an essential task. Methods to overcome this problem often involve robust least-squares regression, but few methods perform well when confronted with severe adaptive adversarial attacks. In many applications, prior knowledge is often available from historical data or engineering experience, and by incorporating prior information into a robust regression method, we develop an effective robust regression method that can resist adaptive adversarial attacks. First, we propose the novel TRIP (hard Thresholding approach to Robust regression with sImple Prior) algorithm, which improves the breakdown point when facing adaptive adversarial attacks. Then, to improve the robustness and reduce the estimation error caused by the inclusion of priors, we use the idea of Bayesian reweighting to construct the more robust BRHT (robust Bayesian Reweighting regression via Hard Thresholding) algorithm. We prove the theoretical convergence of the proposed algorithms under mild conditions, and extensive experiments show that under different types of dataset attacks, our algorithms outperform other benchmark ones. Finally, we apply our methods to a data-recovery problem in a real-world application involving a space solar array, demonstrating their good applicability.
New Designed Loss Functions to Solve Ordinary Differential Equations with Artificial Neural Network
Dec 29, 2022Abstract:This paper investigates the use of artificial neural networks (ANNs) to solve differential equations (DEs) and the construction of the loss function which meets both differential equation and its initial/boundary condition of a certain DE. In section 2, the loss function is generalized to $n^\text{th}$ order ordinary differential equation(ODE). Other methods of construction are examined in Section 3 and applied to three different models to assess their effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge