Belen Alastruey
Large Concept Models: Language Modeling in a Sentence Representation Space
Dec 11, 2024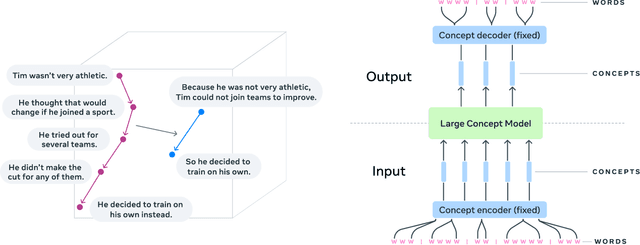
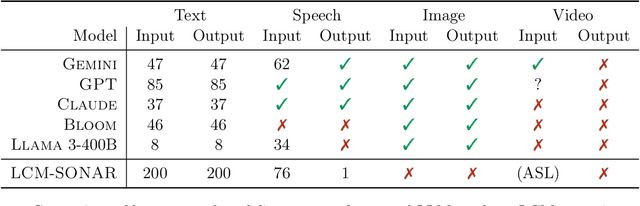
Abstract:LLMs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence and have emerged as the de-facto tool for many tasks. The current established technology of LLMs is to process input and generate output at the token level. This is in sharp contrast to humans who operate at multiple levels of abstraction, well beyond single words, to analyze information and to generate creative content. In this paper, we present an attempt at an architecture which operates on an explicit higher-level semantic representation, which we name a concept. Concepts are language- and modality-agnostic and represent a higher level idea or action in a flow. Hence, we build a "Large Concept Model". In this study, as proof of feasibility, we assume that a concept corresponds to a sentence, and use an existing sentence embedding space, SONAR, which supports up to 200 languages in both text and speech modalities. The Large Concept Model is trained to perform autoregressive sentence prediction in an embedding space. We explore multiple approaches, namely MSE regression, variants of diffusion-based generation, and models operating in a quantized SONAR space. These explorations are performed using 1.6B parameter models and training data in the order of 1.3T tokens. We then scale one architecture to a model size of 7B parameters and training data of about 2.7T tokens. We perform an experimental evaluation on several generative tasks, namely summarization and a new task of summary expansion. Finally, we show that our model exhibits impressive zero-shot generalization performance to many languages, outperforming existing LLMs of the same size. The training code of our models is freely available.
2M-BELEBELE: Highly Multilingual Speech and American Sign Language Comprehension Dataset
Dec 11, 2024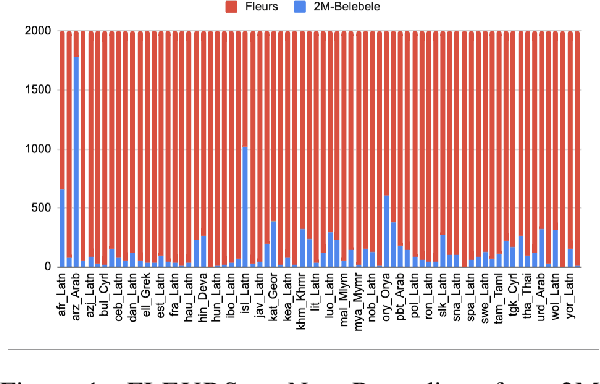
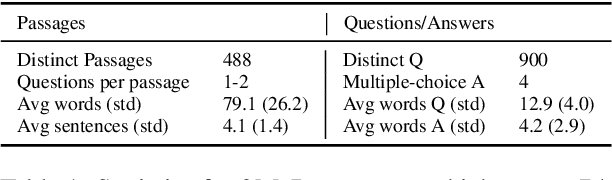
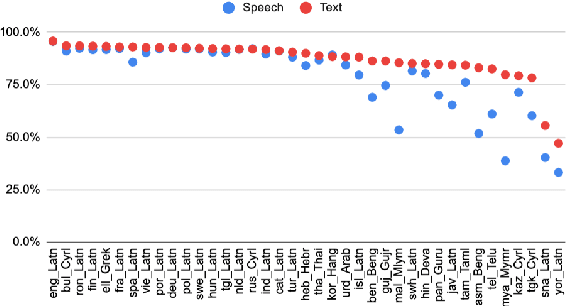
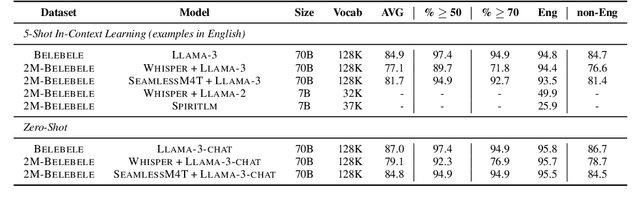
Abstract:We introduce the first highly multilingual speech and American Sign Language (ASL) comprehension dataset by extending BELEBELE. Our dataset covers 74 spoken languages at the intersection of BELEBELE and FLEURS, and one sign language (ASL). We evaluate 2M-BELEBELE dataset for both 5-shot and zero-shot settings and across languages, the speech comprehension accuracy is ~ 8% average lower compared to reading comprehension.
Unveiling the Role of Pretraining in Direct Speech Translation
Sep 26, 2024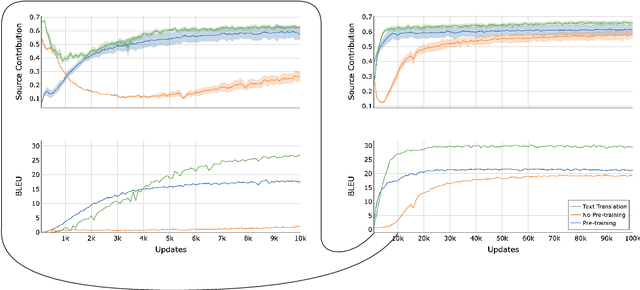
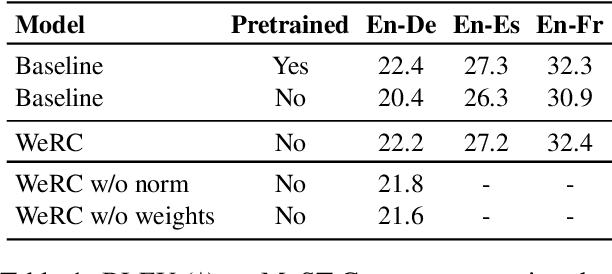
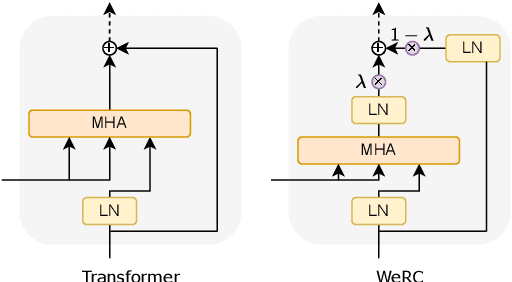
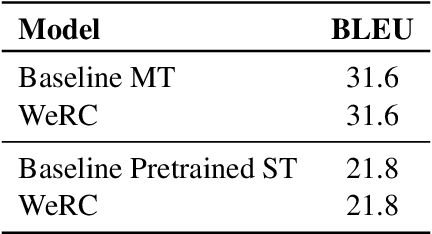
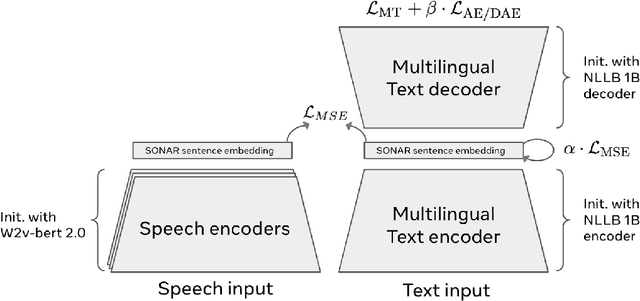
Abstract:Direct speech-to-text translation systems encounter an important drawback in data scarcity. A common solution consists on pretraining the encoder on automatic speech recognition, hence losing efficiency in the training process. In this study, we compare the training dynamics of a system using a pretrained encoder, the conventional approach, and one trained from scratch. We observe that, throughout the training, the randomly initialized model struggles to incorporate information from the speech inputs for its predictions. Hence, we hypothesize that this issue stems from the difficulty of effectively training an encoder for direct speech translation. While a model trained from scratch needs to learn acoustic and semantic modeling simultaneously, a pretrained one can just focus on the latter. Based on these findings, we propose a subtle change in the decoder cross-attention to integrate source information from earlier steps in training. We show that with this change, the model trained from scratch can achieve comparable performance to the pretrained one, while reducing the training time.
Linguini: A benchmark for language-agnostic linguistic reasoning
Sep 18, 2024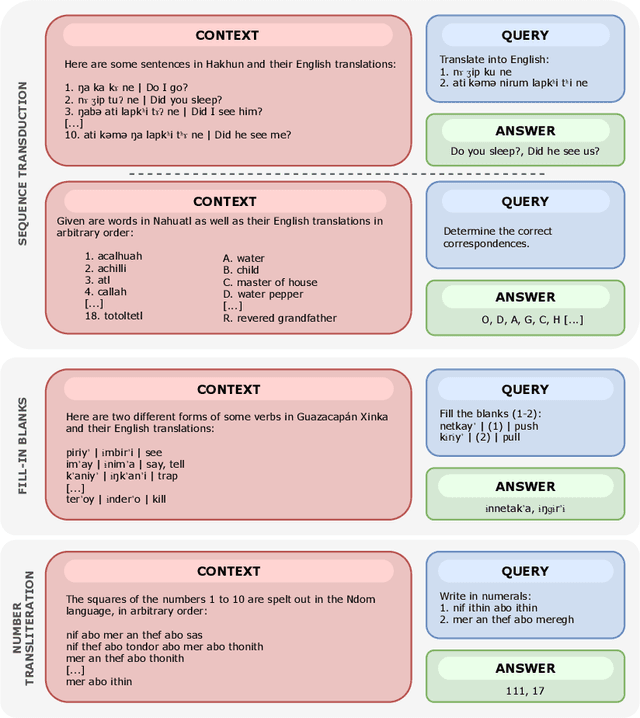
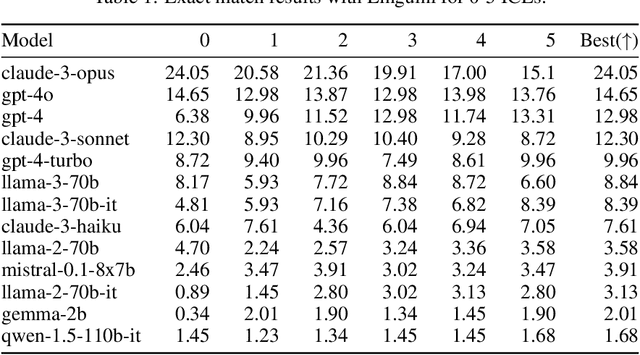

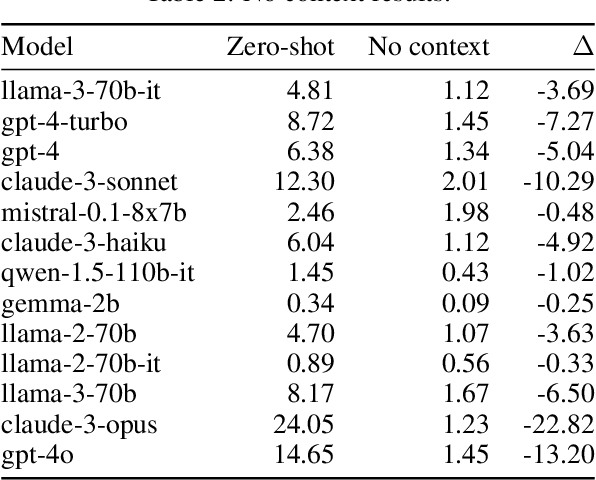
Abstract:We propose a new benchmark to measure a language model's linguistic reasoning skills without relying on pre-existing language-specific knowledge. The test covers 894 questions grouped in 160 problems across 75 (mostly) extremely low-resource languages, extracted from the International Linguistic Olympiad corpus. To attain high accuracy on this benchmark, models don't need previous knowledge of the tested language, as all the information needed to solve the linguistic puzzle is presented in the context. We find that, while all analyzed models rank below 25% accuracy, there is a significant gap between open and closed models, with the best-performing proprietary model at 24.05% and the best-performing open model at 8.84%.
Towards Real-World Streaming Speech Translation for Code-Switched Speech
Oct 23, 2023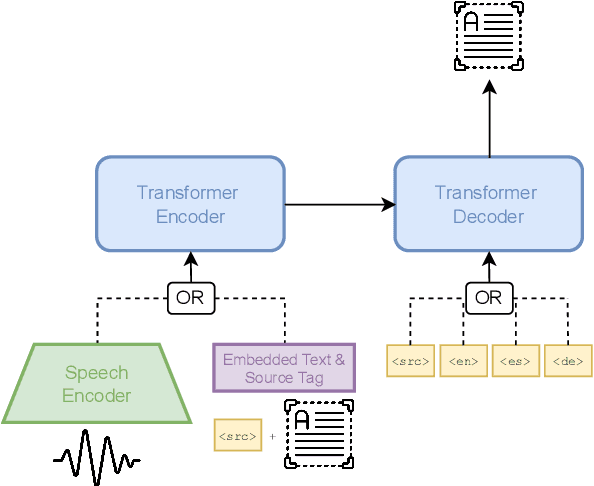
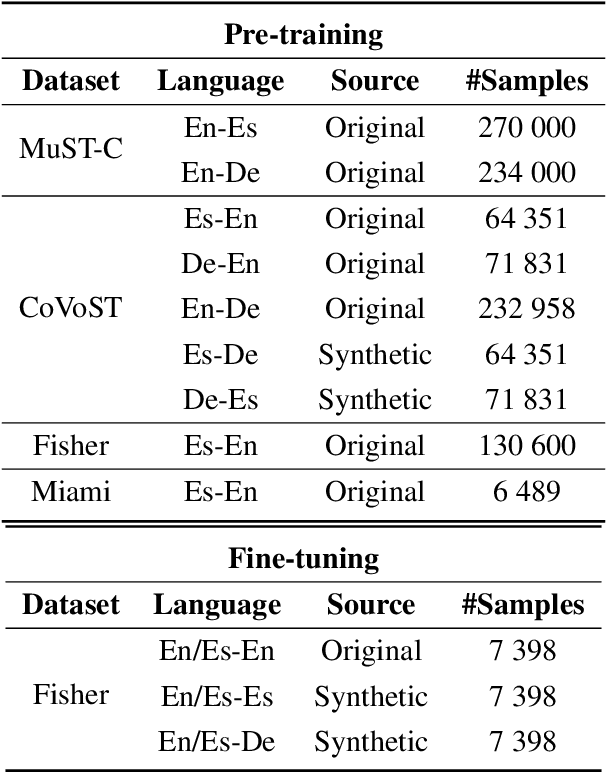
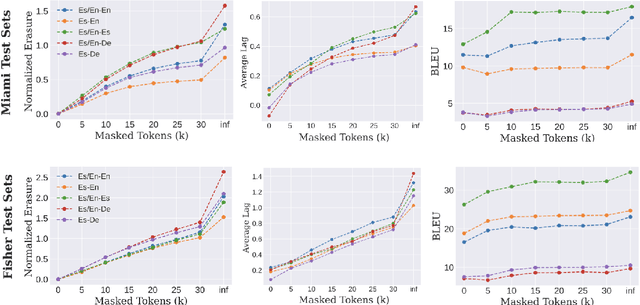
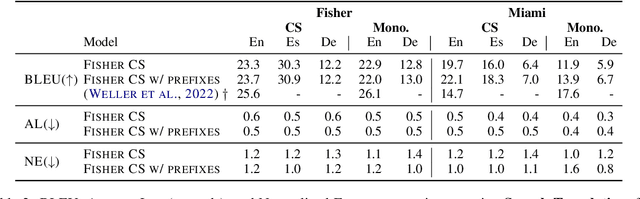
Abstract:Code-switching (CS), i.e. mixing different languages in a single sentence, is a common phenomenon in communication and can be challenging in many Natural Language Processing (NLP) settings. Previous studies on CS speech have shown promising results for end-to-end speech translation (ST), but have been limited to offline scenarios and to translation to one of the languages present in the source (\textit{monolingual transcription}). In this paper, we focus on two essential yet unexplored areas for real-world CS speech translation: streaming settings, and translation to a third language (i.e., a language not included in the source). To this end, we extend the Fisher and Miami test and validation datasets to include new targets in Spanish and German. Using this data, we train a model for both offline and streaming ST and we establish baseline results for the two settings mentioned earlier.
SpeechAlign: a Framework for Speech Translation Alignment Evaluation
Sep 20, 2023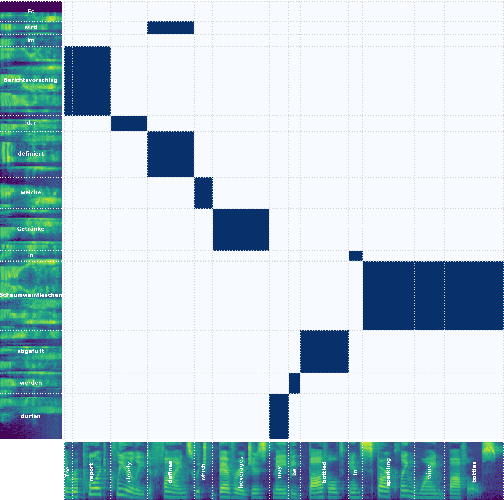

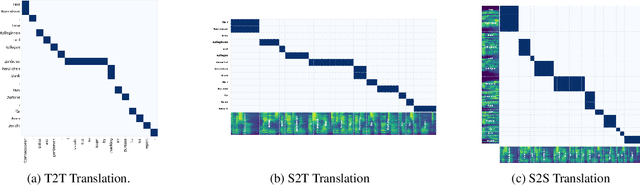
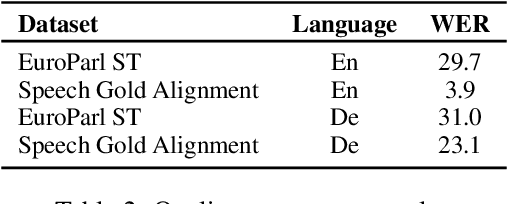
Abstract:Speech-to-Speech and Speech-to-Text translation are currently dynamic areas of research. To contribute to these fields, we present SpeechAlign, a framework to evaluate the underexplored field of source-target alignment in speech models. Our framework has two core components. First, to tackle the absence of suitable evaluation datasets, we introduce the Speech Gold Alignment dataset, built upon a English-German text translation gold alignment dataset. Secondly, we introduce two novel metrics, Speech Alignment Error Rate (SAER) and Time-weighted Speech Alignment Error Rate (TW-SAER), to evaluate alignment quality in speech models. By publishing SpeechAlign we provide an accessible evaluation framework for model assessment, and we employ it to benchmark open-source Speech Translation models.
The Gender-GAP Pipeline: A Gender-Aware Polyglot Pipeline for Gender Characterisation in 55 Languages
Aug 31, 2023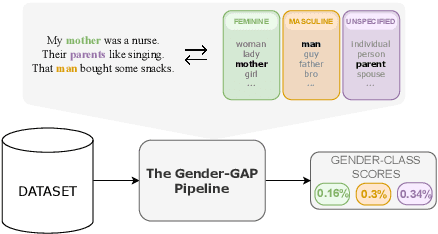
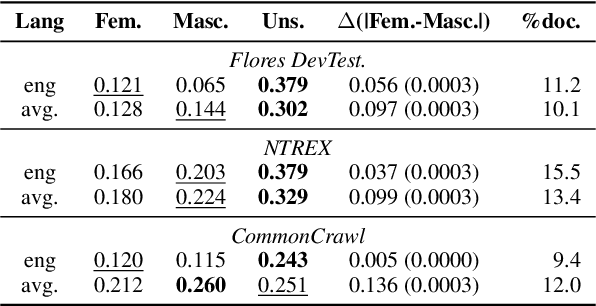
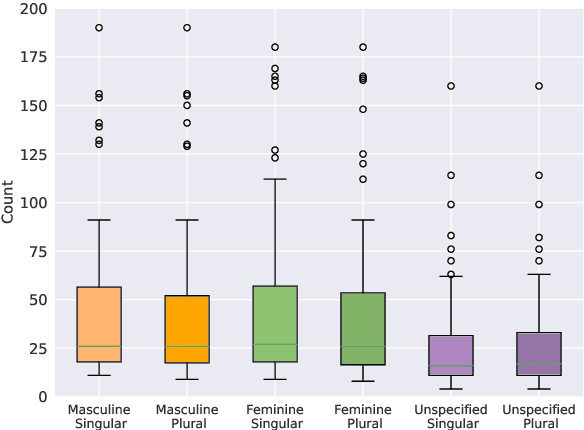
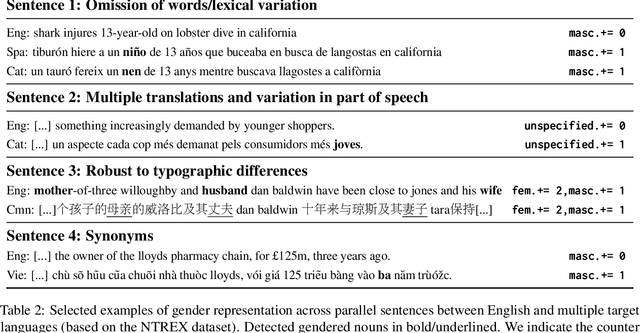
Abstract:Gender biases in language generation systems are challenging to mitigate. One possible source for these biases is gender representation disparities in the training and evaluation data. Despite recent progress in documenting this problem and many attempts at mitigating it, we still lack shared methodology and tooling to report gender representation in large datasets. Such quantitative reporting will enable further mitigation, e.g., via data augmentation. This paper describes the Gender-GAP Pipeline (for Gender-Aware Polyglot Pipeline), an automatic pipeline to characterize gender representation in large-scale datasets for 55 languages. The pipeline uses a multilingual lexicon of gendered person-nouns to quantify the gender representation in text. We showcase it to report gender representation in WMT training data and development data for the News task, confirming that current data is skewed towards masculine representation. Having unbalanced datasets may indirectly optimize our systems towards outperforming one gender over the others. We suggest introducing our gender quantification pipeline in current datasets and, ideally, modifying them toward a balanced representation.
Multi-View Frequency-Attention Alternative to CNN Frontends for Automatic Speech Recognition
Jun 12, 2023


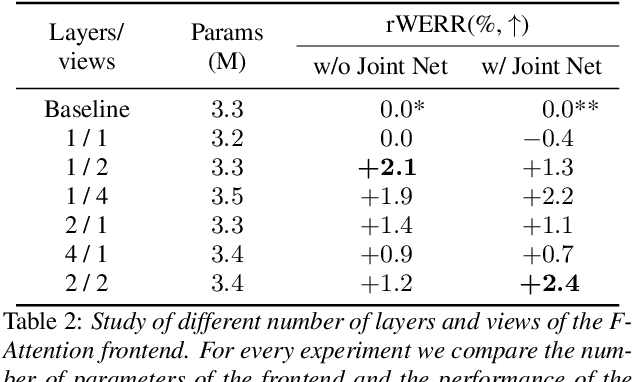
Abstract:Convolutional frontends are a typical choice for Transformer-based automatic speech recognition to preprocess the spectrogram, reduce its sequence length, and combine local information in time and frequency similarly. However, the width and height of an audio spectrogram denote different information, e.g., due to reverberation as well as the articulatory system, the time axis has a clear left-to-right dependency. On the contrary, vowels and consonants demonstrate very different patterns and occupy almost disjoint frequency ranges. Therefore, we hypothesize, global attention over frequencies is beneficial over local convolution. We obtain 2.4 % relative word error rate reduction (rWERR) on a production scale Conformer transducer replacing its convolutional neural network frontend by the proposed F-Attention module on Alexa traffic. To demonstrate generalizability, we validate this on public LibriSpeech data with a long short term memory-based listen attend and spell architecture obtaining 4.6 % rWERR and demonstrate robustness to (simulated) noisy conditions.
Towards Opening the Black Box of Neural Machine Translation: Source and Target Interpretations of the Transformer
May 23, 2022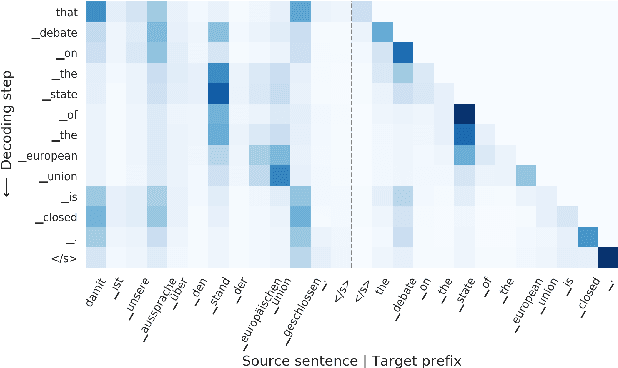
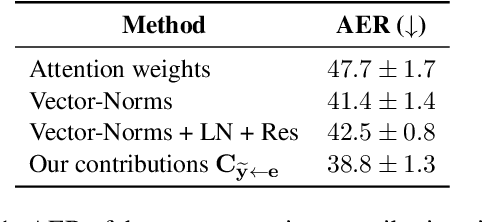
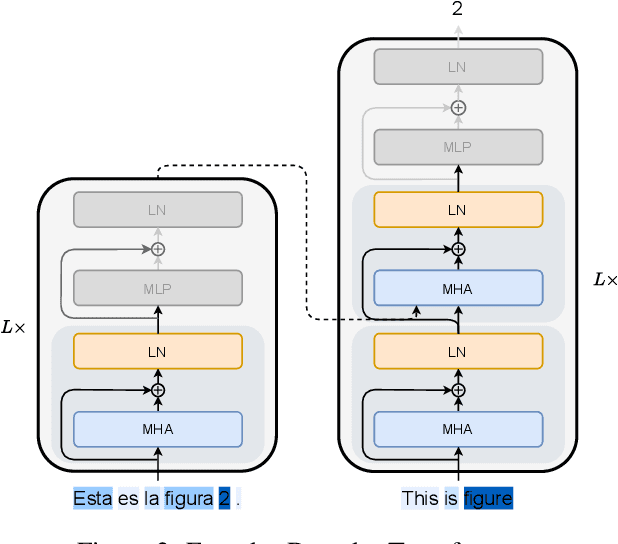
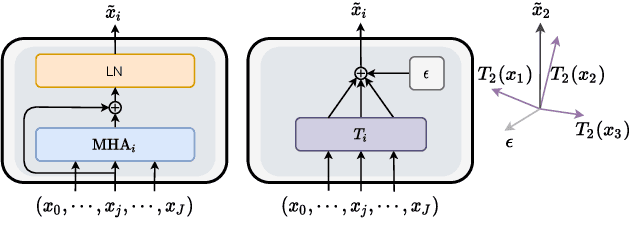
Abstract:In Neural Machine Translation (NMT), each token prediction is conditioned on the source sentence and the target prefix (what has been previously translated at a decoding step). However, previous work on interpretability in NMT has focused solely on source sentence tokens attributions. Therefore, we lack a full understanding of the influences of every input token (source sentence and target prefix) in the model predictions. In this work, we propose an interpretability method that tracks complete input token attributions. Our method, which can be extended to any encoder-decoder Transformer-based model, allows us to better comprehend the inner workings of current NMT models. We apply the proposed method to both bilingual and multilingual Transformers and present insights into their behaviour.
Multiformer: A Head-Configurable Transformer-Based Model for Direct Speech Translation
May 14, 2022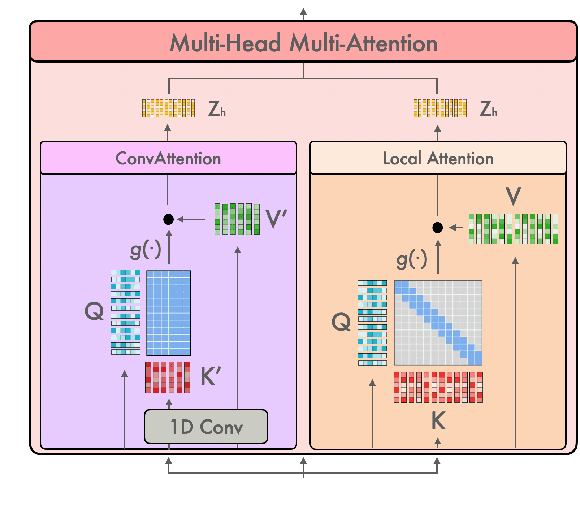
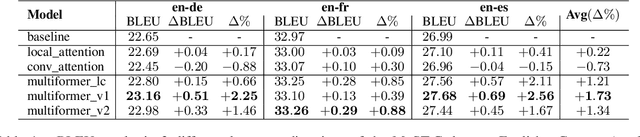
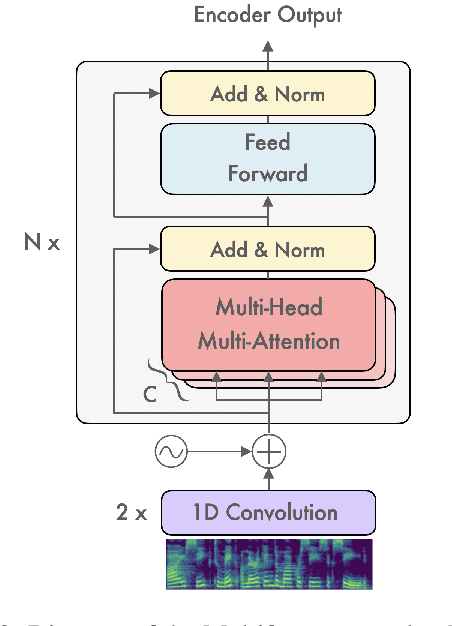
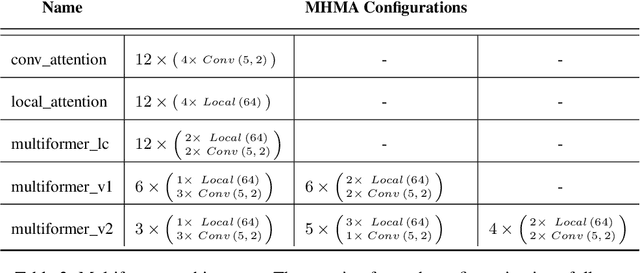
Abstract:Transformer-based models have been achieving state-of-the-art results in several fields of Natural Language Processing. However, its direct application to speech tasks is not trivial. The nature of this sequences carries problems such as long sequence lengths and redundancy between adjacent tokens. Therefore, we believe that regular self-attention mechanism might not be well suited for it. Different approaches have been proposed to overcome these problems, such as the use of efficient attention mechanisms. However, the use of these methods usually comes with a cost, which is a performance reduction caused by information loss. In this study, we present the Multiformer, a Transformer-based model which allows the use of different attention mechanisms on each head. By doing this, the model is able to bias the self-attention towards the extraction of more diverse token interactions, and the information loss is reduced. Finally, we perform an analysis of the head contributions, and we observe that those architectures where all heads relevance is uniformly distributed obtain better results. Our results show that mixing attention patterns along the different heads and layers outperforms our baseline by up to 0.7 BLEU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge