Dominic Telaar
Towards Real-World Streaming Speech Translation for Code-Switched Speech
Oct 23, 2023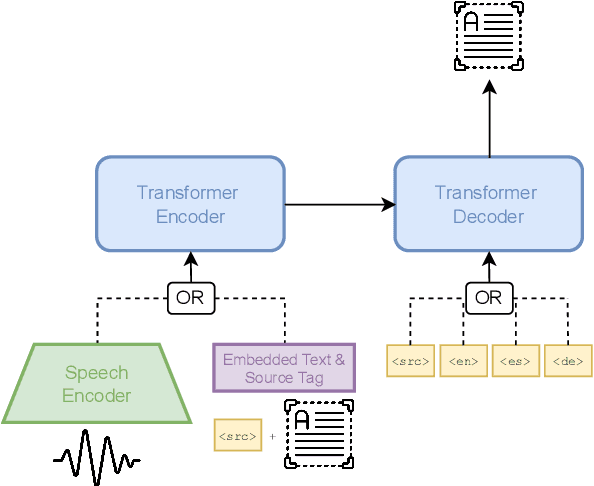
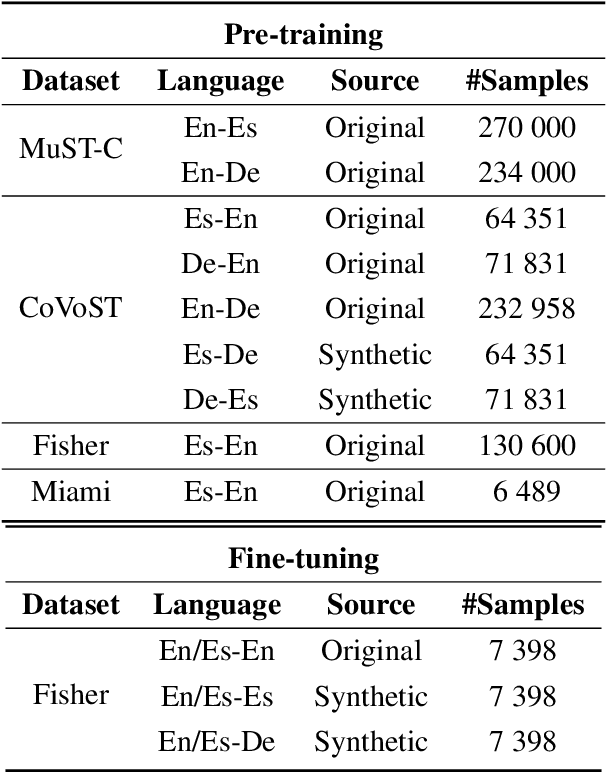
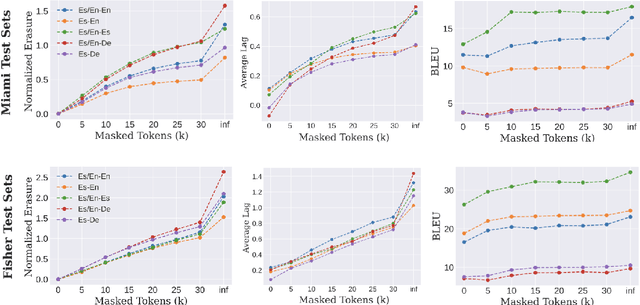
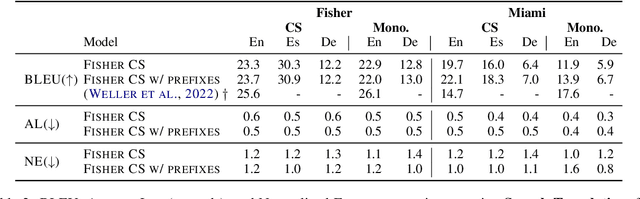
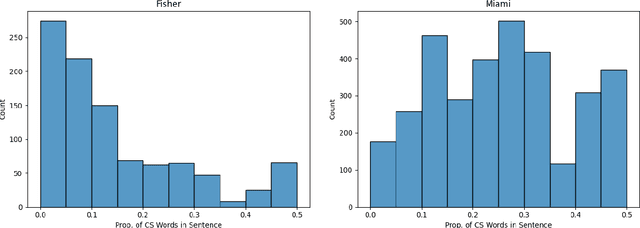
Abstract:Code-switching (CS), i.e. mixing different languages in a single sentence, is a common phenomenon in communication and can be challenging in many Natural Language Processing (NLP) settings. Previous studies on CS speech have shown promising results for end-to-end speech translation (ST), but have been limited to offline scenarios and to translation to one of the languages present in the source (\textit{monolingual transcription}). In this paper, we focus on two essential yet unexplored areas for real-world CS speech translation: streaming settings, and translation to a third language (i.e., a language not included in the source). To this end, we extend the Fisher and Miami test and validation datasets to include new targets in Spanish and German. Using this data, we train a model for both offline and streaming ST and we establish baseline results for the two settings mentioned earlier.
Automating Behavioral Testing in Machine Translation
Sep 07, 2023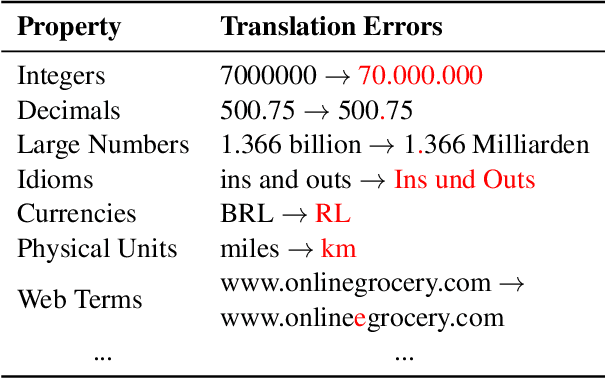
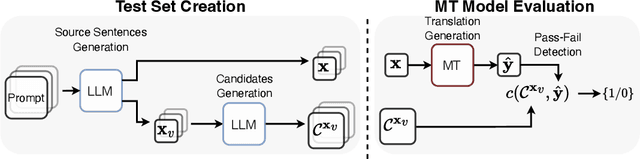

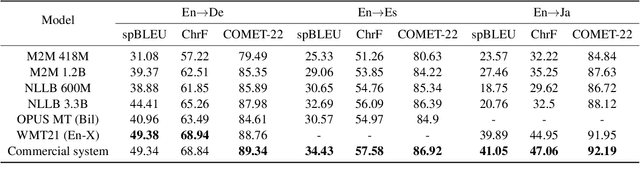
Abstract:Behavioral testing in NLP allows fine-grained evaluation of systems by examining their linguistic capabilities through the analysis of input-output behavior. Unfortunately, existing work on behavioral testing in Machine Translation (MT) is currently restricted to largely handcrafted tests covering a limited range of capabilities and languages. To address this limitation, we propose to use Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate a diverse set of source sentences tailored to test the behavior of MT models in a range of situations. We can then verify whether the MT model exhibits the expected behavior through matching candidate sets that are also generated using LLMs. Our approach aims to make behavioral testing of MT systems practical while requiring only minimal human effort. In our experiments, we apply our proposed evaluation framework to assess multiple available MT systems, revealing that while in general pass-rates follow the trends observable from traditional accuracy-based metrics, our method was able to uncover several important differences and potential bugs that go unnoticed when relying only on accuracy.
End-to-End Speech Translation for Code Switched Speech
Apr 11, 2022

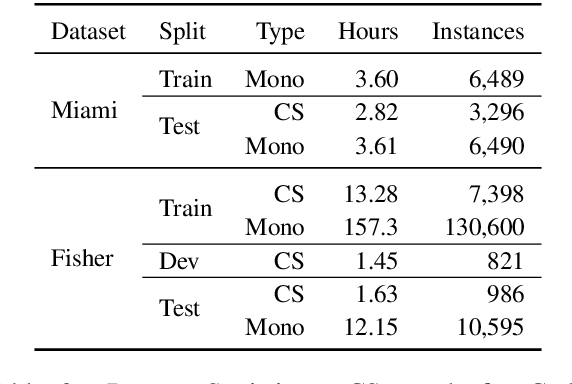
Abstract:Code switching (CS) refers to the phenomenon of interchangeably using words and phrases from different languages. CS can pose significant accuracy challenges to NLP, due to the often monolingual nature of the underlying systems. In this work, we focus on CS in the context of English/Spanish conversations for the task of speech translation (ST), generating and evaluating both transcript and translation. To evaluate model performance on this task, we create a novel ST corpus derived from existing public data sets. We explore various ST architectures across two dimensions: cascaded (transcribe then translate) vs end-to-end (jointly transcribe and translate) and unidirectional (source -> target) vs bidirectional (source <-> target). We show that our ST architectures, and especially our bidirectional end-to-end architecture, perform well on CS speech, even when no CS training data is used.
Federated Evaluation and Tuning for On-Device Personalization: System Design & Applications
Feb 16, 2021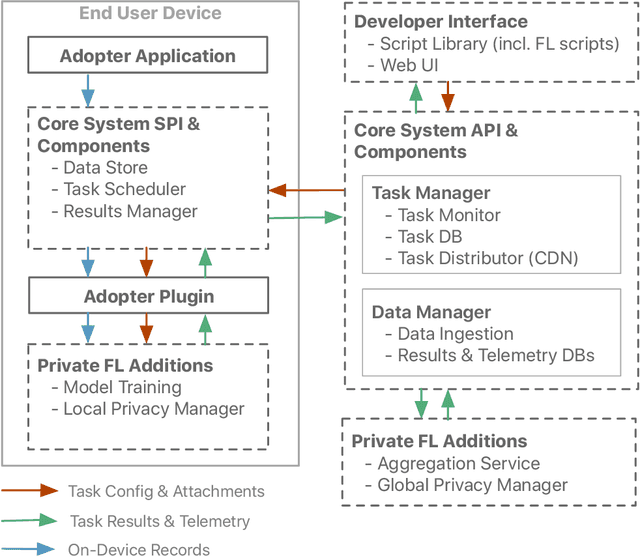
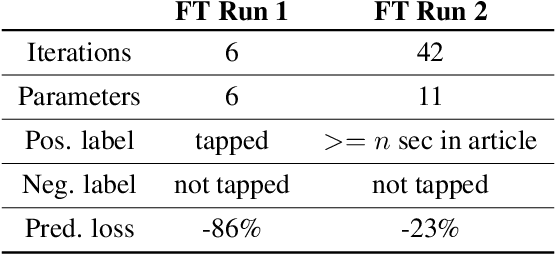

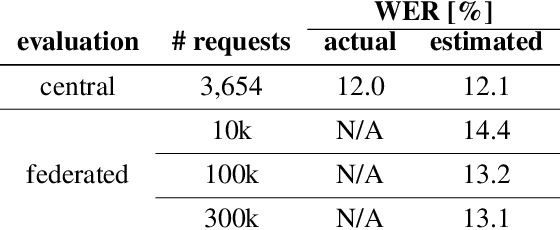
Abstract:We describe the design of our federated task processing system. Originally, the system was created to support two specific federated tasks: evaluation and tuning of on-device ML systems, primarily for the purpose of personalizing these systems. In recent years, support for an additional federated task has been added: federated learning (FL) of deep neural networks. To our knowledge, only one other system has been described in literature that supports FL at scale. We include comparisons to that system to help discuss design decisions and attached trade-offs. Finally, we describe two specific large scale personalization use cases in detail to showcase the applicability of federated tuning to on-device personalization and to highlight application specific solutions.
Syntactic and Semantic Features For Code-Switching Factored Language Models
Oct 04, 2017



Abstract:This paper presents our latest investigations on different features for factored language models for Code-Switching speech and their effect on automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance. We focus on syntactic and semantic features which can be extracted from Code-Switching text data and integrate them into factored language models. Different possible factors, such as words, part-of-speech tags, Brown word clusters, open class words and clusters of open class word embeddings are explored. The experimental results reveal that Brown word clusters, part-of-speech tags and open-class words are the most effective at reducing the perplexity of factored language models on the Mandarin-English Code-Switching corpus SEAME. In ASR experiments, the model containing Brown word clusters and part-of-speech tags and the model also including clusters of open class word embeddings yield the best mixed error rate results. In summary, the best language model can significantly reduce the perplexity on the SEAME evaluation set by up to 10.8% relative and the mixed error rate by up to 3.4% relative.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge