Matthias Sperber
Toward Machine Interpreting: Lessons from Human Interpreting Studies
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Current speech translation systems, while having achieved impressive accuracies, are rather static in their behavior and do not adapt to real-world situations in ways human interpreters do. In order to improve their practical usefulness and enable interpreting-like experiences, a precise understanding of the nature of human interpreting is crucial. To this end, we discuss human interpreting literature from the perspective of the machine translation field, while considering both operational and qualitative aspects. We identify implications for the development of speech translation systems and argue that there is great potential to adopt many human interpreting principles using recent modeling techniques. We hope that our findings provide inspiration for closing the perceived usability gap, and can motivate progress toward true machine interpreting.
Findings of the IWSLT 2024 Evaluation Campaign
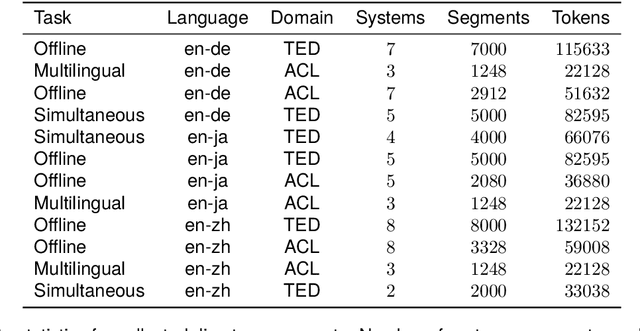
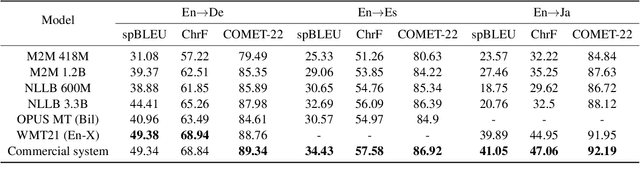
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:This paper reports on the shared tasks organized by the 21st IWSLT Conference. The shared tasks address 7 scientific challenges in spoken language translation: simultaneous and offline translation, automatic subtitling and dubbing, speech-to-speech translation, dialect and low-resource speech translation, and Indic languages. The shared tasks attracted 18 teams whose submissions are documented in 26 system papers. The growing interest towards spoken language translation is also witnessed by the constantly increasing number of shared task organizers and contributors to the overview paper, almost evenly distributed across industry and academia.
Speech is More Than Words: Do Speech-to-Text Translation Systems Leverage Prosody?
Oct 31, 2024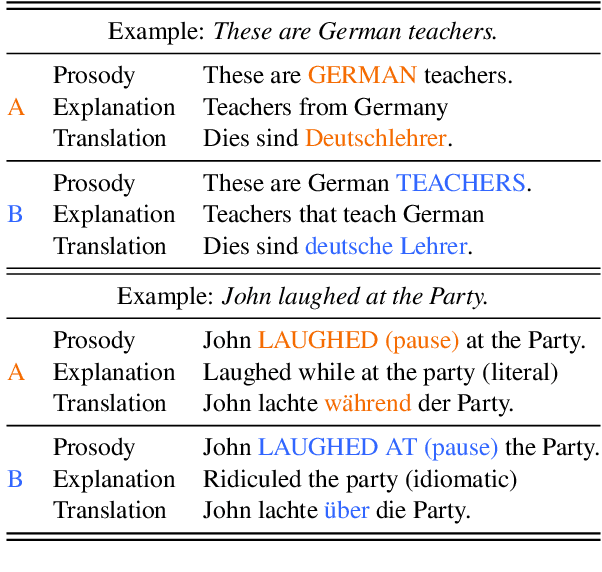
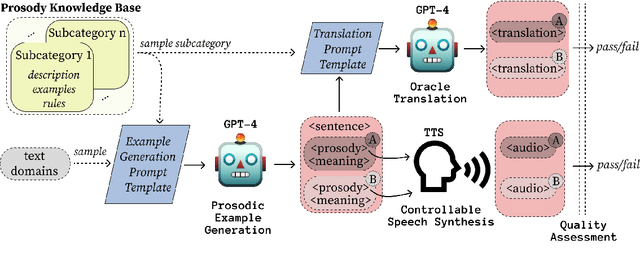
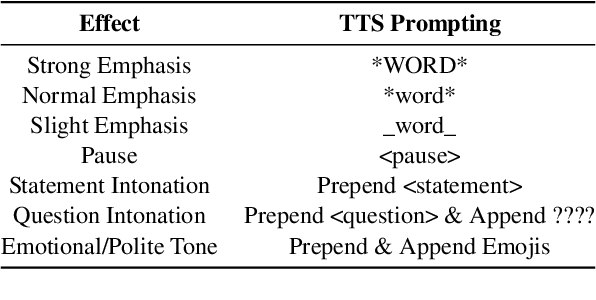
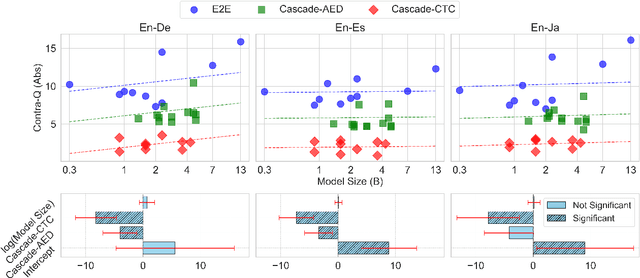
Abstract:The prosody of a spoken utterance, including features like stress, intonation and rhythm, can significantly affect the underlying semantics, and as a consequence can also affect its textual translation. Nevertheless, prosody is rarely studied within the context of speech-to-text translation (S2TT) systems. In particular, end-to-end (E2E) systems have been proposed as well-suited for prosody-aware translation because they have direct access to the speech signal when making translation decisions, but the understanding of whether this is successful in practice is still limited. A main challenge is the difficulty of evaluating prosody awareness in translation. To address this challenge, we introduce an evaluation methodology and a focused benchmark (named ContraProST) aimed at capturing a wide range of prosodic phenomena. Our methodology uses large language models and controllable text-to-speech (TTS) to generate contrastive examples. Through experiments in translating English speech into German, Spanish, and Japanese, we find that (a) S2TT models possess some internal representation of prosody, but the prosody signal is often not strong enough to affect the translations, (b) E2E systems outperform cascades of speech recognition and text translation systems, confirming their theoretical advantage in this regard, and (c) certain cascaded systems also capture prosodic information in the translation, but only to a lesser extent that depends on the particulars of the transcript's surface form.
Evaluating the IWSLT2023 Speech Translation Tasks: Human Annotations, Automatic Metrics, and Segmentation
Jun 06, 2024
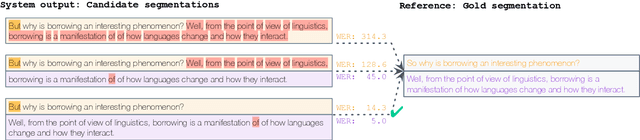

Abstract:Human evaluation is a critical component in machine translation system development and has received much attention in text translation research. However, little prior work exists on the topic of human evaluation for speech translation, which adds additional challenges such as noisy data and segmentation mismatches. We take first steps to fill this gap by conducting a comprehensive human evaluation of the results of several shared tasks from the last International Workshop on Spoken Language Translation (IWSLT 2023). We propose an effective evaluation strategy based on automatic resegmentation and direct assessment with segment context. Our analysis revealed that: 1) the proposed evaluation strategy is robust and scores well-correlated with other types of human judgements; 2) automatic metrics are usually, but not always, well-correlated with direct assessment scores; and 3) COMET as a slightly stronger automatic metric than chrF, despite the segmentation noise introduced by the resegmentation step systems. We release the collected human-annotated data in order to encourage further investigation.
* LREC-COLING2024 publication (with corrections for Table 3)
Towards Real-World Streaming Speech Translation for Code-Switched Speech
Oct 23, 2023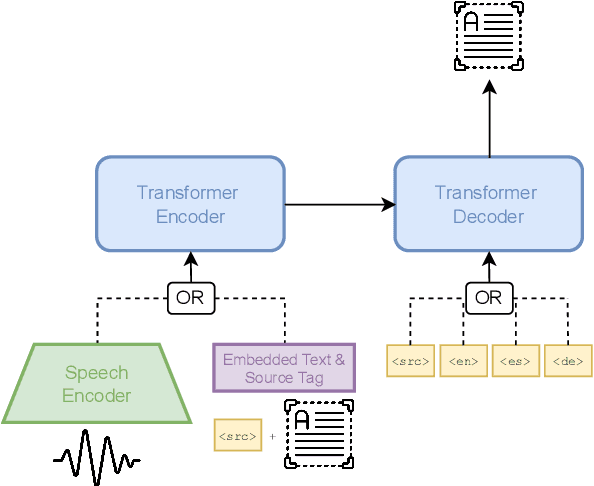
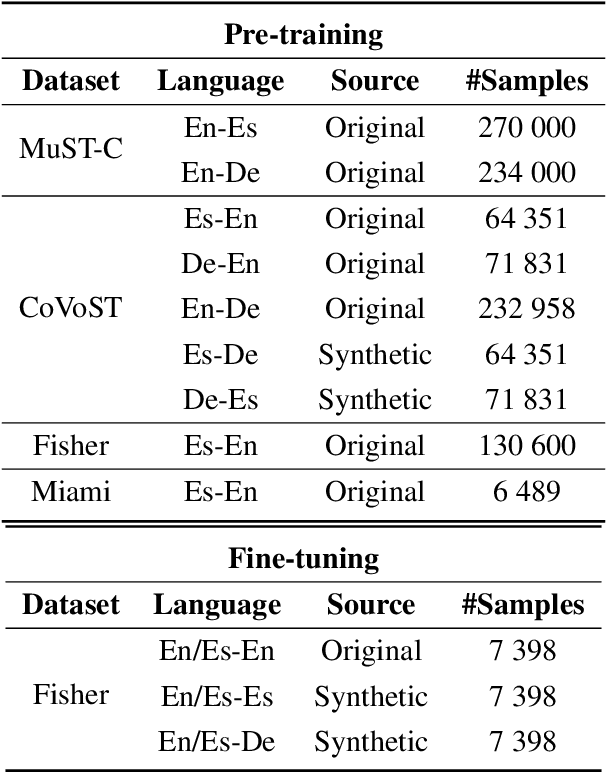
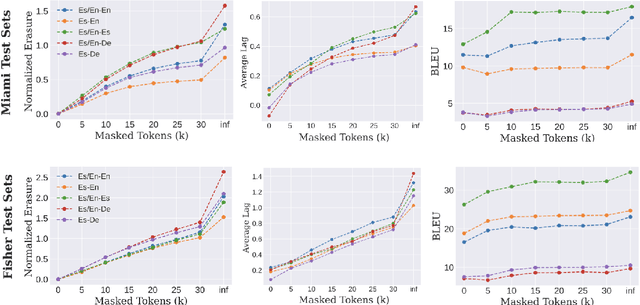
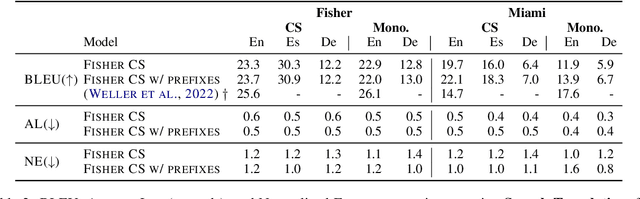
Abstract:Code-switching (CS), i.e. mixing different languages in a single sentence, is a common phenomenon in communication and can be challenging in many Natural Language Processing (NLP) settings. Previous studies on CS speech have shown promising results for end-to-end speech translation (ST), but have been limited to offline scenarios and to translation to one of the languages present in the source (\textit{monolingual transcription}). In this paper, we focus on two essential yet unexplored areas for real-world CS speech translation: streaming settings, and translation to a third language (i.e., a language not included in the source). To this end, we extend the Fisher and Miami test and validation datasets to include new targets in Spanish and German. Using this data, we train a model for both offline and streaming ST and we establish baseline results for the two settings mentioned earlier.
Automating Behavioral Testing in Machine Translation
Sep 07, 2023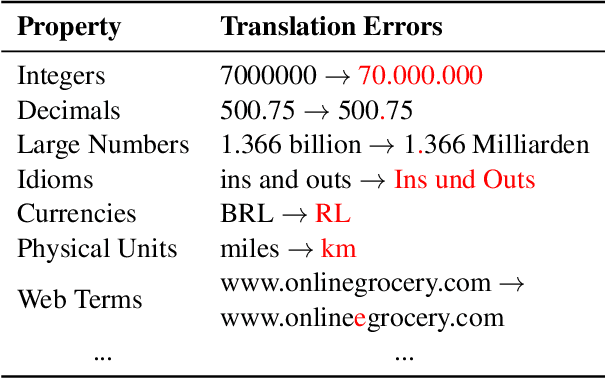
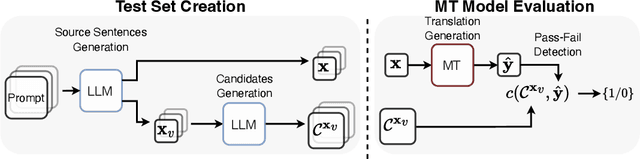

Abstract:Behavioral testing in NLP allows fine-grained evaluation of systems by examining their linguistic capabilities through the analysis of input-output behavior. Unfortunately, existing work on behavioral testing in Machine Translation (MT) is currently restricted to largely handcrafted tests covering a limited range of capabilities and languages. To address this limitation, we propose to use Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate a diverse set of source sentences tailored to test the behavior of MT models in a range of situations. We can then verify whether the MT model exhibits the expected behavior through matching candidate sets that are also generated using LLMs. Our approach aims to make behavioral testing of MT systems practical while requiring only minimal human effort. In our experiments, we apply our proposed evaluation framework to assess multiple available MT systems, revealing that while in general pass-rates follow the trends observable from traditional accuracy-based metrics, our method was able to uncover several important differences and potential bugs that go unnoticed when relying only on accuracy.
Joint Speech Transcription and Translation: Pseudo-Labeling with Out-of-Distribution Data
Dec 20, 2022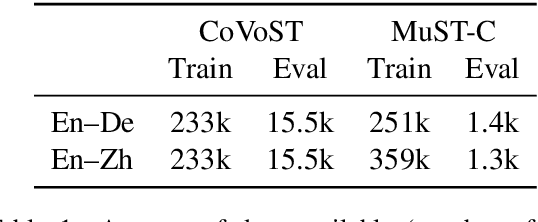
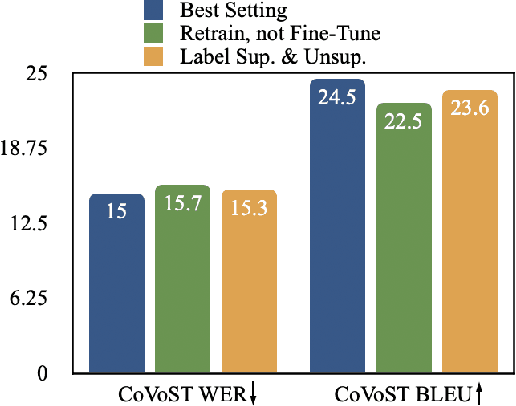

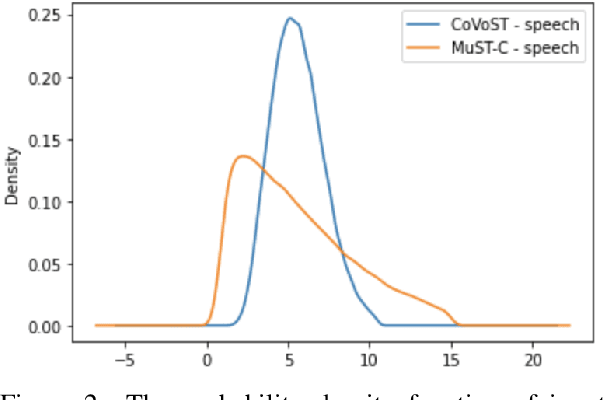
Abstract:Self-training has been shown to be helpful in addressing data scarcity for many domains, including vision, speech, and language. Specifically, self-training, or pseudo-labeling, labels unsupervised data and adds that to the training pool. In this work, we investigate and use pseudo-labeling for a recently proposed novel setup: joint transcription and translation of speech, which suffers from an absence of sufficient data resources. We show that under such data-deficient circumstances, the unlabeled data can significantly vary in domain from the supervised data, which results in pseudo-label quality degradation. We investigate two categories of remedies that require no additional supervision and target the domain mismatch: pseudo-label filtering and data augmentation. We show that pseudo-label analysis and processing as such results in additional gains on top of the vanilla pseudo-labeling setup resulting in total improvements of up to 0.6% absolute WER and 2.2 BLEU points.
End-to-End Speech Translation for Code Switched Speech
Apr 11, 2022

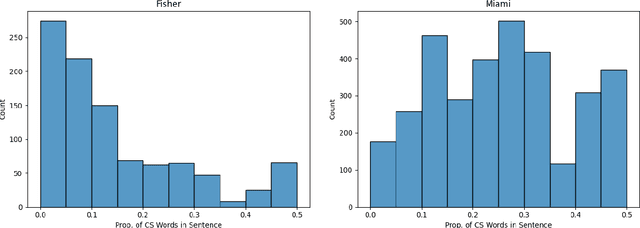
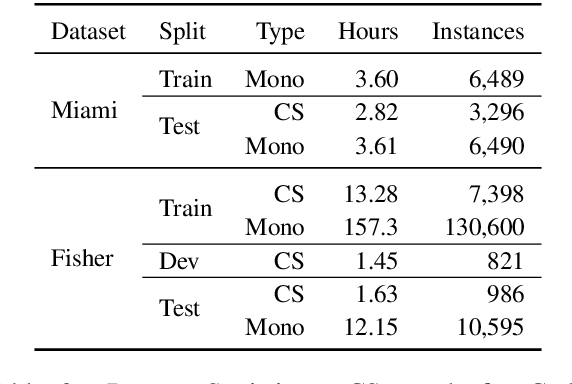
Abstract:Code switching (CS) refers to the phenomenon of interchangeably using words and phrases from different languages. CS can pose significant accuracy challenges to NLP, due to the often monolingual nature of the underlying systems. In this work, we focus on CS in the context of English/Spanish conversations for the task of speech translation (ST), generating and evaluating both transcript and translation. To evaluate model performance on this task, we create a novel ST corpus derived from existing public data sets. We explore various ST architectures across two dimensions: cascaded (transcribe then translate) vs end-to-end (jointly transcribe and translate) and unidirectional (source -> target) vs bidirectional (source <-> target). We show that our ST architectures, and especially our bidirectional end-to-end architecture, perform well on CS speech, even when no CS training data is used.
Streaming Models for Joint Speech Recognition and Translation
Jan 22, 2021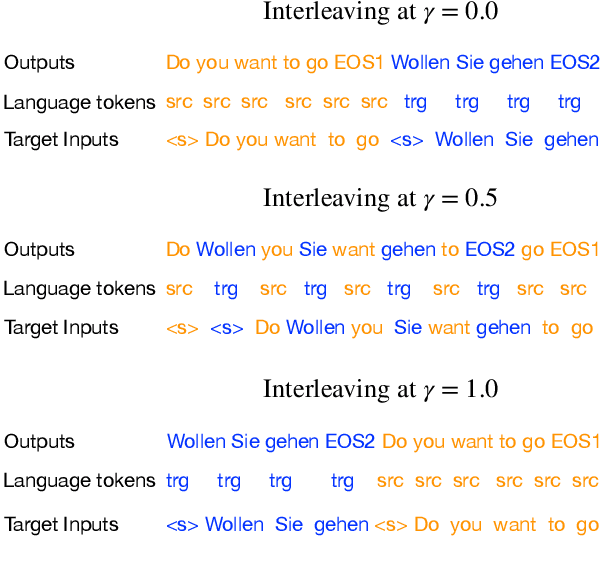
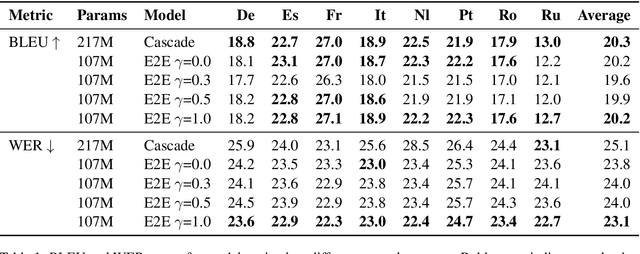
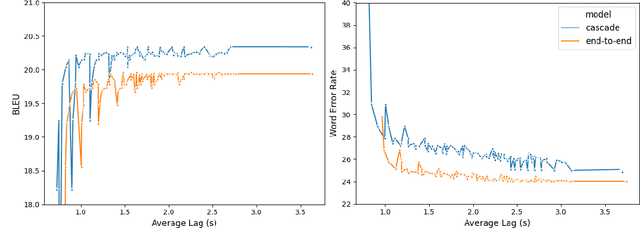
Abstract:Using end-to-end models for speech translation (ST) has increasingly been the focus of the ST community. These models condense the previously cascaded systems by directly converting sound waves into translated text. However, cascaded models have the advantage of including automatic speech recognition output, useful for a variety of practical ST systems that often display transcripts to the user alongside the translations. To bridge this gap, recent work has shown initial progress into the feasibility for end-to-end models to produce both of these outputs. However, all previous work has only looked at this problem from the consecutive perspective, leaving uncertainty on whether these approaches are effective in the more challenging streaming setting. We develop an end-to-end streaming ST model based on a re-translation approach and compare against standard cascading approaches. We also introduce a novel inference method for the joint case, interleaving both transcript and translation in generation and removing the need to use separate decoders. Our evaluation across a range of metrics capturing accuracy, latency, and consistency shows that our end-to-end models are statistically similar to cascading models, while having half the number of parameters. We also find that both systems provide strong translation quality at low latency, keeping 99% of consecutive quality at a lag of just under a second.
Consistent Transcription and Translation of Speech
Aug 28, 2020
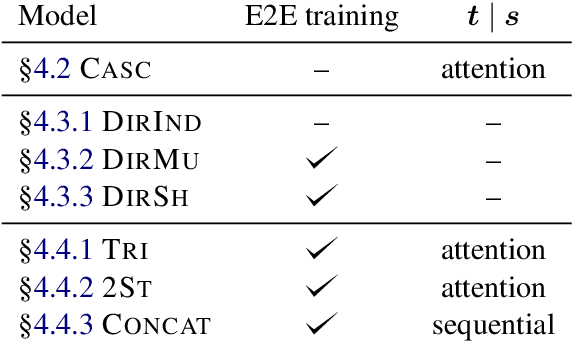

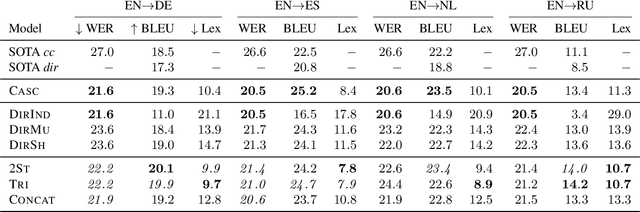
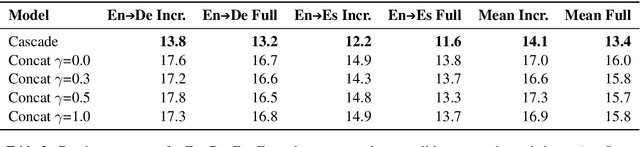
Abstract:The conventional paradigm in speech translation starts with a speech recognition step to generate transcripts, followed by a translation step with the automatic transcripts as input. To address various shortcomings of this paradigm, recent work explores end-to-end trainable direct models that translate without transcribing. However, transcripts can be an indispensable output in practical applications, which often display transcripts alongside the translations to users. We make this common requirement explicit and explore the task of jointly transcribing and translating speech. While high accuracy of transcript and translation are crucial, even highly accurate systems can suffer from inconsistencies between both outputs that degrade the user experience. We introduce a methodology to evaluate consistency and compare several modeling approaches, including the traditional cascaded approach and end-to-end models. We find that direct models are poorly suited to the joint transcription/translation task, but that end-to-end models that feature a coupled inference procedure are able to achieve strong consistency. We further introduce simple techniques for directly optimizing for consistency, and analyze the resulting trade-offs between consistency, transcription accuracy, and translation accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge