Maha Elbayad
NLLB Team
Large Concept Models: Language Modeling in a Sentence Representation Space
Dec 11, 2024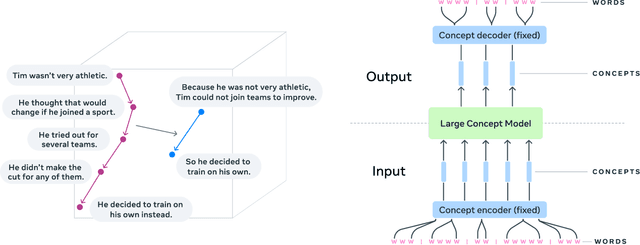
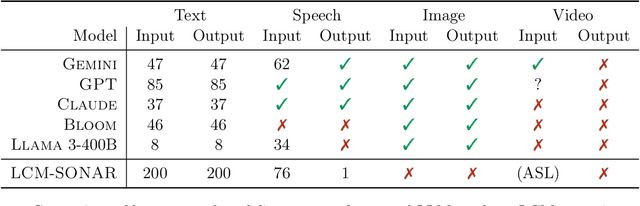
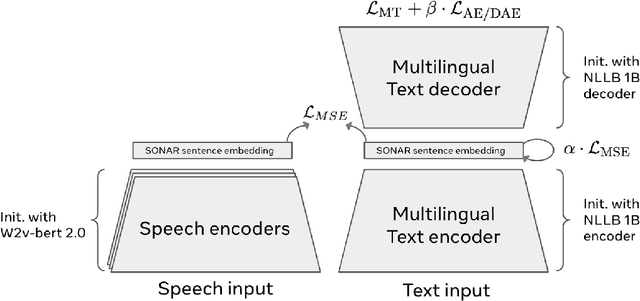
Abstract:LLMs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence and have emerged as the de-facto tool for many tasks. The current established technology of LLMs is to process input and generate output at the token level. This is in sharp contrast to humans who operate at multiple levels of abstraction, well beyond single words, to analyze information and to generate creative content. In this paper, we present an attempt at an architecture which operates on an explicit higher-level semantic representation, which we name a concept. Concepts are language- and modality-agnostic and represent a higher level idea or action in a flow. Hence, we build a "Large Concept Model". In this study, as proof of feasibility, we assume that a concept corresponds to a sentence, and use an existing sentence embedding space, SONAR, which supports up to 200 languages in both text and speech modalities. The Large Concept Model is trained to perform autoregressive sentence prediction in an embedding space. We explore multiple approaches, namely MSE regression, variants of diffusion-based generation, and models operating in a quantized SONAR space. These explorations are performed using 1.6B parameter models and training data in the order of 1.3T tokens. We then scale one architecture to a model size of 7B parameters and training data of about 2.7T tokens. We perform an experimental evaluation on several generative tasks, namely summarization and a new task of summary expansion. Finally, we show that our model exhibits impressive zero-shot generalization performance to many languages, outperforming existing LLMs of the same size. The training code of our models is freely available.
Merging Text Transformer Models from Different Initializations
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:Recent work on one-shot permutation-based model merging has shown impressive low- or zero-barrier mode connectivity between models from completely different initializations. However, this line of work has not yet extended to the Transformer architecture, despite its dominant popularity in the language domain. Therefore, in this work, we investigate the extent to which separate Transformer minima learn similar features, and propose a model merging technique to investigate the relationship between these minima in the loss landscape. The specifics of the architecture, like its residual connections, multi-headed attention, and discrete, sequential input, require specific interventions in order to compute model permutations that remain within the same functional equivalence class. In merging these models with our method, we consistently find lower loss barriers between minima compared to model averaging for several models trained on a masked-language modeling task or fine-tuned on a language understanding benchmark. Our results show that the minima of these models are less sharp and isolated than previously understood, and provide a basis for future work on merging separately trained Transformer models.
SpiRit-LM: Interleaved Spoken and Written Language Model
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:We introduce SPIRIT-LM, a foundation multimodal language model that freely mixes text and speech. Our model is based on a pretrained text language model that we extend to the speech modality by continuously training it on text and speech units. Speech and text sequences are concatenated as a single set of tokens, and trained with a word-level interleaving method using a small automatically-curated speech-text parallel corpus. SPIRIT-LM comes in two versions: a BASE version that uses speech semantic units and an EXPRESSIVE version that models expressivity using pitch and style units in addition to the semantic units. For both versions, the text is encoded with subword BPE tokens. The resulting model displays both the semantic abilities of text models and the expressive abilities of speech models. Additionally, we demonstrate that SPIRIT-LM is able to learn new tasks in a few-shot fashion across modalities (i.e. ASR, TTS, Speech Classification).
Seamless: Multilingual Expressive and Streaming Speech Translation
Dec 08, 2023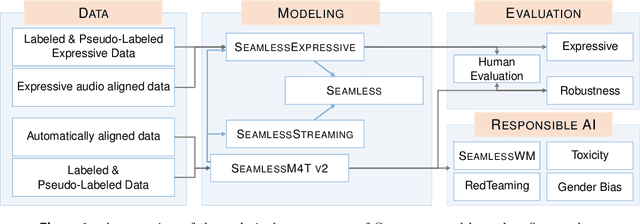
Abstract:Large-scale automatic speech translation systems today lack key features that help machine-mediated communication feel seamless when compared to human-to-human dialogue. In this work, we introduce a family of models that enable end-to-end expressive and multilingual translations in a streaming fashion. First, we contribute an improved version of the massively multilingual and multimodal SeamlessM4T model-SeamlessM4T v2. This newer model, incorporating an updated UnitY2 framework, was trained on more low-resource language data. SeamlessM4T v2 provides the foundation on which our next two models are initiated. SeamlessExpressive enables translation that preserves vocal styles and prosody. Compared to previous efforts in expressive speech research, our work addresses certain underexplored aspects of prosody, such as speech rate and pauses, while also preserving the style of one's voice. As for SeamlessStreaming, our model leverages the Efficient Monotonic Multihead Attention mechanism to generate low-latency target translations without waiting for complete source utterances. As the first of its kind, SeamlessStreaming enables simultaneous speech-to-speech/text translation for multiple source and target languages. To ensure that our models can be used safely and responsibly, we implemented the first known red-teaming effort for multimodal machine translation, a system for the detection and mitigation of added toxicity, a systematic evaluation of gender bias, and an inaudible localized watermarking mechanism designed to dampen the impact of deepfakes. Consequently, we bring major components from SeamlessExpressive and SeamlessStreaming together to form Seamless, the first publicly available system that unlocks expressive cross-lingual communication in real-time. The contributions to this work are publicly released and accessible at https://github.com/facebookresearch/seamless_communication
Added Toxicity Mitigation at Inference Time for Multimodal and Massively Multilingual Translation
Nov 11, 2023



Abstract:Added toxicity in the context of translation refers to the fact of producing a translation output with more toxicity than there exists in the input. In this paper, we present MinTox which is a novel pipeline to identify added toxicity and mitigate this issue which works at inference time. MinTox uses a toxicity detection classifier which is multimodal (speech and text) and works in languages at scale. The mitigation method is applied to languages at scale and directly in text outputs. MinTox is applied to SEAMLESSM4T, which is the latest multimodal and massively multilingual machine translation system. For this system, MinTox achieves significant added toxicity mitigation across domains, modalities and language directions. MinTox manages to approximately filter out from 25% to 95% of added toxicity (depending on the modality and domain) while keeping translation quality.
SeamlessM4T-Massively Multilingual & Multimodal Machine Translation
Aug 23, 2023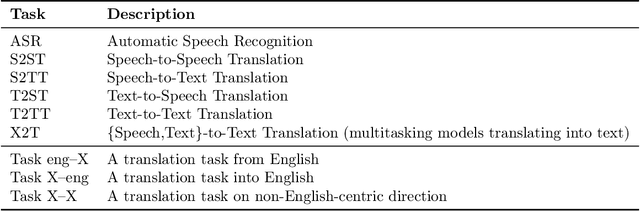
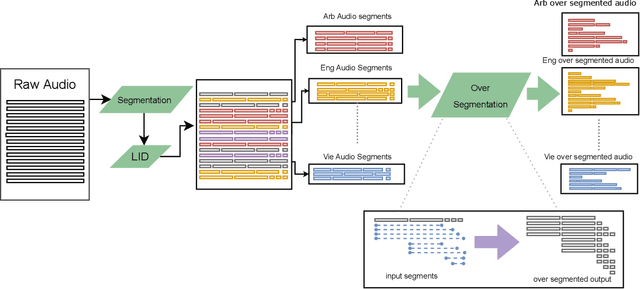
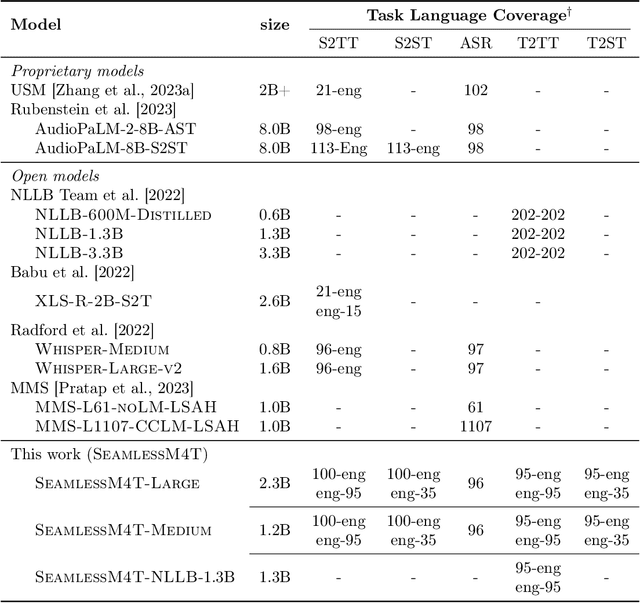
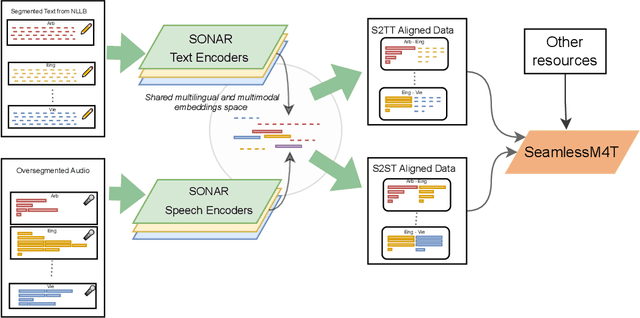
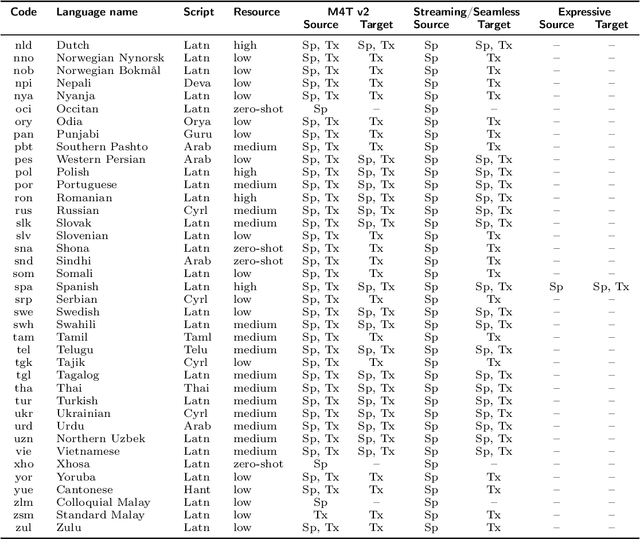
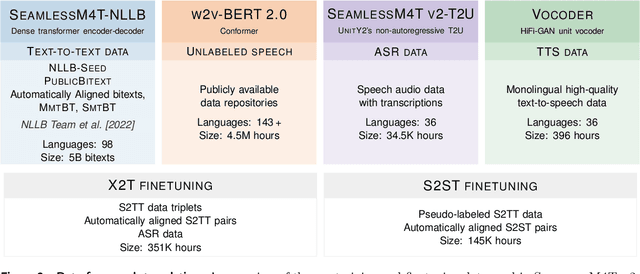
Abstract:What does it take to create the Babel Fish, a tool that can help individuals translate speech between any two languages? While recent breakthroughs in text-based models have pushed machine translation coverage beyond 200 languages, unified speech-to-speech translation models have yet to achieve similar strides. More specifically, conventional speech-to-speech translation systems rely on cascaded systems that perform translation progressively, putting high-performing unified systems out of reach. To address these gaps, we introduce SeamlessM4T, a single model that supports speech-to-speech translation, speech-to-text translation, text-to-speech translation, text-to-text translation, and automatic speech recognition for up to 100 languages. To build this, we used 1 million hours of open speech audio data to learn self-supervised speech representations with w2v-BERT 2.0. Subsequently, we created a multimodal corpus of automatically aligned speech translations. Filtered and combined with human-labeled and pseudo-labeled data, we developed the first multilingual system capable of translating from and into English for both speech and text. On FLEURS, SeamlessM4T sets a new standard for translations into multiple target languages, achieving an improvement of 20% BLEU over the previous SOTA in direct speech-to-text translation. Compared to strong cascaded models, SeamlessM4T improves the quality of into-English translation by 1.3 BLEU points in speech-to-text and by 2.6 ASR-BLEU points in speech-to-speech. Tested for robustness, our system performs better against background noises and speaker variations in speech-to-text tasks compared to the current SOTA model. Critically, we evaluated SeamlessM4T on gender bias and added toxicity to assess translation safety. Finally, all contributions in this work are open-sourced and accessible at https://github.com/facebookresearch/seamless_communication
Towards Being Parameter-Efficient: A Stratified Sparsely Activated Transformer with Dynamic Capacity
May 03, 2023



Abstract:Mixture-of-experts (MoE) models that employ sparse activation have demonstrated effectiveness in significantly increasing the number of parameters while maintaining low computational requirements per token. However, recent studies have established that MoE models are inherently parameter-inefficient as the improvement in performance diminishes with an increasing number of experts. We hypothesize this parameter inefficiency is a result of all experts having equal capacity, which may not adequately meet the varying complexity requirements of different tokens or tasks, e.g., in a multilingual setting, languages based on their resource levels might require different capacities. In light of this, we propose Stratified Mixture of Experts(SMoE) models, which feature a stratified structure and can assign dynamic capacity to different tokens. We demonstrate the effectiveness of SMoE on two multilingual machine translation benchmarks, where it outperforms multiple state-of-the-art MoE models. On a diverse 15-language dataset, SMoE improves the translation quality over vanilla MoE by +0.93 BLEU points on average. Additionally, SMoE is parameter-efficient, matching vanilla MoE performance with around 50\% fewer parameters.
Efficiently Upgrading Multilingual Machine Translation Models to Support More Languages
Feb 07, 2023

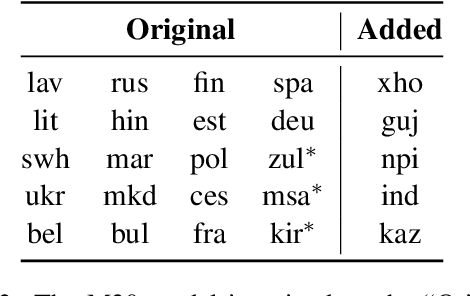

Abstract:With multilingual machine translation (MMT) models continuing to grow in size and number of supported languages, it is natural to reuse and upgrade existing models to save computation as data becomes available in more languages. However, adding new languages requires updating the vocabulary, which complicates the reuse of embeddings. The question of how to reuse existing models while also making architectural changes to provide capacity for both old and new languages has also not been closely studied. In this work, we introduce three techniques that help speed up effective learning of the new languages and alleviate catastrophic forgetting despite vocabulary and architecture mismatches. Our results show that by (1) carefully initializing the network, (2) applying learning rate scaling, and (3) performing data up-sampling, it is possible to exceed the performance of a same-sized baseline model with 30% computation and recover the performance of a larger model trained from scratch with over 50% reduction in computation. Furthermore, our analysis reveals that the introduced techniques help learn the new directions more effectively and alleviate catastrophic forgetting at the same time. We hope our work will guide research into more efficient approaches to growing languages for these MMT models and ultimately maximize the reuse of existing models.
Fixing MoE Over-Fitting on Low-Resource Languages in Multilingual Machine Translation
Dec 15, 2022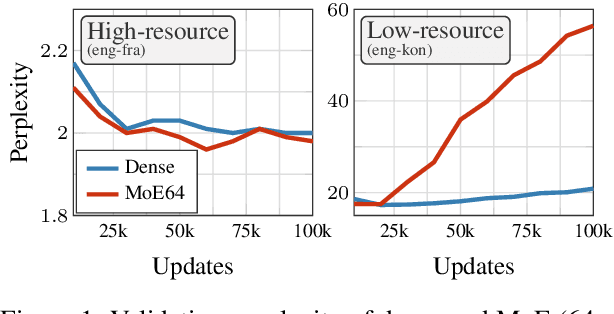
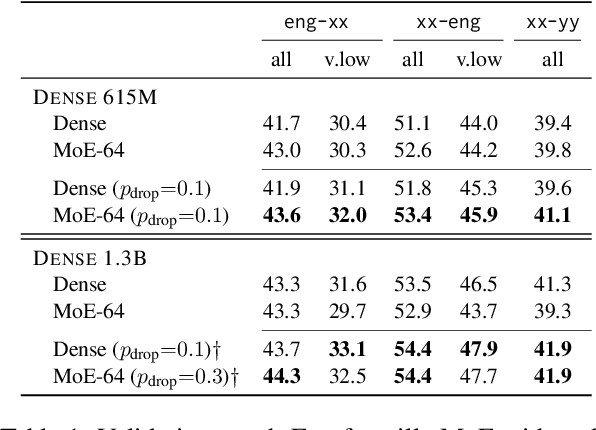
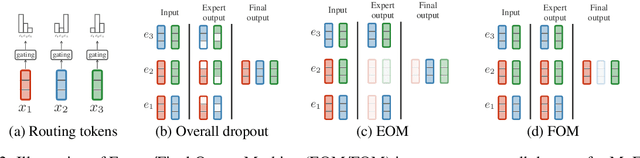
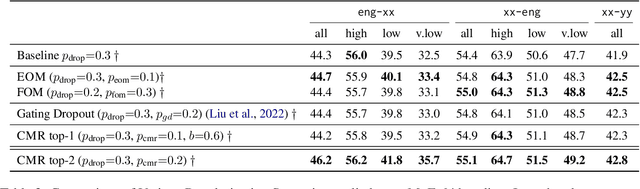
Abstract:Sparsely gated Mixture of Experts (MoE) models have been shown to be a compute-efficient method to scale model capacity for multilingual machine translation. However, for low-resource tasks, MoE models severely over-fit. We show effective regularization strategies, namely dropout techniques for MoE layers in EOM and FOM, Conditional MoE Routing and Curriculum Learning methods that prevent over-fitting and improve the performance of MoE models on low-resource tasks without adversely affecting high-resource tasks. On a massively multilingual machine translation benchmark, our strategies result in about +1 chrF++ improvement in very low resource language pairs. We perform an extensive analysis of the learned MoE routing to better understand the impact of our regularization methods and how we can improve them.
Causes and Cures for Interference in Multilingual Translation
Dec 14, 2022Abstract:Multilingual machine translation models can benefit from synergy between different language pairs, but also suffer from interference. While there is a growing number of sophisticated methods that aim to eliminate interference, our understanding of interference as a phenomenon is still limited. This work identifies the main factors that contribute to interference in multilingual machine translation. Through systematic experimentation, we find that interference (or synergy) are primarily determined by model size, data size, and the proportion of each language pair within the total dataset. We observe that substantial interference occurs mainly when the model is very small with respect to the available training data, and that using standard transformer configurations with less than one billion parameters largely alleviates interference and promotes synergy. Moreover, we show that tuning the sampling temperature to control the proportion of each language pair in the data is key to balancing the amount of interference between low and high resource language pairs effectively, and can lead to superior performance overall.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge