Marta R. Costa-jussà
NLLB Team
Translate, then Detect: Leveraging Machine Translation for Cross-Lingual Toxicity Classification
Sep 17, 2025



Abstract:Multilingual toxicity detection remains a significant challenge due to the scarcity of training data and resources for many languages. While prior work has leveraged the translate-test paradigm to support cross-lingual transfer across a range of classification tasks, the utility of translation in supporting toxicity detection at scale remains unclear. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive comparison of translation-based and language-specific/multilingual classification pipelines. We find that translation-based pipelines consistently outperform out-of-distribution classifiers in 81.3% of cases (13 of 16 languages), with translation benefits strongly correlated with both the resource level of the target language and the quality of the machine translation (MT) system. Our analysis reveals that traditional classifiers outperform large language model (LLM) judges, with this advantage being particularly pronounced for low-resource languages, where translate-classify methods dominate translate-judge approaches in 6 out of 7 cases. We additionally show that MT-specific fine-tuning on LLMs yields lower refusal rates compared to standard instruction-tuned models, but it can negatively impact toxicity detection accuracy for low-resource languages. These findings offer actionable guidance for practitioners developing scalable multilingual content moderation systems.
Improving Language and Modality Transfer in Translation by Character-level Modeling
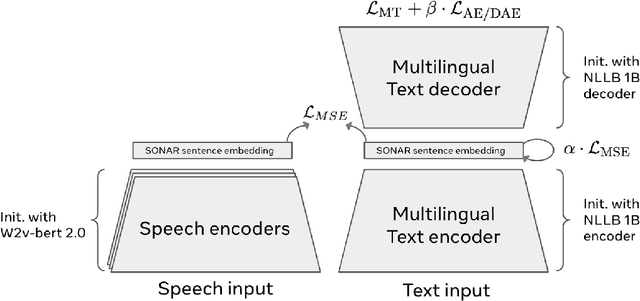
May 30, 2025Abstract:Current translation systems, despite being highly multilingual, cover only 5% of the world's languages. Expanding language coverage to the long-tail of low-resource languages requires data-efficient methods that rely on cross-lingual and cross-modal knowledge transfer. To this end, we propose a character-based approach to improve adaptability to new languages and modalities. Our method leverages SONAR, a multilingual fixed-size embedding space with different modules for encoding and decoding. We use a teacher-student approach with parallel translation data to obtain a character-level encoder. Then, using ASR data, we train a lightweight adapter to connect a massively multilingual CTC ASR model (MMS), to the character-level encoder, potentially enabling speech translation from 1,000+ languages. Experimental results in text translation for 75 languages on FLORES+ demonstrate that our character-based approach can achieve better language transfer than traditional subword-based models, especially outperforming them in low-resource settings, and demonstrating better zero-shot generalizability to unseen languages. Our speech adaptation, maximizing knowledge transfer from the text modality, achieves state-of-the-art results in speech-to-text translation on the FLEURS benchmark on 33 languages, surpassing previous supervised and cascade models, albeit being a zero-shot model with minimal supervision from ASR data.
BOUQuET: dataset, Benchmark and Open initiative for Universal Quality Evaluation in Translation
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents BOUQuET, a multicentric and multi-register/domain dataset and benchmark, and its broader collaborative extension initiative. This dataset is handcrafted in non-English languages first, each of these source languages being represented among the 23 languages commonly used by half of the world's population and therefore having the potential to serve as pivot languages that will enable more accurate translations. The dataset is specially designed to avoid contamination and be multicentric, so as to enforce representation of multilingual language features. In addition, the dataset goes beyond the sentence level, as it is organized in paragraphs of various lengths. Compared with related machine translation (MT) datasets, we show that BOUQuET has a broader representation of domains while simplifying the translation task for non-experts. Therefore, BOUQuET is specially suitable for the open initiative and call for translation participation that we are launching to extend it to a multi-way parallel corpus to any written language.
LCFO: Long Context and Long Form Output Dataset and Benchmarking
Dec 12, 2024



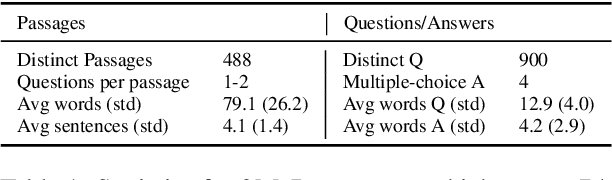
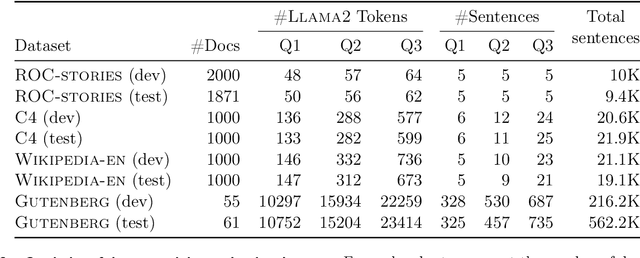
Abstract:This paper presents the Long Context and Form Output (LCFO) benchmark, a novel evaluation framework for assessing gradual summarization and summary expansion capabilities across diverse domains. LCFO consists of long input documents (5k words average length), each of which comes with three summaries of different lengths (20%, 10%, and 5% of the input text), as well as approximately 15 questions and answers (QA) related to the input content. Notably, LCFO also provides alignments between specific QA pairs and corresponding summaries in 7 domains. The primary motivation behind providing summaries of different lengths is to establish a controllable framework for generating long texts from shorter inputs, i.e. summary expansion. To establish an evaluation metric framework for summarization and summary expansion, we provide human evaluation scores for human-generated outputs, as well as results from various state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). GPT-4o-mini achieves best human scores among automatic systems in both summarization and summary expansion tasks (~ +10% and +20%, respectively). It even surpasses human output quality in the case of short summaries (~ +7%). Overall automatic metrics achieve low correlations with human evaluation scores (~ 0.4) but moderate correlation on specific evaluation aspects such as fluency and attribution (~ 0.6). The LCFO benchmark offers a standardized platform for evaluating summarization and summary expansion performance, as well as corresponding automatic metrics, thereby providing an important evaluation framework to advance generative AI.
2M-BELEBELE: Highly Multilingual Speech and American Sign Language Comprehension Dataset
Dec 11, 2024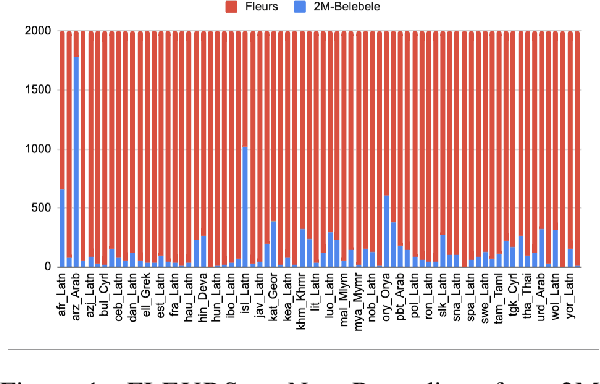
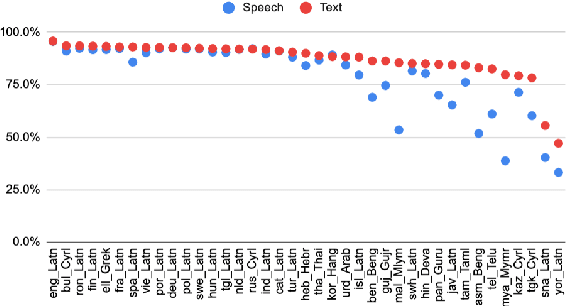
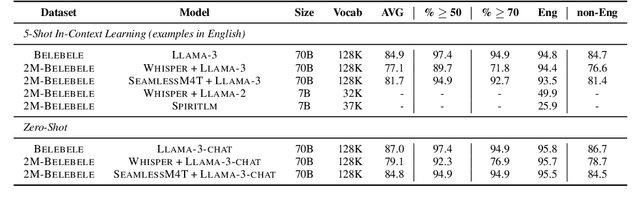
Abstract:We introduce the first highly multilingual speech and American Sign Language (ASL) comprehension dataset by extending BELEBELE. Our dataset covers 74 spoken languages at the intersection of BELEBELE and FLEURS, and one sign language (ASL). We evaluate 2M-BELEBELE dataset for both 5-shot and zero-shot settings and across languages, the speech comprehension accuracy is ~ 8% average lower compared to reading comprehension.
Large Concept Models: Language Modeling in a Sentence Representation Space
Dec 11, 2024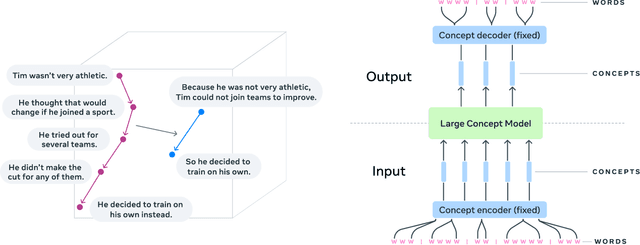
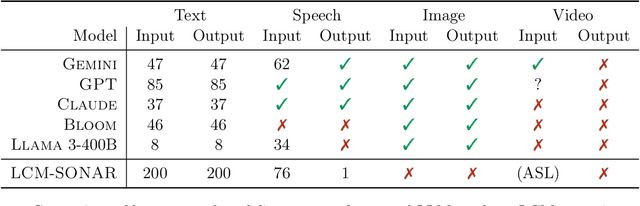
Abstract:LLMs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence and have emerged as the de-facto tool for many tasks. The current established technology of LLMs is to process input and generate output at the token level. This is in sharp contrast to humans who operate at multiple levels of abstraction, well beyond single words, to analyze information and to generate creative content. In this paper, we present an attempt at an architecture which operates on an explicit higher-level semantic representation, which we name a concept. Concepts are language- and modality-agnostic and represent a higher level idea or action in a flow. Hence, we build a "Large Concept Model". In this study, as proof of feasibility, we assume that a concept corresponds to a sentence, and use an existing sentence embedding space, SONAR, which supports up to 200 languages in both text and speech modalities. The Large Concept Model is trained to perform autoregressive sentence prediction in an embedding space. We explore multiple approaches, namely MSE regression, variants of diffusion-based generation, and models operating in a quantized SONAR space. These explorations are performed using 1.6B parameter models and training data in the order of 1.3T tokens. We then scale one architecture to a model size of 7B parameters and training data of about 2.7T tokens. We perform an experimental evaluation on several generative tasks, namely summarization and a new task of summary expansion. Finally, we show that our model exhibits impressive zero-shot generalization performance to many languages, outperforming existing LLMs of the same size. The training code of our models is freely available.
Y-NQ: English-Yorùbá Evaluation dataset for Open-Book Reading Comprehension and Text Generation
Dec 11, 2024
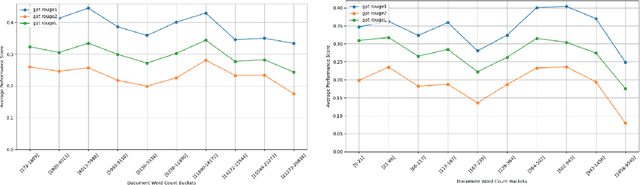
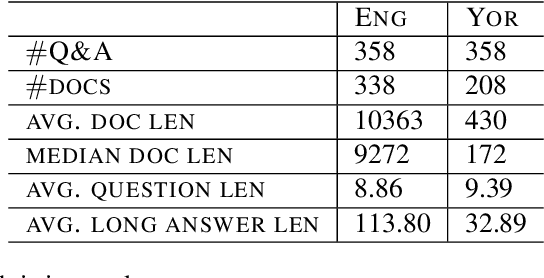
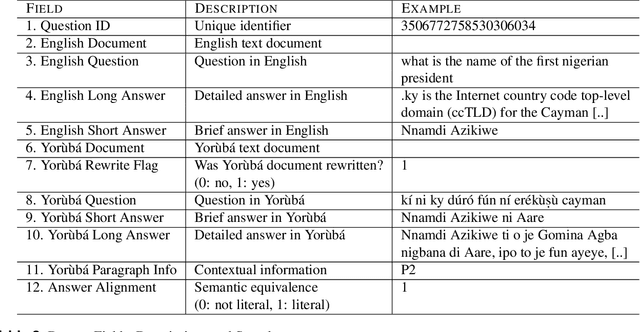
Abstract:The purpose of this work is to share an English-Yor\`ub\'a evaluation dataset for open-book reading comprehension and text generation to assess the performance of models both in a high- and a low- resource language. The dataset contains 358 questions and answers on 338 English documents and 208 Yor\`ub\'a documents. The average document length is ~ 10k words for English and 430 words for Yor\`ub\'a. Experiments show a consistent disparity in performance between the two languages, with Yor\`ub\'a falling behind English for automatic metrics even if documents are much shorter for this language. For a small set of documents with comparable length, performance of Yor\`ub\'a drops by x2.5 times. When analyzing performance by length, we observe that Yor\`ub\'a decreases performance dramatically for documents that reach 1500 words while English performance is barely affected at that length. Our dataset opens the door to showcasing if English LLM reading comprehension capabilities extend to Yor\`ub\'a, which for the evaluated LLMs is not the case.
On the Role of Speech Data in Reducing Toxicity Detection Bias
Nov 12, 2024
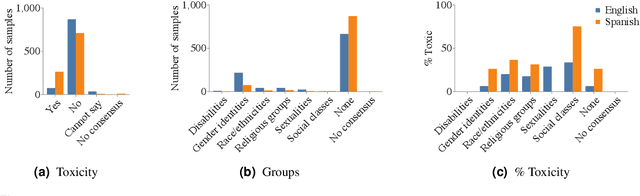
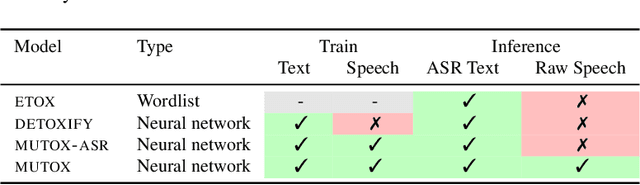
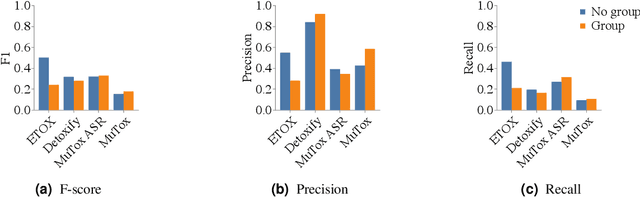
Abstract:Text toxicity detection systems exhibit significant biases, producing disproportionate rates of false positives on samples mentioning demographic groups. But what about toxicity detection in speech? To investigate the extent to which text-based biases are mitigated by speech-based systems, we produce a set of high-quality group annotations for the multilingual MuTox dataset, and then leverage these annotations to systematically compare speech- and text-based toxicity classifiers. Our findings indicate that access to speech data during inference supports reduced bias against group mentions, particularly for ambiguous and disagreement-inducing samples. Our results also suggest that improving classifiers, rather than transcription pipelines, is more helpful for reducing group bias. We publicly release our annotations and provide recommendations for future toxicity dataset construction.
On the Similarity of Circuits across Languages: a Case Study on the Subject-verb Agreement Task
Oct 09, 2024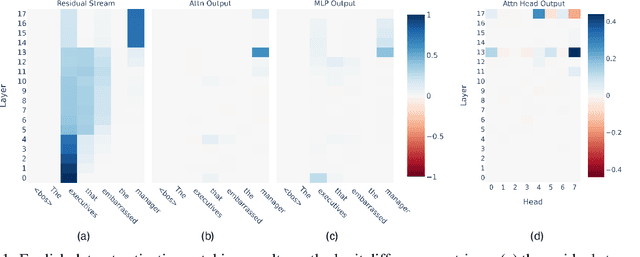
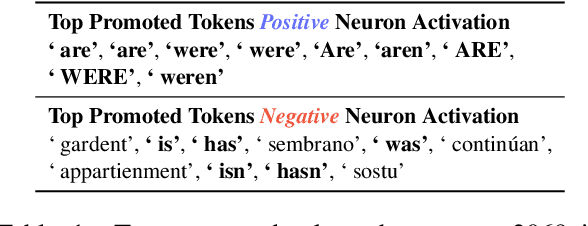
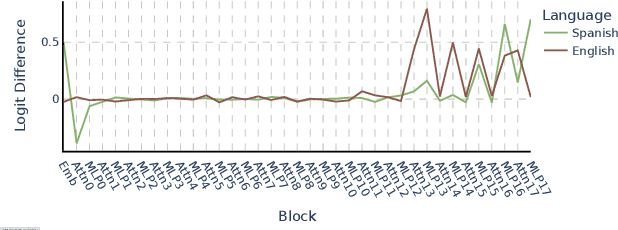

Abstract:Several algorithms implemented by language models have recently been successfully reversed-engineered. However, these findings have been concentrated on specific tasks and models, leaving it unclear how universal circuits are across different settings. In this paper, we study the circuits implemented by Gemma 2B for solving the subject-verb agreement task across two different languages, English and Spanish. We discover that both circuits are highly consistent, being mainly driven by a particular attention head writing a `subject number' signal to the last residual stream, which is read by a small set of neurons in the final MLPs. Notably, this subject number signal is represented as a direction in the residual stream space, and is language-independent. We demonstrate that this direction has a causal effect on the model predictions, effectively flipping the Spanish predicted verb number by intervening with the direction found in English. Finally, we present evidence of similar behavior in other models within the Gemma 1 and Gemma 2 families.
Unveiling the Role of Pretraining in Direct Speech Translation
Sep 26, 2024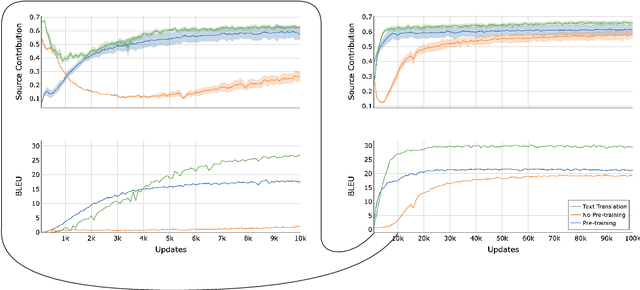
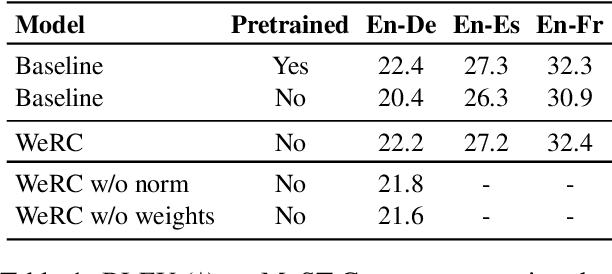
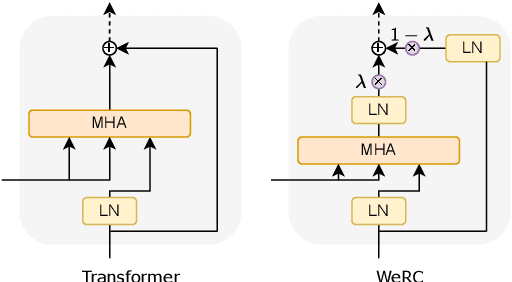
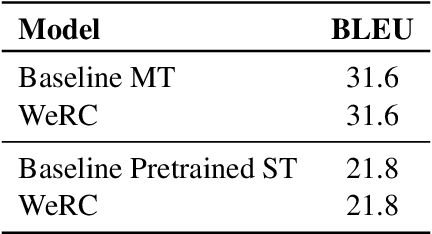
Abstract:Direct speech-to-text translation systems encounter an important drawback in data scarcity. A common solution consists on pretraining the encoder on automatic speech recognition, hence losing efficiency in the training process. In this study, we compare the training dynamics of a system using a pretrained encoder, the conventional approach, and one trained from scratch. We observe that, throughout the training, the randomly initialized model struggles to incorporate information from the speech inputs for its predictions. Hence, we hypothesize that this issue stems from the difficulty of effectively training an encoder for direct speech translation. While a model trained from scratch needs to learn acoustic and semantic modeling simultaneously, a pretrained one can just focus on the latter. Based on these findings, we propose a subtle change in the decoder cross-attention to integrate source information from earlier steps in training. We show that with this change, the model trained from scratch can achieve comparable performance to the pretrained one, while reducing the training time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge