Necati Cihan Camgoz
POET: Prompt Offset Tuning for Continual Human Action Adaptation
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:As extended reality (XR) is redefining how users interact with computing devices, research in human action recognition is gaining prominence. Typically, models deployed on immersive computing devices are static and limited to their default set of classes. The goal of our research is to provide users and developers with the capability to personalize their experience by adding new action classes to their device models continually. Importantly, a user should be able to add new classes in a low-shot and efficient manner, while this process should not require storing or replaying any of user's sensitive training data. We formalize this problem as privacy-aware few-shot continual action recognition. Towards this end, we propose POET: Prompt-Offset Tuning. While existing prompt tuning approaches have shown great promise for continual learning of image, text, and video modalities; they demand access to extensively pretrained transformers. Breaking away from this assumption, POET demonstrates the efficacy of prompt tuning a significantly lightweight backbone, pretrained exclusively on the base class data. We propose a novel spatio-temporal learnable prompt offset tuning approach, and are the first to apply such prompt tuning to Graph Neural Networks. We contribute two new benchmarks for our new problem setting in human action recognition: (i) NTU RGB+D dataset for activity recognition, and (ii) SHREC-2017 dataset for hand gesture recognition. We find that POET consistently outperforms comprehensive benchmarks. Source code at https://github.com/humansensinglab/POET-continual-action-recognition.
* ECCV 2024 (Oral), webpage https://humansensinglab.github.io/POET-continual-action-recognition/
SignRep: Enhancing Self-Supervised Sign Representations
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Sign language representation learning presents unique challenges due to the complex spatio-temporal nature of signs and the scarcity of labeled datasets. Existing methods often rely either on models pre-trained on general visual tasks, that lack sign-specific features, or use complex multimodal and multi-branch architectures. To bridge this gap, we introduce a scalable, self-supervised framework for sign representation learning. We leverage important inductive (sign) priors during the training of our RGB model. To do this, we leverage simple but important cues based on skeletons while pretraining a masked autoencoder. These sign specific priors alongside feature regularization and an adversarial style agnostic loss provide a powerful backbone. Notably, our model does not require skeletal keypoints during inference, avoiding the limitations of keypoint-based models during downstream tasks. When finetuned, we achieve state-of-the-art performance for sign recognition on the WLASL, ASL-Citizen and NMFs-CSL datasets, using a simpler architecture and with only a single-modality. Beyond recognition, our frozen model excels in sign dictionary retrieval and sign translation, surpassing standard MAE pretraining and skeletal-based representations in retrieval. It also reduces computational costs for training existing sign translation models while maintaining strong performance on Phoenix2014T, CSL-Daily and How2Sign.
2M-BELEBELE: Highly Multilingual Speech and American Sign Language Comprehension Dataset
Dec 11, 2024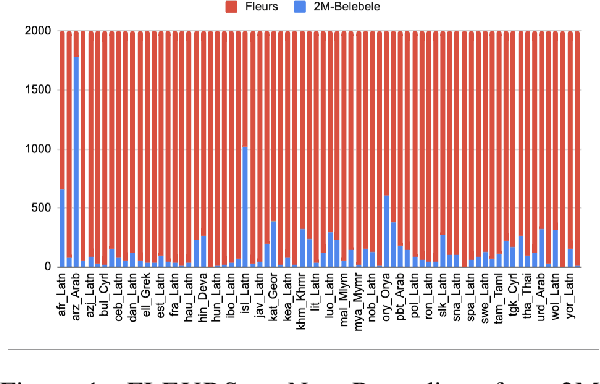
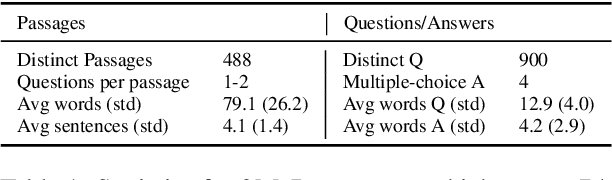
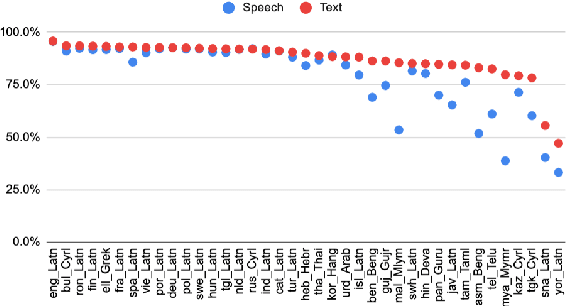
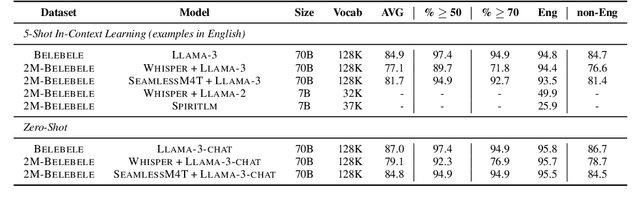
Abstract:We introduce the first highly multilingual speech and American Sign Language (ASL) comprehension dataset by extending BELEBELE. Our dataset covers 74 spoken languages at the intersection of BELEBELE and FLEURS, and one sign language (ASL). We evaluate 2M-BELEBELE dataset for both 5-shot and zero-shot settings and across languages, the speech comprehension accuracy is ~ 8% average lower compared to reading comprehension.
Sign2GPT: Leveraging Large Language Models for Gloss-Free Sign Language Translation
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Automatic Sign Language Translation requires the integration of both computer vision and natural language processing to effectively bridge the communication gap between sign and spoken languages. However, the deficiency in large-scale training data to support sign language translation means we need to leverage resources from spoken language. We introduce, Sign2GPT, a novel framework for sign language translation that utilizes large-scale pretrained vision and language models via lightweight adapters for gloss-free sign language translation. The lightweight adapters are crucial for sign language translation, due to the constraints imposed by limited dataset sizes and the computational requirements when training with long sign videos. We also propose a novel pretraining strategy that directs our encoder to learn sign representations from automatically extracted pseudo-glosses without requiring gloss order information or annotations. We evaluate our approach on two public benchmark sign language translation datasets, namely RWTH-PHOENIX-Weather 2014T and CSL-Daily, and improve on state-of-the-art gloss-free translation performance with a significant margin.
Using an LLM to Turn Sign Spottings into Spoken Language Sentences
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Sign Language Translation (SLT) is a challenging task that aims to generate spoken language sentences from sign language videos. In this paper, we introduce a hybrid SLT approach, Spotter+GPT, that utilizes a sign spotter and a pretrained large language model to improve SLT performance. Our method builds upon the strengths of both components. The videos are first processed by the spotter, which is trained on a linguistic sign language dataset, to identify individual signs. These spotted signs are then passed to the powerful language model, which transforms them into coherent and contextually appropriate spoken language sentences.
Learnt Contrastive Concept Embeddings for Sign Recognition
Aug 18, 2023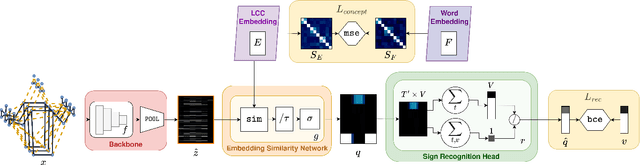
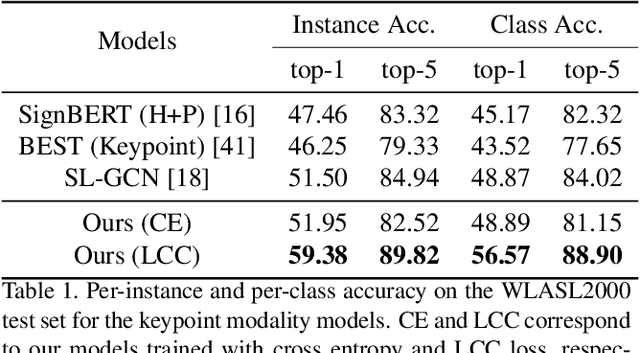
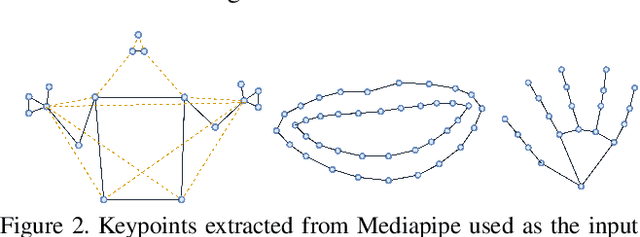
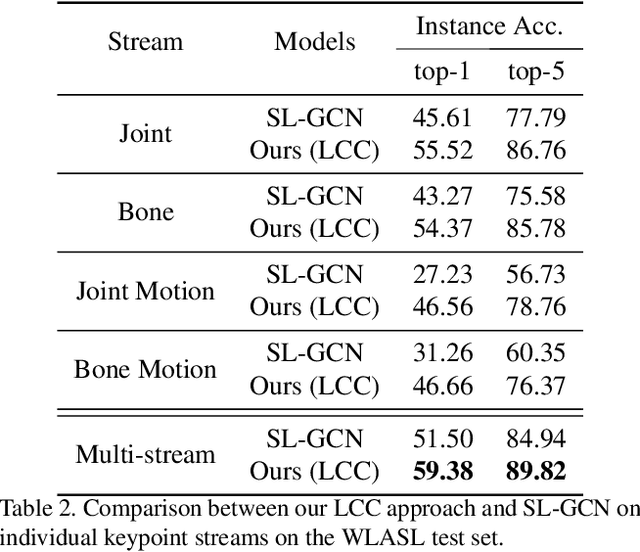
Abstract:In natural language processing (NLP) of spoken languages, word embeddings have been shown to be a useful method to encode the meaning of words. Sign languages are visual languages, which require sign embeddings to capture the visual and linguistic semantics of sign. Unlike many common approaches to Sign Recognition, we focus on explicitly creating sign embeddings that bridge the gap between sign language and spoken language. We propose a learning framework to derive LCC (Learnt Contrastive Concept) embeddings for sign language, a weakly supervised contrastive approach to learning sign embeddings. We train a vocabulary of embeddings that are based on the linguistic labels for sign video. Additionally, we develop a conceptual similarity loss which is able to utilise word embeddings from NLP methods to create sign embeddings that have better sign language to spoken language correspondence. These learnt representations allow the model to automatically localise the sign in time. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art keypoint-based sign recognition performance on the WLASL and BOBSL datasets.
Is context all you need? Scaling Neural Sign Language Translation to Large Domains of Discourse
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:Sign Language Translation (SLT) is a challenging task that aims to generate spoken language sentences from sign language videos, both of which have different grammar and word/gloss order. From a Neural Machine Translation (NMT) perspective, the straightforward way of training translation models is to use sign language phrase-spoken language sentence pairs. However, human interpreters heavily rely on the context to understand the conveyed information, especially for sign language interpretation, where the vocabulary size may be significantly smaller than their spoken language equivalent. Taking direct inspiration from how humans translate, we propose a novel multi-modal transformer architecture that tackles the translation task in a context-aware manner, as a human would. We use the context from previous sequences and confident predictions to disambiguate weaker visual cues. To achieve this we use complementary transformer encoders, namely: (1) A Video Encoder, that captures the low-level video features at the frame-level, (2) A Spotting Encoder, that models the recognized sign glosses in the video, and (3) A Context Encoder, which captures the context of the preceding sign sequences. We combine the information coming from these encoders in a final transformer decoder to generate spoken language translations. We evaluate our approach on the recently published large-scale BOBSL dataset, which contains ~1.2M sequences, and on the SRF dataset, which was part of the WMT-SLT 2022 challenge. We report significant improvements on state-of-the-art translation performance using contextual information, nearly doubling the reported BLEU-4 scores of baseline approaches.
Signing at Scale: Learning to Co-Articulate Signs for Large-Scale Photo-Realistic Sign Language Production
Mar 29, 2022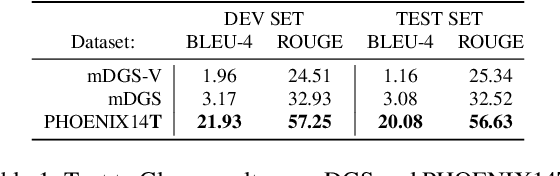
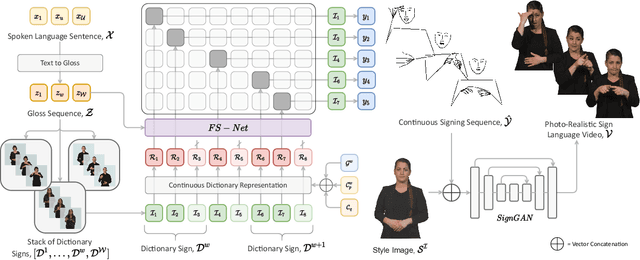
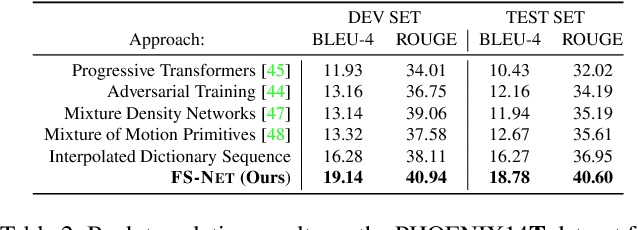
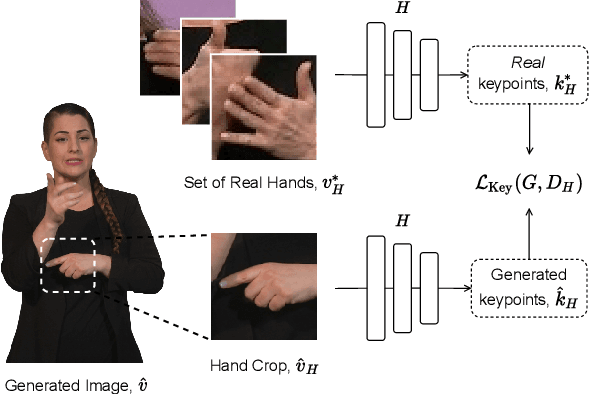
Abstract:Sign languages are visual languages, with vocabularies as rich as their spoken language counterparts. However, current deep-learning based Sign Language Production (SLP) models produce under-articulated skeleton pose sequences from constrained vocabularies and this limits applicability. To be understandable and accepted by the deaf, an automatic SLP system must be able to generate co-articulated photo-realistic signing sequences for large domains of discourse. In this work, we tackle large-scale SLP by learning to co-articulate between dictionary signs, a method capable of producing smooth signing while scaling to unconstrained domains of discourse. To learn sign co-articulation, we propose a novel Frame Selection Network (FS-Net) that improves the temporal alignment of interpolated dictionary signs to continuous signing sequences. Additionally, we propose SignGAN, a pose-conditioned human synthesis model that produces photo-realistic sign language videos direct from skeleton pose. We propose a novel keypoint-based loss function which improves the quality of synthesized hand images. We evaluate our SLP model on the large-scale meineDGS (mDGS) corpus, conducting extensive user evaluation showing our FS-Net approach improves co-articulation of interpolated dictionary signs. Additionally, we show that SignGAN significantly outperforms all baseline methods for quantitative metrics, human perceptual studies and native deaf signer comprehension.
A Free Lunch with Influence Functions? Improving Neural Network Estimates with Concepts from Semiparametric Statistics
Feb 18, 2022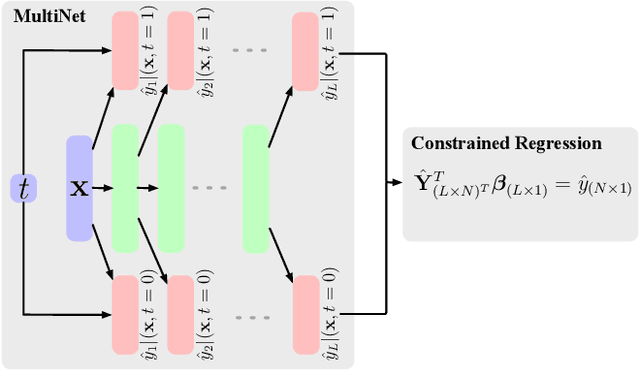
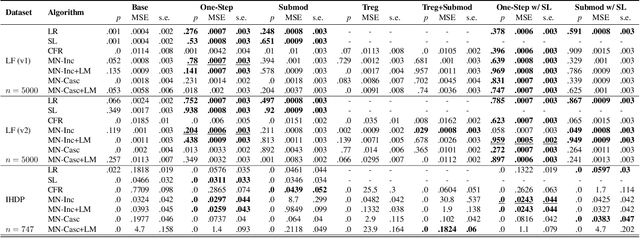
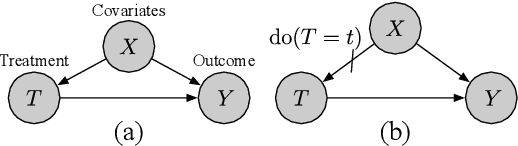
Abstract:Parameter estimation in the empirical fields is usually undertaken using parametric models, and such models are convenient because they readily facilitate statistical inference. Unfortunately, they are unlikely to have a sufficiently flexible functional form to be able to adequately model real-world phenomena, and their usage may therefore result in biased estimates and invalid inference. Unfortunately, whilst non-parametric machine learning models may provide the needed flexibility to adapt to the complexity of real-world phenomena, they do not readily facilitate statistical inference, and may still exhibit residual bias. We explore the potential for semiparametric theory (in particular, the Influence Function) to be used to improve neural networks and machine learning algorithms in terms of (a) improving initial estimates without needing more data (b) increasing the robustness of our models, and (c) yielding confidence intervals for statistical inference. We propose a new neural network method MultiNet, which seeks the flexibility and diversity of an ensemble using a single architecture. Results on causal inference tasks indicate that MultiNet yields better performance than other approaches, and that all considered methods are amenable to improvement from semiparametric techniques under certain conditions. In other words, with these techniques we show that we can improve existing neural networks for `free', without needing more data, and without needing to retrain them. Finally, we provide the expression for deriving influence functions for estimands from a general graph, and the code to do so automatically.
Skeletal Graph Self-Attention: Embedding a Skeleton Inductive Bias into Sign Language Production
Dec 06, 2021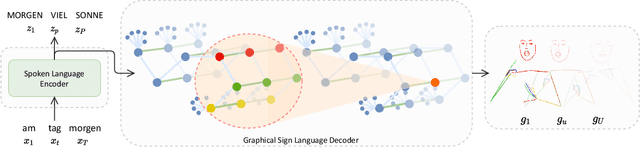

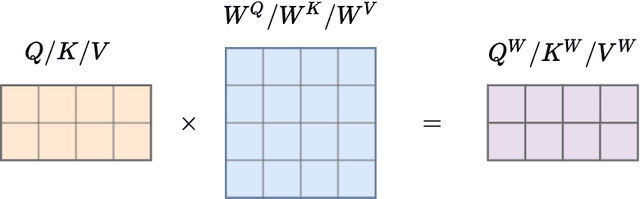

Abstract:Recent approaches to Sign Language Production (SLP) have adopted spoken language Neural Machine Translation (NMT) architectures, applied without sign-specific modifications. In addition, these works represent sign language as a sequence of skeleton pose vectors, projected to an abstract representation with no inherent skeletal structure. In this paper, we represent sign language sequences as a skeletal graph structure, with joints as nodes and both spatial and temporal connections as edges. To operate on this graphical structure, we propose Skeletal Graph Self-Attention (SGSA), a novel graphical attention layer that embeds a skeleton inductive bias into the SLP model. Retaining the skeletal feature representation throughout, we directly apply a spatio-temporal adjacency matrix into the self-attention formulation. This provides structure and context to each skeletal joint that is not possible when using a non-graphical abstract representation, enabling fluid and expressive sign language production. We evaluate our Skeletal Graph Self-Attention architecture on the challenging RWTH-PHOENIX-Weather-2014T(PHOENIX14T) dataset, achieving state-of-the-art back translation performance with an 8% and 7% improvement over competing methods for the dev and test sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge