Joe Chuang
Omnilingual ASR: Open-Source Multilingual Speech Recognition for 1600+ Languages
Nov 12, 2025



Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) has advanced in high-resource languages, but most of the world's 7,000+ languages remain unsupported, leaving thousands of long-tail languages behind. Expanding ASR coverage has been costly and limited by architectures that restrict language support, making extension inaccessible to most--all while entangled with ethical concerns when pursued without community collaboration. To transcend these limitations, we introduce Omnilingual ASR, the first large-scale ASR system designed for extensibility. Omnilingual ASR enables communities to introduce unserved languages with only a handful of data samples. It scales self-supervised pre-training to 7B parameters to learn robust speech representations and introduces an encoder-decoder architecture designed for zero-shot generalization, leveraging a LLM-inspired decoder. This capability is grounded in a massive and diverse training corpus; by combining breadth of coverage with linguistic variety, the model learns representations robust enough to adapt to unseen languages. Incorporating public resources with community-sourced recordings gathered through compensated local partnerships, Omnilingual ASR expands coverage to over 1,600 languages, the largest such effort to date--including over 500 never before served by ASR. Automatic evaluations show substantial gains over prior systems, especially in low-resource conditions, and strong generalization. We release Omnilingual ASR as a family of models, from 300M variants for low-power devices to 7B for maximum accuracy. We reflect on the ethical considerations shaping this design and conclude by discussing its societal impact. In particular, we highlight how open-sourcing models and tools can lower barriers for researchers and communities, inviting new forms of participation. Open-source artifacts are available at https://github.com/facebookresearch/omnilingual-asr.
BOUQuET: dataset, Benchmark and Open initiative for Universal Quality Evaluation in Translation
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents BOUQuET, a multicentric and multi-register/domain dataset and benchmark, and its broader collaborative extension initiative. This dataset is handcrafted in non-English languages first, each of these source languages being represented among the 23 languages commonly used by half of the world's population and therefore having the potential to serve as pivot languages that will enable more accurate translations. The dataset is specially designed to avoid contamination and be multicentric, so as to enforce representation of multilingual language features. In addition, the dataset goes beyond the sentence level, as it is organized in paragraphs of various lengths. Compared with related machine translation (MT) datasets, we show that BOUQuET has a broader representation of domains while simplifying the translation task for non-experts. Therefore, BOUQuET is specially suitable for the open initiative and call for translation participation that we are launching to extend it to a multi-way parallel corpus to any written language.
LCFO: Long Context and Long Form Output Dataset and Benchmarking
Dec 12, 2024



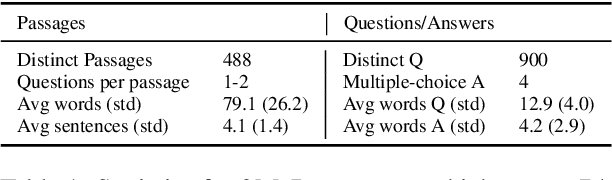
Abstract:This paper presents the Long Context and Form Output (LCFO) benchmark, a novel evaluation framework for assessing gradual summarization and summary expansion capabilities across diverse domains. LCFO consists of long input documents (5k words average length), each of which comes with three summaries of different lengths (20%, 10%, and 5% of the input text), as well as approximately 15 questions and answers (QA) related to the input content. Notably, LCFO also provides alignments between specific QA pairs and corresponding summaries in 7 domains. The primary motivation behind providing summaries of different lengths is to establish a controllable framework for generating long texts from shorter inputs, i.e. summary expansion. To establish an evaluation metric framework for summarization and summary expansion, we provide human evaluation scores for human-generated outputs, as well as results from various state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). GPT-4o-mini achieves best human scores among automatic systems in both summarization and summary expansion tasks (~ +10% and +20%, respectively). It even surpasses human output quality in the case of short summaries (~ +7%). Overall automatic metrics achieve low correlations with human evaluation scores (~ 0.4) but moderate correlation on specific evaluation aspects such as fluency and attribution (~ 0.6). The LCFO benchmark offers a standardized platform for evaluating summarization and summary expansion performance, as well as corresponding automatic metrics, thereby providing an important evaluation framework to advance generative AI.
2M-BELEBELE: Highly Multilingual Speech and American Sign Language Comprehension Dataset
Dec 11, 2024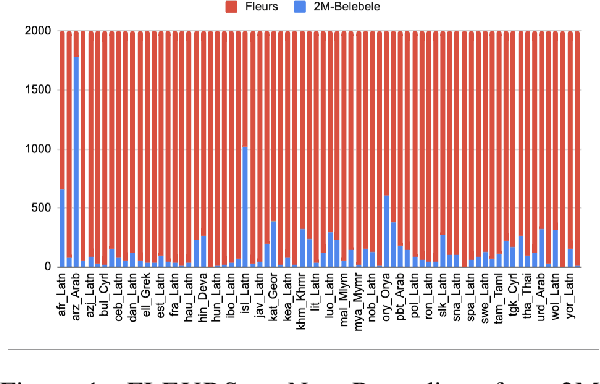
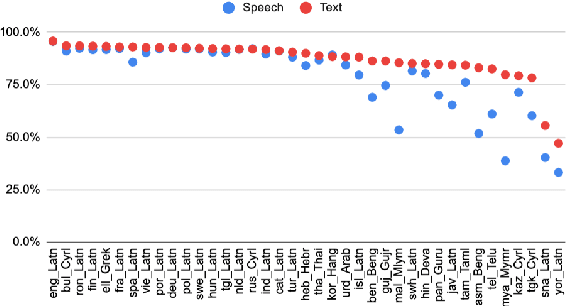
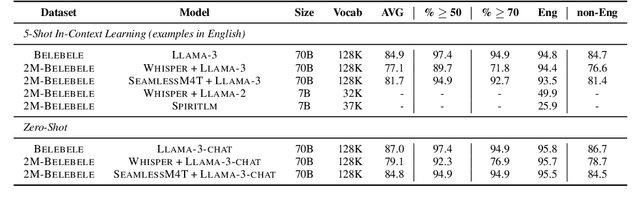
Abstract:We introduce the first highly multilingual speech and American Sign Language (ASL) comprehension dataset by extending BELEBELE. Our dataset covers 74 spoken languages at the intersection of BELEBELE and FLEURS, and one sign language (ASL). We evaluate 2M-BELEBELE dataset for both 5-shot and zero-shot settings and across languages, the speech comprehension accuracy is ~ 8% average lower compared to reading comprehension.
Y-NQ: English-Yorùbá Evaluation dataset for Open-Book Reading Comprehension and Text Generation
Dec 11, 2024
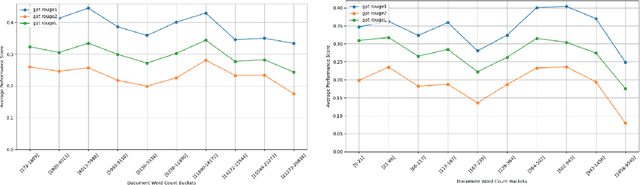
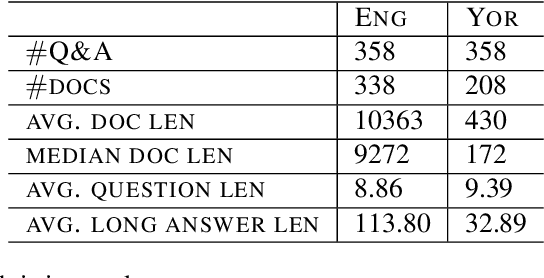
Abstract:The purpose of this work is to share an English-Yor\`ub\'a evaluation dataset for open-book reading comprehension and text generation to assess the performance of models both in a high- and a low- resource language. The dataset contains 358 questions and answers on 338 English documents and 208 Yor\`ub\'a documents. The average document length is ~ 10k words for English and 430 words for Yor\`ub\'a. Experiments show a consistent disparity in performance between the two languages, with Yor\`ub\'a falling behind English for automatic metrics even if documents are much shorter for this language. For a small set of documents with comparable length, performance of Yor\`ub\'a drops by x2.5 times. When analyzing performance by length, we observe that Yor\`ub\'a decreases performance dramatically for documents that reach 1500 words while English performance is barely affected at that length. Our dataset opens the door to showcasing if English LLM reading comprehension capabilities extend to Yor\`ub\'a, which for the evaluated LLMs is not the case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge