Unveiling the Role of Pretraining in Direct Speech Translation
Paper and Code
Sep 26, 2024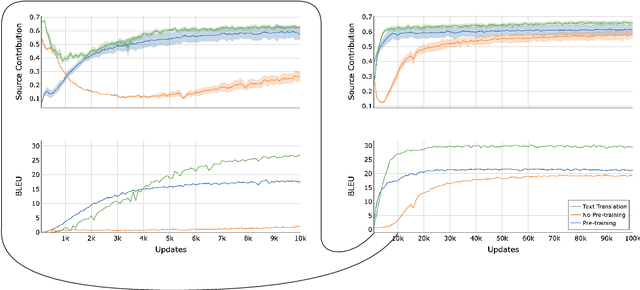
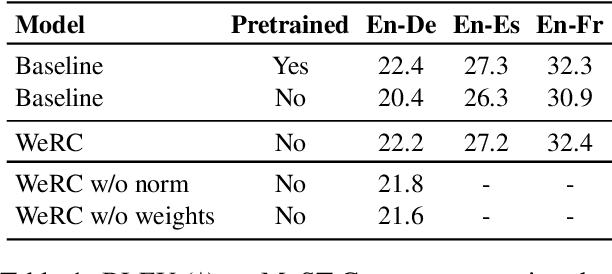
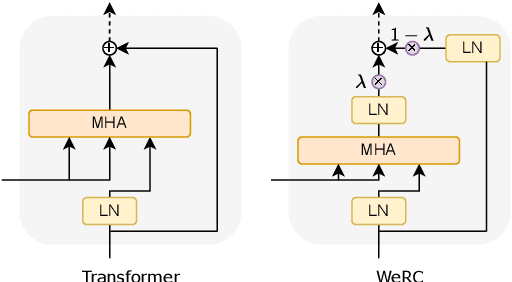
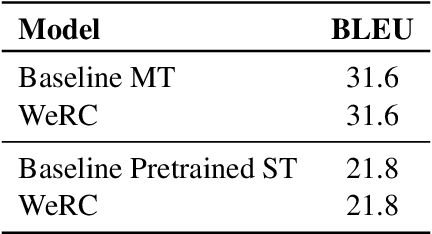
Direct speech-to-text translation systems encounter an important drawback in data scarcity. A common solution consists on pretraining the encoder on automatic speech recognition, hence losing efficiency in the training process. In this study, we compare the training dynamics of a system using a pretrained encoder, the conventional approach, and one trained from scratch. We observe that, throughout the training, the randomly initialized model struggles to incorporate information from the speech inputs for its predictions. Hence, we hypothesize that this issue stems from the difficulty of effectively training an encoder for direct speech translation. While a model trained from scratch needs to learn acoustic and semantic modeling simultaneously, a pretrained one can just focus on the latter. Based on these findings, we propose a subtle change in the decoder cross-attention to integrate source information from earlier steps in training. We show that with this change, the model trained from scratch can achieve comparable performance to the pretrained one, while reducing the training time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge