Bao Ge
FNF: Functional Network Fingerprint for Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The development of large language models (LLMs) is costly and has significant commercial value. Consequently, preventing unauthorized appropriation of open-source LLMs and protecting developers' intellectual property rights have become critical challenges. In this work, we propose the Functional Network Fingerprint (FNF), a training-free, sample-efficient method for detecting whether a suspect LLM is derived from a victim model, based on the consistency between their functional network activity. We demonstrate that models that share a common origin, even with differences in scale or architecture, exhibit highly consistent patterns of neuronal activity within their functional networks across diverse input samples. In contrast, models trained independently on distinct data or with different objectives fail to preserve such activity alignment. Unlike conventional approaches, our method requires only a few samples for verification, preserves model utility, and remains robust to common model modifications (such as fine-tuning, pruning, and parameter permutation), as well as to comparisons across diverse architectures and dimensionalities. FNF thus provides model owners and third parties with a simple, non-invasive, and effective tool for protecting LLM intellectual property. The code is available at https://github.com/WhatAboutMyStar/LLM_ACTIVATION.
The performances of the Chinese and U.S. Large Language Models on the Topic of Chinese Culture
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Cultural backgrounds shape individuals' perspectives and approaches to problem-solving. Since the emergence of GPT-1 in 2018, large language models (LLMs) have undergone rapid development. To date, the world's ten leading LLM developers are primarily based in China and the United States. To examine whether LLMs released by Chinese and U.S. developers exhibit cultural differences in Chinese-language settings, we evaluate their performance on questions about Chinese culture. This study adopts a direct-questioning paradigm to evaluate models such as GPT-5.1, DeepSeek-V3.2, Qwen3-Max, and Gemini2.5Pro. We assess their understanding of traditional Chinese culture, including history, literature, poetry, and related domains. Comparative analyses between LLMs developed in China and the U.S. indicate that Chinese models generally outperform their U.S. counterparts on these tasks. Among U.S.-developed models, Gemini 2.5Pro and GPT-5.1 achieve relatively higher accuracy. The observed performance differences may potentially arise from variations in training data distribution, localization strategies, and the degree of emphasis on Chinese cultural content during model development.
Pruning Large Language Models by Identifying and Preserving Functional Networks
Aug 07, 2025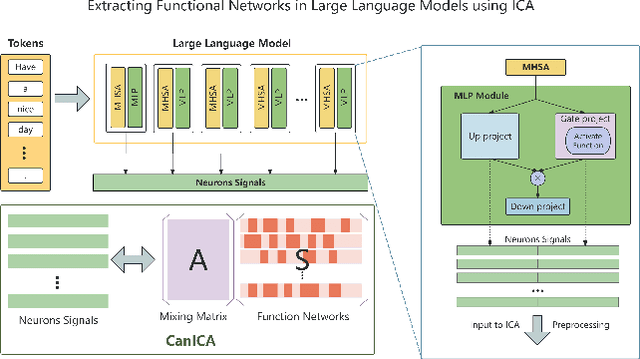
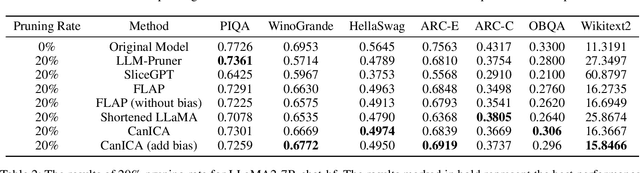
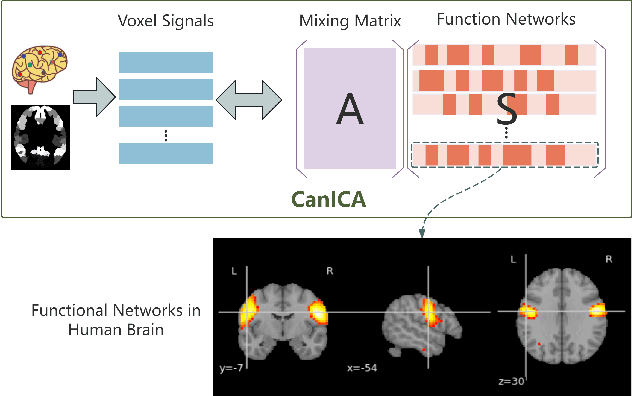

Abstract:Structured pruning is one of the representative techniques for compressing large language models (LLMs) to reduce GPU memory consumption and accelerate inference speed. It offers significant practical value in improving the efficiency of LLMs in real-world applications. Current structured pruning methods typically rely on assessment of the importance of the structure units and pruning the units with less importance. Most of them overlooks the interaction and collaboration among artificial neurons that are crucial for the functionalities of LLMs, leading to a disruption in the macro functional architecture of LLMs and consequently a pruning performance degradation. Inspired by the inherent similarities between artificial neural networks and functional neural networks in the human brain, we alleviate this challenge and propose to prune LLMs by identifying and preserving functional networks within LLMs in this study. To achieve this, we treat an LLM as a digital brain and decompose the LLM into functional networks, analogous to identifying functional brain networks in neuroimaging data. Afterwards, an LLM is pruned by preserving the key neurons within these functional networks. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can successfully identify and locate functional networks and key neurons in LLMs, enabling efficient model pruning. Our code is available at https://github.com/WhatAboutMyStar/LLM_ACTIVATION.
SwinECAT: A Transformer-based fundus disease classification model with Shifted Window Attention and Efficient Channel Attention
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:In recent years, artificial intelligence has been increasingly applied in the field of medical imaging. Among these applications, fundus image analysis presents special challenges, including small lesion areas in certain fundus diseases and subtle inter-disease differences, which can lead to reduced prediction accuracy and overfitting in the models. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the Transformer-based model SwinECAT, which combines the Shifted Window (Swin) Attention with the Efficient Channel Attention (ECA) Attention. SwinECAT leverages the Swin Attention mechanism in the Swin Transformer backbone to effectively capture local spatial structures and long-range dependencies within fundus images. The lightweight ECA mechanism is incorporated to guide the SwinECAT's attention toward critical feature channels, enabling more discriminative feature representation. In contrast to previous studies that typically classify fundus images into 4 to 6 categories, this work expands fundus disease classification to 9 distinct types, thereby enhancing the granularity of diagnosis. We evaluate our method on the Eye Disease Image Dataset (EDID) containing 16,140 fundus images for 9-category classification. Experimental results demonstrate that SwinECAT achieves 88.29\% accuracy, with weighted F1-score of 0.88 and macro F1-score of 0.90. The classification results of our proposed model SwinECAT significantly outperform the baseline Swin Transformer and multiple compared baseline models. To our knowledge, this represents the highest reported performance for 9-category classification on this public dataset.
Bridging Technology and Humanities: Evaluating the Impact of Large Language Models on Social Sciences Research with DeepSeek-R1
Mar 21, 2025



Abstract:In recent years, the development of Large Language Models (LLMs) has made significant breakthroughs in the field of natural language processing and has gradually been applied to the field of humanities and social sciences research. LLMs have a wide range of application value in the field of humanities and social sciences because of its strong text understanding, generation and reasoning capabilities. In humanities and social sciences research, LLMs can analyze large-scale text data and make inferences. This article analyzes the large language model DeepSeek-R1 from seven aspects: low-resource language translation, educational question-answering, student writing improvement in higher education, logical reasoning, educational measurement and psychometrics, public health policy analysis, and art education.Then we compare the answers given by DeepSeek-R1 in the seven aspects with the answers given by o1-preview. DeepSeek-R1 performs well in the humanities and social sciences, answering most questions correctly and logically, and can give reasonable analysis processes and explanations. Compared with o1-preview, it can automatically generate reasoning processes and provide more detailed explanations, which is suitable for beginners or people who need to have a detailed understanding of this knowledge, while o1-preview is more suitable for quick reading. Through analysis, it is found that LLM has broad application potential in the field of humanities and social sciences, and shows great advantages in improving text analysis efficiency, language communication and other fields. LLM's powerful language understanding and generation capabilities enable it to deeply explore complex problems in the field of humanities and social sciences, and provide innovative tools for academic research and practical applications.
Evaluation of OpenAI o1: Opportunities and Challenges of AGI
Sep 27, 2024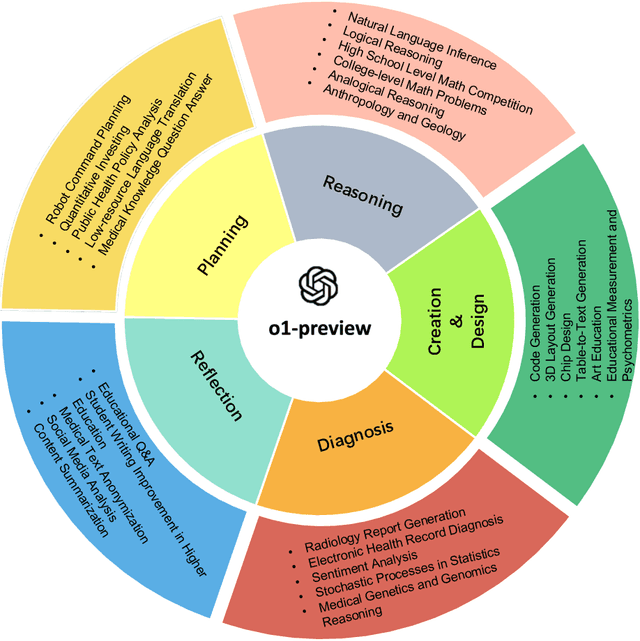
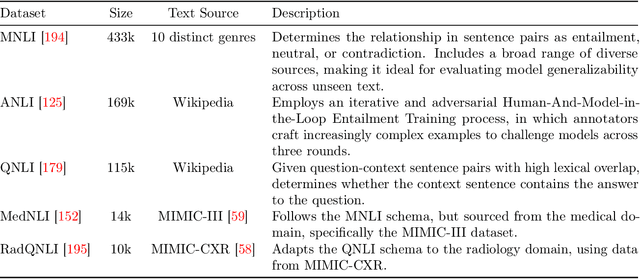
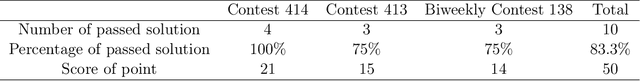
Abstract:This comprehensive study evaluates the performance of OpenAI's o1-preview large language model across a diverse array of complex reasoning tasks, spanning multiple domains, including computer science, mathematics, natural sciences, medicine, linguistics, and social sciences. Through rigorous testing, o1-preview demonstrated remarkable capabilities, often achieving human-level or superior performance in areas ranging from coding challenges to scientific reasoning and from language processing to creative problem-solving. Key findings include: -83.3% success rate in solving complex competitive programming problems, surpassing many human experts. -Superior ability in generating coherent and accurate radiology reports, outperforming other evaluated models. -100% accuracy in high school-level mathematical reasoning tasks, providing detailed step-by-step solutions. -Advanced natural language inference capabilities across general and specialized domains like medicine. -Impressive performance in chip design tasks, outperforming specialized models in areas such as EDA script generation and bug analysis. -Remarkable proficiency in anthropology and geology, demonstrating deep understanding and reasoning in these specialized fields. -Strong capabilities in quantitative investing. O1 has comprehensive financial knowledge and statistical modeling skills. -Effective performance in social media analysis, including sentiment analysis and emotion recognition. The model excelled particularly in tasks requiring intricate reasoning and knowledge integration across various fields. While some limitations were observed, including occasional errors on simpler problems and challenges with certain highly specialized concepts, the overall results indicate significant progress towards artificial general intelligence.
A Survey of Foundation Models for Music Understanding
Sep 15, 2024
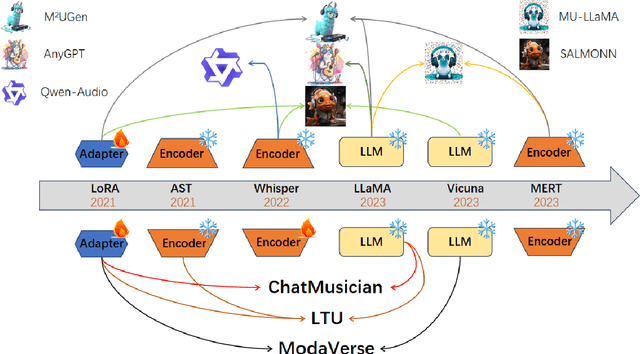
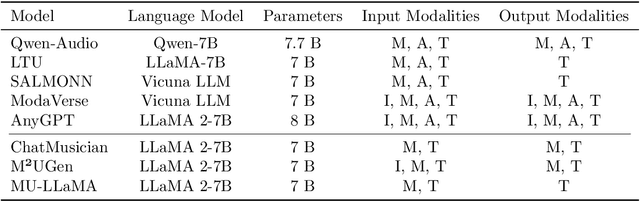
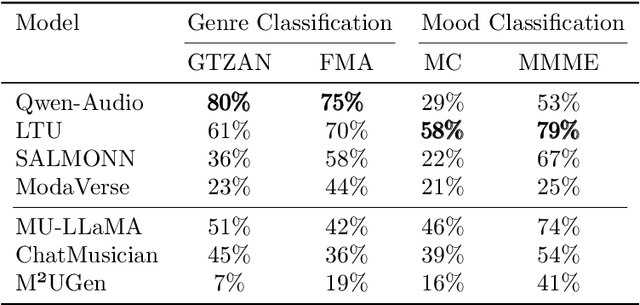
Abstract:Music is essential in daily life, fulfilling emotional and entertainment needs, and connecting us personally, socially, and culturally. A better understanding of music can enhance our emotions, cognitive skills, and cultural connections. The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has introduced new ways to analyze music, aiming to replicate human understanding of music and provide related services. While the traditional models focused on audio features and simple tasks, the recent development of large language models (LLMs) and foundation models (FMs), which excel in various fields by integrating semantic information and demonstrating strong reasoning abilities, could capture complex musical features and patterns, integrate music with language and incorporate rich musical, emotional and psychological knowledge. Therefore, they have the potential in handling complex music understanding tasks from a semantic perspective, producing outputs closer to human perception. This work, to our best knowledge, is one of the early reviews of the intersection of AI techniques and music understanding. We investigated, analyzed, and tested recent large-scale music foundation models in respect of their music comprehension abilities. We also discussed their limitations and proposed possible future directions, offering insights for researchers in this field.
A Comprehensive Review of Multimodal Large Language Models: Performance and Challenges Across Different Tasks
Aug 02, 2024
Abstract:In an era defined by the explosive growth of data and rapid technological advancements, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) stand at the forefront of artificial intelligence (AI) systems. Designed to seamlessly integrate diverse data types-including text, images, videos, audio, and physiological sequences-MLLMs address the complexities of real-world applications far beyond the capabilities of single-modality systems. In this paper, we systematically sort out the applications of MLLM in multimodal tasks such as natural language, vision, and audio. We also provide a comparative analysis of the focus of different MLLMs in the tasks, and provide insights into the shortcomings of current MLLMs, and suggest potential directions for future research. Through these discussions, this paper hopes to provide valuable insights for the further development and application of MLLM.
Investigation of the effectiveness of applying ChatGPT in Dialogic Teaching Using Electroencephalography
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, especially the emergence of large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, has presented significant prospects for application in the field of education. LLMs possess the capability to interpret knowledge, answer questions, and consider context, thus providing support for dialogic teaching to students. Therefore, an examination of the capacity of LLMs to effectively fulfill instructional roles, thereby facilitating student learning akin to human educators within dialogic teaching scenarios, is an exceptionally valuable research topic. This research recruited 34 undergraduate students as participants, who were randomly divided into two groups. The experimental group engaged in dialogic teaching using ChatGPT, while the control group interacted with human teachers. Both groups learned the histogram equalization unit in the information-related course "Digital Image Processing". The research findings show comparable scores between the two groups on the retention test. However, students who engaged in dialogue with ChatGPT exhibited lower performance on the transfer test. Electroencephalography data revealed that students who interacted with ChatGPT exhibited higher levels of cognitive activity, suggesting that ChatGPT could help students establish a knowledge foundation and stimulate cognitive activity. However, its strengths on promoting students. knowledge application and creativity were insignificant. Based upon the research findings, it is evident that ChatGPT cannot fully excel in fulfilling teaching tasks in the dialogue teaching in information related courses. Combining ChatGPT with traditional human teachers might be a more ideal approach. The synergistic use of both can provide students with more comprehensive learning support, thus contributing to enhancing the quality of teaching.
Large Language Models for Robotics: Opportunities, Challenges, and Perspectives
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have undergone significant expansion and have been increasingly integrated across various domains. Notably, in the realm of robot task planning, LLMs harness their advanced reasoning and language comprehension capabilities to formulate precise and efficient action plans based on natural language instructions. However, for embodied tasks, where robots interact with complex environments, text-only LLMs often face challenges due to a lack of compatibility with robotic visual perception. This study provides a comprehensive overview of the emerging integration of LLMs and multimodal LLMs into various robotic tasks. Additionally, we propose a framework that utilizes multimodal GPT-4V to enhance embodied task planning through the combination of natural language instructions and robot visual perceptions. Our results, based on diverse datasets, indicate that GPT-4V effectively enhances robot performance in embodied tasks. This extensive survey and evaluation of LLMs and multimodal LLMs across a variety of robotic tasks enriches the understanding of LLM-centric embodied intelligence and provides forward-looking insights toward bridging the gap in Human-Robot-Environment interaction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge