Image Imputation
Image imputation is the task of creating plausible images from low-resolution images or images with missing data.
Papers and Code
Theoretical Analysis of Measure Consistency Regularization for Partially Observed Data
Feb 01, 2026The problem of corrupted data, missing features, or missing modalities continues to plague the modern machine learning landscape. To address this issue, a class of regularization methods that enforce consistency between imputed and fully observed data has emerged as a promising approach for improving model generalization, particularly in partially observed settings. We refer to this class of methods as Measure Consistency Regularization (MCR). Despite its empirical success in various applications, such as image inpainting, data imputation and semi-supervised learning, a fundamental understanding of the theoretical underpinnings of MCR remains limited. This paper bridges this gap by offering theoretical insights into why, when, and how MCR enhances imputation quality under partial observability, viewed through the lens of neural network distance. Our theoretical analysis identifies the term responsible for MCR's generalization advantage and extends to the imperfect training regime, demonstrating that this advantage is not always guaranteed. Guided by these insights, we propose a novel training protocol that monitors the duality gap to determine an early stopping point that preserves the generalization benefit. We then provide detailed empirical evidence to support our theoretical claims and to show the effectiveness and accuracy of our proposed stopping condition. We further provide a set of real-world data simulations to show the versatility of MCR under different model architectures designed for different data sources.
Multi-modal Imputation for Alzheimer's Disease Classification
Jan 28, 2026Deep learning has been successful in predicting neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Combining multiple imaging modalities, such as T1-weighted (T1) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) scans, can increase diagnostic performance. However, complete multimodal datasets are not always available. We use a conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic model to impute missing DWI scans from T1 scans. We perform extensive experiments to evaluate whether such imputation improves the accuracy of uni-modal and bi-modal deep learning models for 3-way Alzheimer's disease classification-cognitively normal, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's disease. We observe improvements in several metrics, particularly those sensitive to minority classes, for several imputation configurations.
Inference-Time Dynamic Modality Selection for Incomplete Multimodal Classification
Jan 30, 2026Multimodal deep learning (MDL) has achieved remarkable success across various domains, yet its practical deployment is often hindered by incomplete multimodal data. Existing incomplete MDL methods either discard missing modalities, risking the loss of valuable task-relevant information, or recover them, potentially introducing irrelevant noise, leading to the discarding-imputation dilemma. To address this dilemma, in this paper, we propose DyMo, a new inference-time dynamic modality selection framework that adaptively identifies and integrates reliable recovered modalities, fully exploring task-relevant information beyond the conventional discard-or-impute paradigm. Central to DyMo is a novel selection algorithm that maximizes multimodal task-relevant information for each test sample. Since direct estimation of such information at test time is intractable due to the unknown data distribution, we theoretically establish a connection between information and the task loss, which we compute at inference time as a tractable proxy. Building on this, a novel principled reward function is proposed to guide modality selection. In addition, we design a flexible multimodal network architecture compatible with arbitrary modality combinations, alongside a tailored training strategy for robust representation learning. Extensive experiments on diverse natural and medical image datasets show that DyMo significantly outperforms state-of-the-art incomplete/dynamic MDL methods across various missing-data scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com//siyi-wind/DyMo.
Handling Missing Modalities in Multimodal Survival Prediction for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Jan 15, 2026Accurate survival prediction in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) requires the integration of heterogeneous clinical, radiological, and histopathological information. While Multimodal Deep Learning (MDL) offers a promises for precision prognosis and survival prediction, its clinical applicability is severely limited by small cohort sizes and the presence of missing modalities, often forcing complete-case filtering or aggressive imputation. In this work, we present a missing-aware multimodal survival framework that integrates Computed Tomography (CT), Whole-Slide Histopathology (WSI) Images, and structured clinical variables for overall survival modeling in unresectable stage II-III NSCLC. By leveraging Foundation Models (FM) for modality-specific feature extraction and a missing-aware encoding strategy, the proposed approach enables intermediate multimodal fusion under naturally incomplete modality profiles. The proposed architecture is resilient to missing modalities by design, allowing the model to utilize all available data without being forced to drop patients during training or inference. Experimental results demonstrate that intermediate fusion consistently outperforms unimodal baselines as well as early and late fusion strategies, with the strongest performance achieved by the fusion of WSI and clinical modalities (73.30 C-index). Further analyses of modality importance reveal an adaptive behavior in which less informative modalities, i.e., CT modality, are automatically down-weighted and contribute less to the final survival prediction.
PI-NAIM: Path-Integrated Neural Adaptive Imputation Model
Nov 14, 2025Medical imaging and multi-modal clinical settings often face the challange of missing modality in their diagnostic pipelines. Existing imputation methods either lack representational capacity or are computationally expensive. We propose PI-NAIM, a novel dual-path architecture that dynamically routes samples to optimized imputation approaches based on missingness complexity. Our framework integrates: (1) intelligent path routing that directs low missingness samples to efficient statistical imputation (MICE) and complex patterns to powerful neural networks (GAIN with temporal analysis); (2) cross-path attention fusion that leverages missingness-aware embeddings to intelligently combine both branches; and (3) end-to-end joint optimization of imputation accuracy and downstream task performance. Extensive experiments on MIMIC-III and multimodal benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, achieving RMSE of 0.108 (vs. baselines' 0.119-0.152) and substantial gains in downstream tasks with an AUROC of 0.812 for mortality prediction. PI-NAIM's modular design enables seamless integration into vision pipelines handling incomplete sensor measurements, missing modalities, or corrupted inputs, providing a unified solution for real-world scenario. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/AfifaKhaled/PI-NAIM-Path-Integrated-Neural-Adaptive-Imputation-Model
IBMA: An Imputation-Based Mixup Augmentation Using Self-Supervised Learning for Time Series Data
Nov 11, 2025Data augmentation in time series forecasting plays a crucial role in enhancing model performance by introducing variability while maintaining the underlying temporal patterns. However, time series data offers fewer augmentation strategies compared to fields such as image or text, with advanced techniques like Mixup rarely being used. In this work, we propose a novel approach, Imputation-Based Mixup Augmentation (IBMA), which combines Imputation-Augmented data with Mixup augmentation to bolster model generalization and improve forecasting performance. We evaluate the effectiveness of this method across several forecasting models, including DLinear (MLP), TimesNet (CNN), and iTrainformer (Transformer), these models represent some of the most recent advances in time series forecasting. Our experiments, conducted on four datasets (ETTh1, ETTh2, ETTm1, ETTm2) and compared against eight other augmentation techniques, demonstrate that IBMA consistently enhances performance, achieving 22 improvements out of 24 instances, with 10 of those being the best performances, particularly with iTrainformer imputation.
FrogDeepSDM: Improving Frog Counting and Occurrence Prediction Using Multimodal Data and Pseudo-Absence Imputation
Oct 22, 2025Monitoring species distribution is vital for conservation efforts, enabling the assessment of environmental impacts and the development of effective preservation strategies. Traditional data collection methods, including citizen science, offer valuable insights but remain limited in coverage and completeness. Species Distribution Modelling (SDM) helps address these gaps by using occurrence data and environmental variables to predict species presence across large regions. In this study, we enhance SDM accuracy for frogs (Anura) by applying deep learning and data imputation techniques using data from the "EY - 2022 Biodiversity Challenge." Our experiments show that data balancing significantly improved model performance, reducing the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) from 189 to 29 in frog counting tasks. Feature selection identified key environmental factors influencing occurrence, optimizing inputs while maintaining predictive accuracy. The multimodal ensemble model, integrating land cover, NDVI, and other environmental inputs, outperformed individual models and showed robust generalization across unseen regions. The fusion of image and tabular data improved both frog counting and habitat classification, achieving 84.9% accuracy with an AUC of 0.90. This study highlights the potential of multimodal learning and data preprocessing techniques such as balancing and imputation to improve predictive ecological modeling when data are sparse or incomplete, contributing to more precise and scalable biodiversity monitoring.
SAGCNet: Spatial-Aware Graph Completion Network for Missing Slice Imputation in Population CMR Imaging
Aug 09, 2025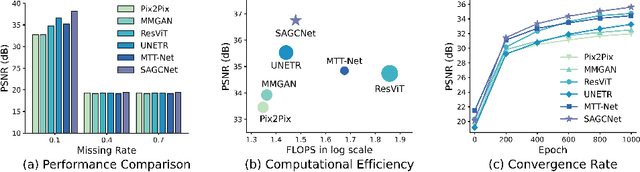
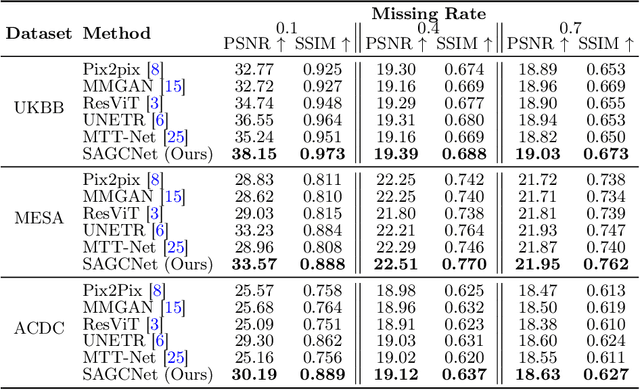
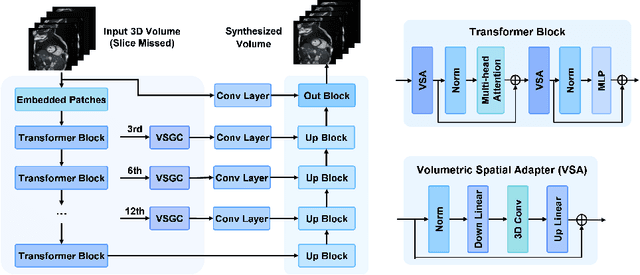
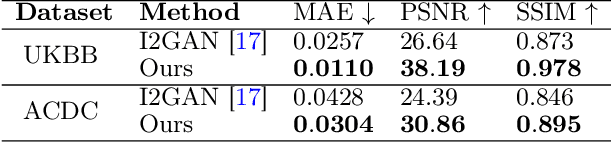
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed soft-tissue characteristics that assist in disease diagnosis and screening. However, the accuracy of clinical practice is often hindered by missing or unusable slices due to various factors. Volumetric MRI synthesis methods have been developed to address this issue by imputing missing slices from available ones. The inherent 3D nature of volumetric MRI data, such as cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR), poses significant challenges for missing slice imputation approaches, including (1) the difficulty of modeling local inter-slice correlations and dependencies of volumetric slices, and (2) the limited exploration of crucial 3D spatial information and global context. In this study, to mitigate these issues, we present Spatial-Aware Graph Completion Network (SAGCNet) to overcome the dependency on complete volumetric data, featuring two main innovations: (1) a volumetric slice graph completion module that incorporates the inter-slice relationships into a graph structure, and (2) a volumetric spatial adapter component that enables our model to effectively capture and utilize various forms of 3D spatial context. Extensive experiments on cardiac MRI datasets demonstrate that SAGCNet is capable of synthesizing absent CMR slices, outperforming competitive state-of-the-art MRI synthesis methods both quantitatively and qualitatively. Notably, our model maintains superior performance even with limited slice data.
Sparser2Sparse: Single-shot Sparser-to-Sparse Learning for Spatial Transcriptomics Imputation with Natural Image Co-learning
Jul 22, 2025Spatial transcriptomics (ST) has revolutionized biomedical research by enabling high resolution gene expression profiling within tissues. However, the high cost and scarcity of high resolution ST data remain significant challenges. We present Single-shot Sparser-to-Sparse (S2S-ST), a novel framework for accurate ST imputation that requires only a single and low-cost sparsely sampled ST dataset alongside widely available natural images for co-training. Our approach integrates three key innovations: (1) a sparser-to-sparse self-supervised learning strategy that leverages intrinsic spatial patterns in ST data, (2) cross-domain co-learning with natural images to enhance feature representation, and (3) a Cascaded Data Consistent Imputation Network (CDCIN) that iteratively refines predictions while preserving sampled gene data fidelity. Extensive experiments on diverse tissue types, including breast cancer, liver, and lymphoid tissue, demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in imputation accuracy. By enabling robust ST reconstruction from sparse inputs, our framework significantly reduces reliance on costly high resolution data, facilitating potential broader adoption in biomedical research and clinical applications.
Generative Feature Imputing - A Technique for Error-resilient Semantic Communication
Aug 25, 2025Semantic communication (SemCom) has emerged as a promising paradigm for achieving unprecedented communication efficiency in sixth-generation (6G) networks by leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to extract and transmit the underlying meanings of source data. However, deploying SemCom over digital systems presents new challenges, particularly in ensuring robustness against transmission errors that may distort semantically critical content. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel framework, termed generative feature imputing, which comprises three key techniques. First, we introduce a spatial error concentration packetization strategy that spatially concentrates feature distortions by encoding feature elements based on their channel mappings, a property crucial for both the effectiveness and reduced complexity of the subsequent techniques. Second, building on this strategy, we propose a generative feature imputing method that utilizes a diffusion model to efficiently reconstruct missing features caused by packet losses. Finally, we develop a semantic-aware power allocation scheme that enables unequal error protection by allocating transmission power according to the semantic importance of each packet. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms conventional approaches, such as Deep Joint Source-Channel Coding (DJSCC) and JPEG2000, under block fading conditions, achieving higher semantic accuracy and lower Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge