Chongyu Qu
Explainable Pathomics Feature Visualization via Correlation-aware Conditional Feature Editing
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Pathomics is a recent approach that offers rich quantitative features beyond what black-box deep learning can provide, supporting more reproducible and explainable biomarkers in digital pathology. However, many derived features (e.g., "second-order moment") remain difficult to interpret, especially across different clinical contexts, which limits their practical adoption. Conditional diffusion models show promise for explainability through feature editing, but they typically assume feature independence**--**an assumption violated by intrinsically correlated pathomics features. Consequently, editing one feature while fixing others can push the model off the biological manifold and produce unrealistic artifacts. To address this, we propose a Manifold-Aware Diffusion (MAD) framework for controllable and biologically plausible cell nuclei editing. Unlike existing approaches, our method regularizes feature trajectories within a disentangled latent space learned by a variational auto-encoder (VAE). This ensures that manipulating a target feature automatically adjusts correlated attributes to remain within the learned distribution of real cells. These optimized features then guide a conditional diffusion model to synthesize high-fidelity images. Experiments demonstrate that our approach is able to navigate the manifold of pathomics features when editing those features. The proposed method outperforms baseline methods in conditional feature editing while preserving structural coherence.
AdaFuse: Adaptive Multimodal Fusion for Lung Cancer Risk Prediction via Reinforcement Learning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Multimodal fusion has emerged as a promising paradigm for disease diagnosis and prognosis, integrating complementary information from heterogeneous data sources such as medical images, clinical records, and radiology reports. However, existing fusion methods process all available modalities through the network, either treating them equally or learning to assign different contribution weights, leaving a fundamental question unaddressed: for a given patient, should certain modalities be used at all? We present AdaFuse, an adaptive multimodal fusion framework that leverages reinforcement learning (RL) to learn patient-specific modality selection and fusion strategies for lung cancer risk prediction. AdaFuse formulates multimodal fusion as a sequential decision process, where the policy network iteratively decides whether to incorporate an additional modality or proceed to prediction based on the information already acquired. This sequential formulation enables the model to condition each selection on previously observed modalities and terminate early when sufficient information is available, rather than committing to a fixed subset upfront. We evaluate AdaFuse on the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that AdaFuse achieves the highest AUC (0.762) compared to the best single-modality baseline (0.732), the best fixed fusion strategy (0.759), and adaptive baselines including DynMM (0.754) and MoE (0.742), while using fewer FLOPs than all triple-modality methods. Our work demonstrates the potential of reinforcement learning for personalized multimodal fusion in medical imaging, representing a shift from uniform fusion strategies toward adaptive diagnostic pipelines that learn when to consult additional modalities and when existing information suffices for accurate prediction.
MASC: Metal-Aware Sampling and Correction via Reinforcement Learning for Accelerated MRI
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Metal implants in MRI cause severe artifacts that degrade image quality and hinder clinical diagnosis. Traditional approaches address metal artifact reduction (MAR) and accelerated MRI acquisition as separate problems. We propose MASC, a unified reinforcement learning framework that jointly optimizes metal-aware k-space sampling and artifact correction for accelerated MRI. To enable supervised training, we construct a paired MRI dataset using physics-based simulation, generating k-space data and reconstructions for phantoms with and without metal implants. This paired dataset provides simulated 3D MRI scans with and without metal implants, where each metal-corrupted sample has an exactly matched clean reference, enabling direct supervision for both artifact reduction and acquisition policy learning. We formulate active MRI acquisition as a sequential decision-making problem, where an artifact-aware Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) agent learns to select k-space phase-encoding lines under a limited acquisition budget. The agent operates on undersampled reconstructions processed through a U-Net-based MAR network, learning patterns that maximize reconstruction quality. We further propose an end-to-end training scheme where the acquisition policy learns to select k-space lines that best support artifact removal while the MAR network simultaneously adapts to the resulting undersampling patterns. Experiments demonstrate that MASC's learned policies outperform conventional sampling strategies, and end-to-end training improves performance compared to using a frozen pre-trained MAR network, validating the benefit of joint optimization. Cross-dataset experiments on FastMRI with physics-based artifact simulation further confirm generalization to realistic clinical MRI data. The code and models of MASC have been made publicly available: https://github.com/hrlblab/masc
SCR2-ST: Combine Single Cell with Spatial Transcriptomics for Efficient Active Sampling via Reinforcement Learning
Dec 15, 2025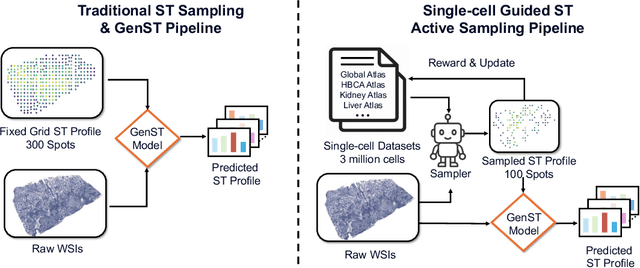
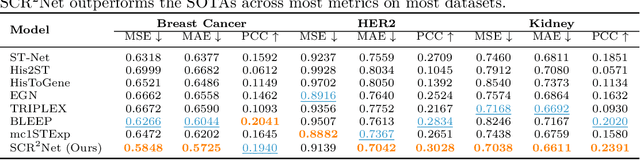
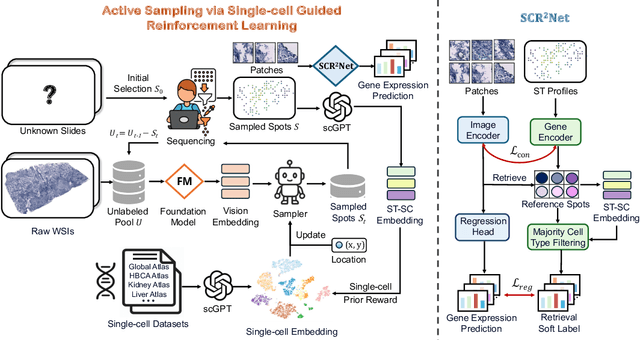
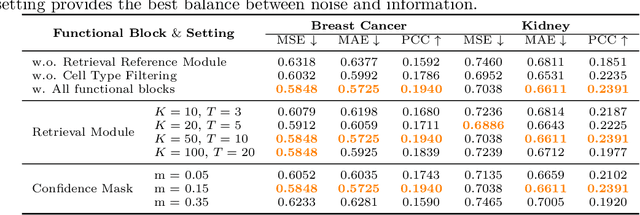
Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics (ST) is an emerging technology that enables researchers to investigate the molecular relationships underlying tissue morphology. However, acquiring ST data remains prohibitively expensive, and traditional fixed-grid sampling strategies lead to redundant measurements of morphologically similar or biologically uninformative regions, thus resulting in scarce data that constrain current methods. The well-established single-cell sequencing field, however, could provide rich biological data as an effective auxiliary source to mitigate this limitation. To bridge these gaps, we introduce SCR2-ST, a unified framework that leverages single-cell prior knowledge to guide efficient data acquisition and accurate expression prediction. SCR2-ST integrates a single-cell guided reinforcement learning-based (SCRL) active sampling and a hybrid regression-retrieval prediction network SCR2Net. SCRL combines single-cell foundation model embeddings with spatial density information to construct biologically grounded reward signals, enabling selective acquisition of informative tissue regions under constrained sequencing budgets. SCR2Net then leverages the actively sampled data through a hybrid architecture combining regression-based modeling with retrieval-augmented inference, where a majority cell-type filtering mechanism suppresses noisy matches and retrieved expression profiles serve as soft labels for auxiliary supervision. We evaluated SCR2-ST on three public ST datasets, demonstrating SOTA performance in both sampling efficiency and prediction accuracy, particularly under low-budget scenarios. Code is publicly available at: https://github.com/hrlblab/SCR2ST
Img2ST-Net: Efficient High-Resolution Spatial Omics Prediction from Whole Slide Histology Images via Fully Convolutional Image-to-Image Learning
Aug 20, 2025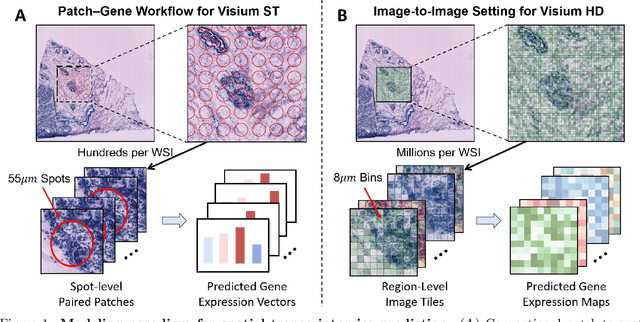
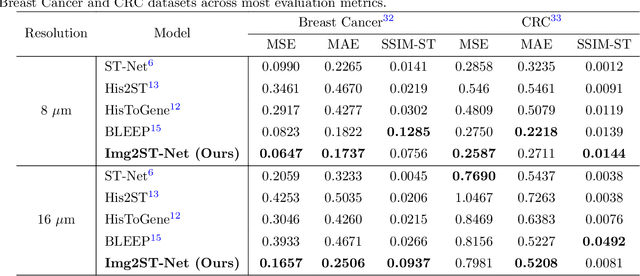
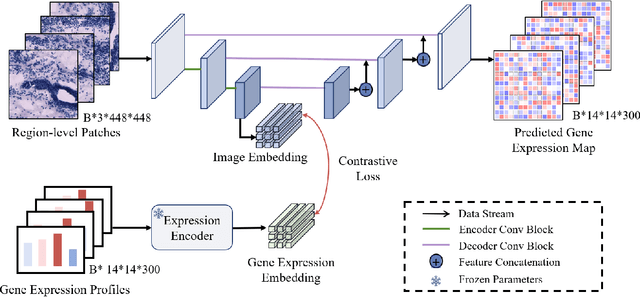
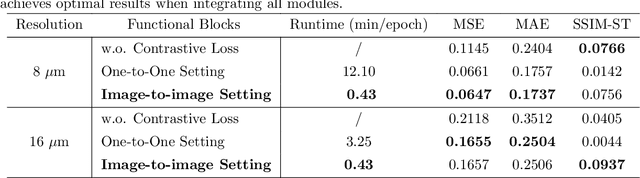
Abstract:Recent advances in multi-modal AI have demonstrated promising potential for generating the currently expensive spatial transcriptomics (ST) data directly from routine histology images, offering a means to reduce the high cost and time-intensive nature of ST data acquisition. However, the increasing resolution of ST, particularly with platforms such as Visium HD achieving 8um or finer, introduces significant computational and modeling challenges. Conventional spot-by-spot sequential regression frameworks become inefficient and unstable at this scale, while the inherent extreme sparsity and low expression levels of high-resolution ST further complicate both prediction and evaluation. To address these limitations, we propose Img2ST-Net, a novel histology-to-ST generation framework for efficient and parallel high-resolution ST prediction. Unlike conventional spot-by-spot inference methods, Img2ST-Net employs a fully convolutional architecture to generate dense, HD gene expression maps in a parallelized manner. By modeling HD ST data as super-pixel representations, the task is reformulated from image-to-omics inference into a super-content image generation problem with hundreds or thousands of output channels. This design not only improves computational efficiency but also better preserves the spatial organization intrinsic to spatial omics data. To enhance robustness under sparse expression patterns, we further introduce SSIM-ST, a structural-similarity-based evaluation metric tailored for high-resolution ST analysis. We present a scalable, biologically coherent framework for high-resolution ST prediction. Img2ST-Net offers a principled solution for efficient and accurate ST inference at scale. Our contributions lay the groundwork for next-generation ST modeling that is robust and resolution-aware. The source code has been made publicly available at https://github.com/hrlblab/Img2ST-Net.
Cohort-Aware Agents for Individualized Lung Cancer Risk Prediction Using a Retrieval-Augmented Model Selection Framework
Aug 20, 2025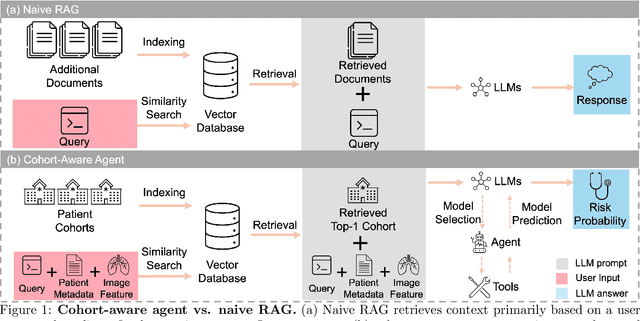
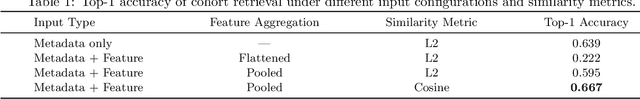
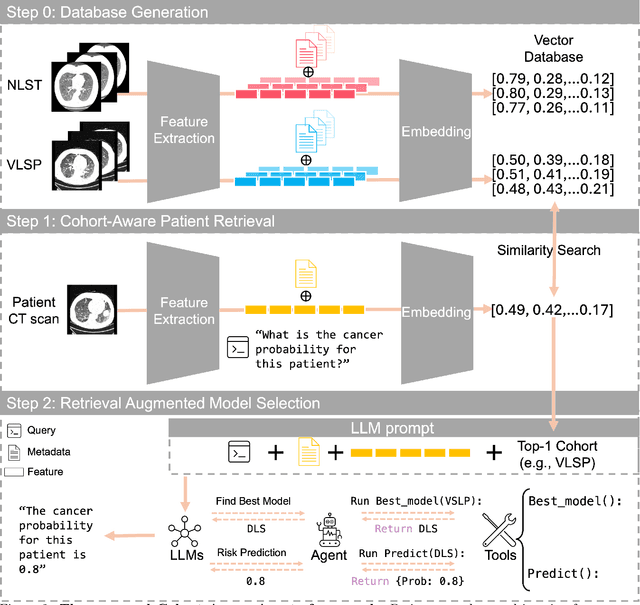
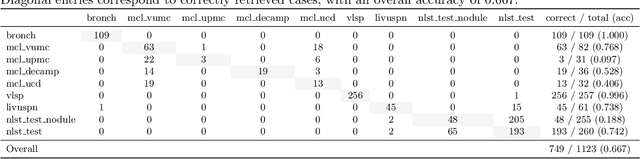
Abstract:Accurate lung cancer risk prediction remains challenging due to substantial variability across patient populations and clinical settings -- no single model performs best for all cohorts. To address this, we propose a personalized lung cancer risk prediction agent that dynamically selects the most appropriate model for each patient by combining cohort-specific knowledge with modern retrieval and reasoning techniques. Given a patient's CT scan and structured metadata -- including demographic, clinical, and nodule-level features -- the agent first performs cohort retrieval using FAISS-based similarity search across nine diverse real-world cohorts to identify the most relevant patient population from a multi-institutional database. Second, a Large Language Model (LLM) is prompted with the retrieved cohort and its associated performance metrics to recommend the optimal prediction algorithm from a pool of eight representative models, including classical linear risk models (e.g., Mayo, Brock), temporally-aware models (e.g., TDVIT, DLSTM), and multi-modal computer vision-based approaches (e.g., Liao, Sybil, DLS, DLI). This two-stage agent pipeline -- retrieval via FAISS and reasoning via LLM -- enables dynamic, cohort-aware risk prediction personalized to each patient's profile. Building on this architecture, the agent supports flexible and cohort-driven model selection across diverse clinical populations, offering a practical path toward individualized risk assessment in real-world lung cancer screening.
DeepAndes: A Self-Supervised Vision Foundation Model for Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing Imagery of the Andes
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:By mapping sites at large scales using remotely sensed data, archaeologists can generate unique insights into long-term demographic trends, inter-regional social networks, and past adaptations to climate change. Remote sensing surveys complement field-based approaches, and their reach can be especially great when combined with deep learning and computer vision techniques. However, conventional supervised deep learning methods face challenges in annotating fine-grained archaeological features at scale. While recent vision foundation models have shown remarkable success in learning large-scale remote sensing data with minimal annotations, most off-the-shelf solutions are designed for RGB images rather than multi-spectral satellite imagery, such as the 8-band data used in our study. In this paper, we introduce DeepAndes, a transformer-based vision foundation model trained on three million multi-spectral satellite images, specifically tailored for Andean archaeology. DeepAndes incorporates a customized DINOv2 self-supervised learning algorithm optimized for 8-band multi-spectral imagery, marking the first foundation model designed explicitly for the Andes region. We evaluate its image understanding performance through imbalanced image classification, image instance retrieval, and pixel-level semantic segmentation tasks. Our experiments show that DeepAndes achieves superior F1 scores, mean average precision, and Dice scores in few-shot learning scenarios, significantly outperforming models trained from scratch or pre-trained on smaller datasets. This underscores the effectiveness of large-scale self-supervised pre-training in archaeological remote sensing. Codes will be available on https://github.com/geopacha/DeepAndes.
MagNet: Multi-Level Attention Graph Network for Predicting High-Resolution Spatial Transcriptomics
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:The rapid development of spatial transcriptomics (ST) offers new opportunities to explore the gene expression patterns within the spatial microenvironment. Current research integrates pathological images to infer gene expression, addressing the high costs and time-consuming processes to generate spatial transcriptomics data. However, as spatial transcriptomics resolution continues to improve, existing methods remain primarily focused on gene expression prediction at low-resolution spot levels. These methods face significant challenges, especially the information bottleneck, when they are applied to high-resolution HD data. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces MagNet, a multi-level attention graph network designed for accurate prediction of high-resolution HD data. MagNet employs cross-attention layers to integrate features from multi-resolution image patches hierarchically and utilizes a GAT-Transformer module to aggregate neighborhood information. By integrating multilevel features, MagNet overcomes the limitations posed by low-resolution inputs in predicting high-resolution gene expression. We systematically evaluated MagNet and existing ST prediction models on both a private spatial transcriptomics dataset and a public dataset at three different resolution levels. The results demonstrate that MagNet achieves state-of-the-art performance at both spot level and high-resolution bin levels, providing a novel methodology and benchmark for future research and applications in high-resolution HD-level spatial transcriptomics. Code is available at https://github.com/Junchao-Zhu/MagNet.
Post-Training Quantization for 3D Medical Image Segmentation: A Practical Study on Real Inference Engines
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:Quantizing deep neural networks ,reducing the precision (bit-width) of their computations, can remarkably decrease memory usage and accelerate processing, making these models more suitable for large-scale medical imaging applications with limited computational resources. However, many existing methods studied "fake quantization", which simulates lower precision operations during inference, but does not actually reduce model size or improve real-world inference speed. Moreover, the potential of deploying real 3D low-bit quantization on modern GPUs is still unexplored. In this study, we introduce a real post-training quantization (PTQ) framework that successfully implements true 8-bit quantization on state-of-the-art (SOTA) 3D medical segmentation models, i.e., U-Net, SegResNet, SwinUNETR, nnU-Net, UNesT, TransUNet, ST-UNet,and VISTA3D. Our approach involves two main steps. First, we use TensorRT to perform fake quantization for both weights and activations with unlabeled calibration dataset. Second, we convert this fake quantization into real quantization via TensorRT engine on real GPUs, resulting in real-world reductions in model size and inference latency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework effectively performs 8-bit quantization on GPUs without sacrificing model performance. This advancement enables the deployment of efficient deep learning models in medical imaging applications where computational resources are constrained. The code and models have been released, including U-Net, TransUNet pretrained on the BTCV dataset for abdominal (13-label) segmentation, UNesT pretrained on the Whole Brain Dataset for whole brain (133-label) segmentation, and nnU-Net, SegResNet, SwinUNETR and VISTA3D pretrained on TotalSegmentator V2 for full body (104-label) segmentation. https://github.com/hrlblab/PTQ.
ASIGN: An Anatomy-aware Spatial Imputation Graphic Network for 3D Spatial Transcriptomics
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics (ST) is an emerging technology that enables medical computer vision scientists to automatically interpret the molecular profiles underlying morphological features. Currently, however, most deep learning-based ST analyses are limited to two-dimensional (2D) sections, which can introduce diagnostic errors due to the heterogeneity of pathological tissues across 3D sections. Expanding ST to three-dimensional (3D) volumes is challenging due to the prohibitive costs; a 2D ST acquisition already costs over 50 times more than whole slide imaging (WSI), and a full 3D volume with 10 sections can be an order of magnitude more expensive. To reduce costs, scientists have attempted to predict ST data directly from WSI without performing actual ST acquisition. However, these methods typically yield unsatisfying results. To address this, we introduce a novel problem setting: 3D ST imputation using 3D WSI histology sections combined with a single 2D ST slide. To do so, we present the Anatomy-aware Spatial Imputation Graph Network (ASIGN) for more precise, yet affordable, 3D ST modeling. The ASIGN architecture extends existing 2D spatial relationships into 3D by leveraging cross-layer overlap and similarity-based expansion. Moreover, a multi-level spatial attention graph network integrates features comprehensively across different data sources. We evaluated ASIGN on three public spatial transcriptomics datasets, with experimental results demonstrating that ASIGN achieves state-of-the-art performance on both 2D and 3D scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/hrlblab/ASIGN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge