Mengmeng Yin
How Close Are We? Limitations and Progress of AI Models in Banff Lesion Scoring
Oct 31, 2025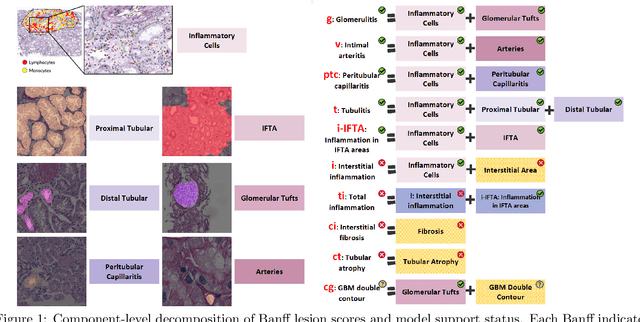
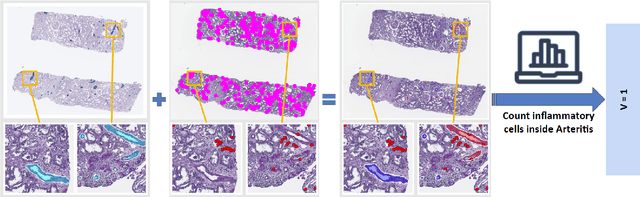
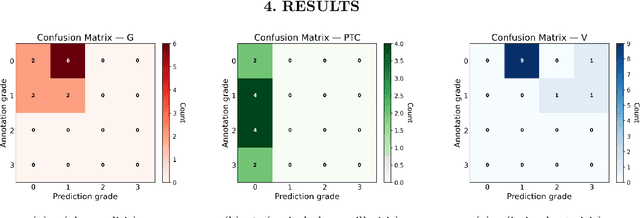
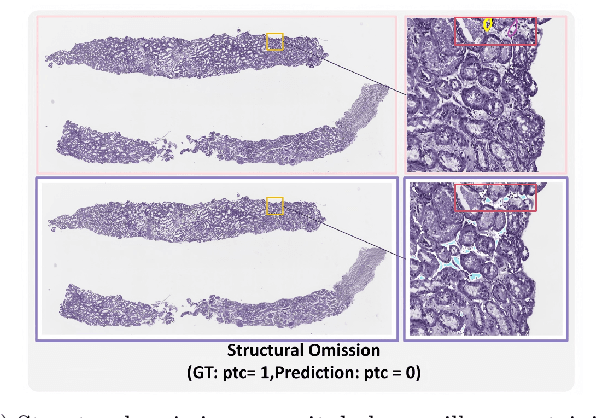
Abstract:The Banff Classification provides the global standard for evaluating renal transplant biopsies, yet its semi-quantitative nature, complex criteria, and inter-observer variability present significant challenges for computational replication. In this study, we explore the feasibility of approximating Banff lesion scores using existing deep learning models through a modular, rule-based framework. We decompose each Banff indicator - such as glomerulitis (g), peritubular capillaritis (ptc), and intimal arteritis (v) - into its constituent structural and inflammatory components, and assess whether current segmentation and detection tools can support their computation. Model outputs are mapped to Banff scores using heuristic rules aligned with expert guidelines, and evaluated against expert-annotated ground truths. Our findings highlight both partial successes and critical failure modes, including structural omission, hallucination, and detection ambiguity. Even when final scores match expert annotations, inconsistencies in intermediate representations often undermine interpretability. These results reveal the limitations of current AI pipelines in replicating computational expert-level grading, and emphasize the importance of modular evaluation and computational Banff grading standard in guiding future model development for transplant pathology.
Img2ST-Net: Efficient High-Resolution Spatial Omics Prediction from Whole Slide Histology Images via Fully Convolutional Image-to-Image Learning
Aug 20, 2025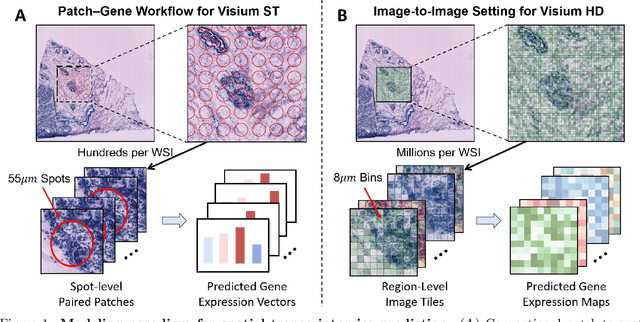
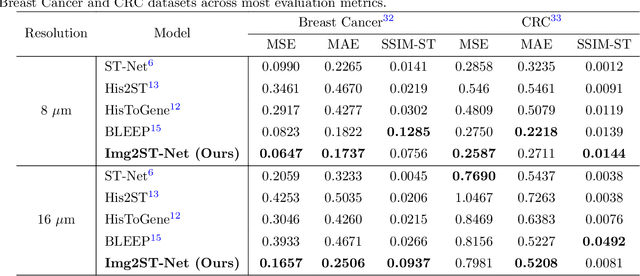
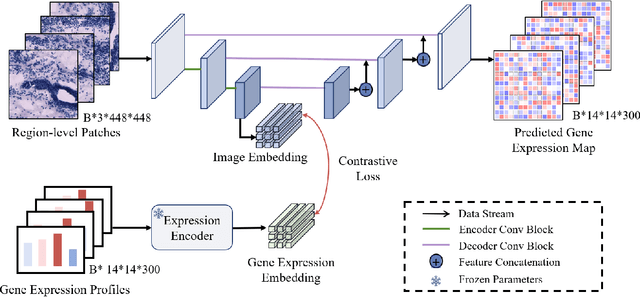
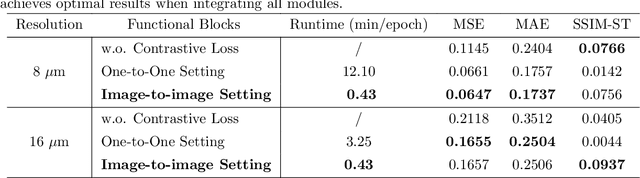
Abstract:Recent advances in multi-modal AI have demonstrated promising potential for generating the currently expensive spatial transcriptomics (ST) data directly from routine histology images, offering a means to reduce the high cost and time-intensive nature of ST data acquisition. However, the increasing resolution of ST, particularly with platforms such as Visium HD achieving 8um or finer, introduces significant computational and modeling challenges. Conventional spot-by-spot sequential regression frameworks become inefficient and unstable at this scale, while the inherent extreme sparsity and low expression levels of high-resolution ST further complicate both prediction and evaluation. To address these limitations, we propose Img2ST-Net, a novel histology-to-ST generation framework for efficient and parallel high-resolution ST prediction. Unlike conventional spot-by-spot inference methods, Img2ST-Net employs a fully convolutional architecture to generate dense, HD gene expression maps in a parallelized manner. By modeling HD ST data as super-pixel representations, the task is reformulated from image-to-omics inference into a super-content image generation problem with hundreds or thousands of output channels. This design not only improves computational efficiency but also better preserves the spatial organization intrinsic to spatial omics data. To enhance robustness under sparse expression patterns, we further introduce SSIM-ST, a structural-similarity-based evaluation metric tailored for high-resolution ST analysis. We present a scalable, biologically coherent framework for high-resolution ST prediction. Img2ST-Net offers a principled solution for efficient and accurate ST inference at scale. Our contributions lay the groundwork for next-generation ST modeling that is robust and resolution-aware. The source code has been made publicly available at https://github.com/hrlblab/Img2ST-Net.
IRS: Incremental Relationship-guided Segmentation for Digital Pathology
May 28, 2025Abstract:Continual learning is rapidly emerging as a key focus in computer vision, aiming to develop AI systems capable of continuous improvement, thereby enhancing their value and practicality in diverse real-world applications. In healthcare, continual learning holds great promise for continuously acquired digital pathology data, which is collected in hospitals on a daily basis. However, panoramic segmentation on digital whole slide images (WSIs) presents significant challenges, as it is often infeasible to obtain comprehensive annotations for all potential objects, spanning from coarse structures (e.g., regions and unit objects) to fine structures (e.g., cells). This results in temporally and partially annotated data, posing a major challenge in developing a holistic segmentation framework. Moreover, an ideal segmentation model should incorporate new phenotypes, unseen diseases, and diverse populations, making this task even more complex. In this paper, we introduce a novel and unified Incremental Relationship-guided Segmentation (IRS) learning scheme to address temporally acquired, partially annotated data while maintaining out-of-distribution (OOD) continual learning capacity in digital pathology. The key innovation of IRS lies in its ability to realize a new spatial-temporal OOD continual learning paradigm by mathematically modeling anatomical relationships between existing and newly introduced classes through a simple incremental universal proposition matrix. Experimental results demonstrate that the IRS method effectively handles the multi-scale nature of pathological segmentation, enabling precise kidney segmentation across various structures (regions, units, and cells) as well as OOD disease lesions at multiple magnifications. This capability significantly enhances domain generalization, making IRS a robust approach for real-world digital pathology applications.
MagNet: Multi-Level Attention Graph Network for Predicting High-Resolution Spatial Transcriptomics
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:The rapid development of spatial transcriptomics (ST) offers new opportunities to explore the gene expression patterns within the spatial microenvironment. Current research integrates pathological images to infer gene expression, addressing the high costs and time-consuming processes to generate spatial transcriptomics data. However, as spatial transcriptomics resolution continues to improve, existing methods remain primarily focused on gene expression prediction at low-resolution spot levels. These methods face significant challenges, especially the information bottleneck, when they are applied to high-resolution HD data. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces MagNet, a multi-level attention graph network designed for accurate prediction of high-resolution HD data. MagNet employs cross-attention layers to integrate features from multi-resolution image patches hierarchically and utilizes a GAT-Transformer module to aggregate neighborhood information. By integrating multilevel features, MagNet overcomes the limitations posed by low-resolution inputs in predicting high-resolution gene expression. We systematically evaluated MagNet and existing ST prediction models on both a private spatial transcriptomics dataset and a public dataset at three different resolution levels. The results demonstrate that MagNet achieves state-of-the-art performance at both spot level and high-resolution bin levels, providing a novel methodology and benchmark for future research and applications in high-resolution HD-level spatial transcriptomics. Code is available at https://github.com/Junchao-Zhu/MagNet.
CASC-AI: Consensus-aware Self-corrective AI Agents for Noise Cell Segmentation
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Multi-class cell segmentation in high-resolution gigapixel whole slide images (WSI) is crucial for various clinical applications. However, training such models typically requires labor-intensive, pixel-wise annotations by domain experts. Recent efforts have democratized this process by involving lay annotators without medical expertise. However, conventional non-agent-based approaches struggle to handle annotation noise adaptively, as they lack mechanisms to mitigate false positives (FP) and false negatives (FN) at both the image-feature and pixel levels. In this paper, we propose a consensus-aware self-corrective AI agent that leverages the Consensus Matrix to guide its learning process. The Consensus Matrix defines regions where both the AI and annotators agree on cell and non-cell annotations, which are prioritized with stronger supervision. Conversely, areas of disagreement are adaptively weighted based on their feature similarity to high-confidence agreement regions, with more similar regions receiving greater attention. Additionally, contrastive learning is employed to separate features of noisy regions from those of reliable agreement regions by maximizing their dissimilarity. This paradigm enables the AI to iteratively refine noisy labels, enhancing its robustness. Validated on one real-world lay-annotated cell dataset and two simulated noisy datasets, our method demonstrates improved segmentation performance, effectively correcting FP and FN errors and showcasing its potential for training robust models on noisy datasets. The official implementation and cell annotations are publicly available at https://github.com/ddrrnn123/CASC-AI.
KPIs 2024 Challenge: Advancing Glomerular Segmentation from Patch- to Slide-Level
Feb 11, 2025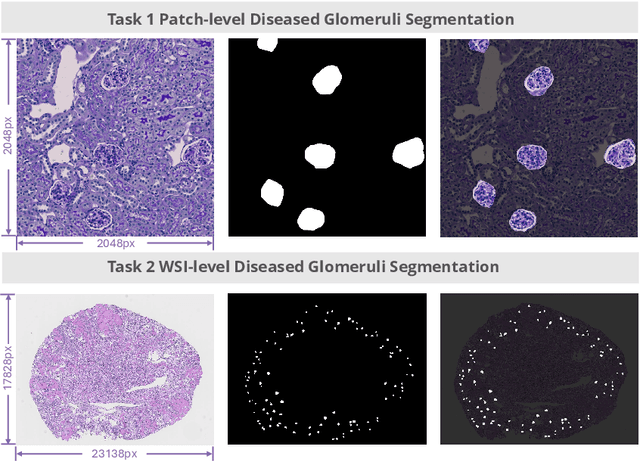
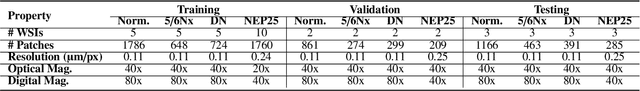
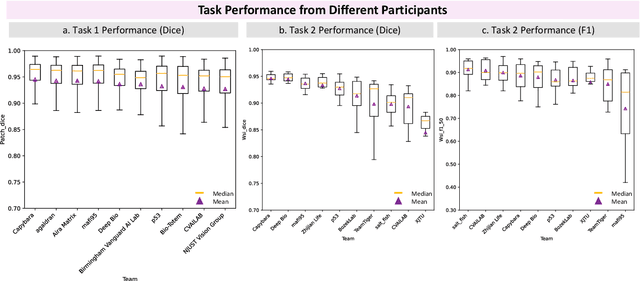
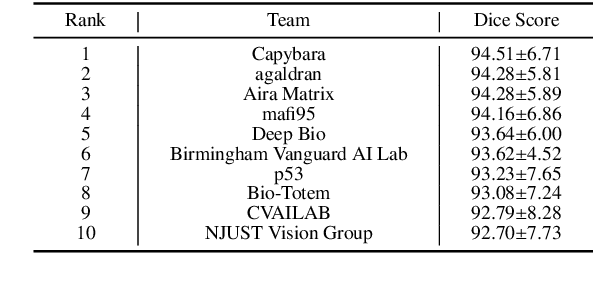
Abstract:Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major global health issue, affecting over 10% of the population and causing significant mortality. While kidney biopsy remains the gold standard for CKD diagnosis and treatment, the lack of comprehensive benchmarks for kidney pathology segmentation hinders progress in the field. To address this, we organized the Kidney Pathology Image Segmentation (KPIs) Challenge, introducing a dataset that incorporates preclinical rodent models of CKD with over 10,000 annotated glomeruli from 60+ Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)-stained whole slide images. The challenge includes two tasks, patch-level segmentation and whole slide image segmentation and detection, evaluated using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and F1-score. By encouraging innovative segmentation methods that adapt to diverse CKD models and tissue conditions, the KPIs Challenge aims to advance kidney pathology analysis, establish new benchmarks, and enable precise, large-scale quantification for disease research and diagnosis.
PySpatial: A High-Speed Whole Slide Image Pathomics Toolkit
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Whole Slide Image (WSI) analysis plays a crucial role in modern digital pathology, enabling large-scale feature extraction from tissue samples. However, traditional feature extraction pipelines based on tools like CellProfiler often involve lengthy workflows, requiring WSI segmentation into patches, feature extraction at the patch level, and subsequent mapping back to the original WSI. To address these challenges, we present PySpatial, a high-speed pathomics toolkit specifically designed for WSI-level analysis. PySpatial streamlines the conventional pipeline by directly operating on computational regions of interest, reducing redundant processing steps. Utilizing rtree-based spatial indexing and matrix-based computation, PySpatial efficiently maps and processes computational regions, significantly accelerating feature extraction while maintaining high accuracy. Our experiments on two datasets-Perivascular Epithelioid Cell (PEC) and data from the Kidney Precision Medicine Project (KPMP)-demonstrate substantial performance improvements. For smaller and sparse objects in PEC datasets, PySpatial achieves nearly a 10-fold speedup compared to standard CellProfiler pipelines. For larger objects, such as glomeruli and arteries in KPMP datasets, PySpatial achieves a 2-fold speedup. These results highlight PySpatial's potential to handle large-scale WSI analysis with enhanced efficiency and accuracy, paving the way for broader applications in digital pathology.
ASIGN: An Anatomy-aware Spatial Imputation Graphic Network for 3D Spatial Transcriptomics
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics (ST) is an emerging technology that enables medical computer vision scientists to automatically interpret the molecular profiles underlying morphological features. Currently, however, most deep learning-based ST analyses are limited to two-dimensional (2D) sections, which can introduce diagnostic errors due to the heterogeneity of pathological tissues across 3D sections. Expanding ST to three-dimensional (3D) volumes is challenging due to the prohibitive costs; a 2D ST acquisition already costs over 50 times more than whole slide imaging (WSI), and a full 3D volume with 10 sections can be an order of magnitude more expensive. To reduce costs, scientists have attempted to predict ST data directly from WSI without performing actual ST acquisition. However, these methods typically yield unsatisfying results. To address this, we introduce a novel problem setting: 3D ST imputation using 3D WSI histology sections combined with a single 2D ST slide. To do so, we present the Anatomy-aware Spatial Imputation Graph Network (ASIGN) for more precise, yet affordable, 3D ST modeling. The ASIGN architecture extends existing 2D spatial relationships into 3D by leveraging cross-layer overlap and similarity-based expansion. Moreover, a multi-level spatial attention graph network integrates features comprehensively across different data sources. We evaluated ASIGN on three public spatial transcriptomics datasets, with experimental results demonstrating that ASIGN achieves state-of-the-art performance on both 2D and 3D scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/hrlblab/ASIGN.
GloFinder: AI-empowered QuPath Plugin for WSI-level Glomerular Detection, Visualization, and Curation
Nov 27, 2024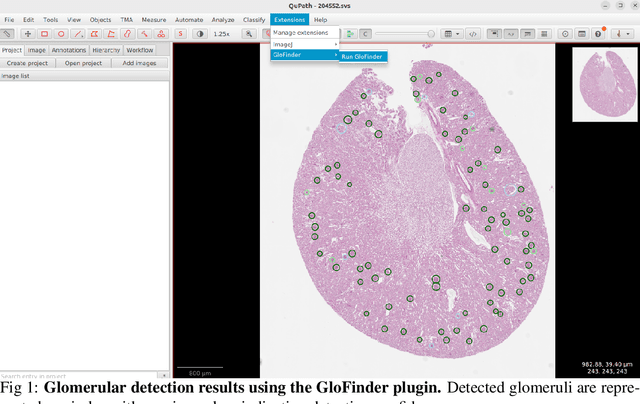
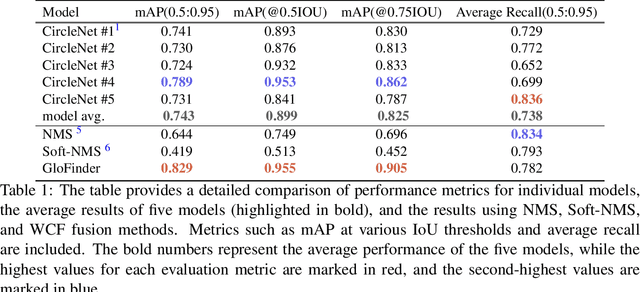
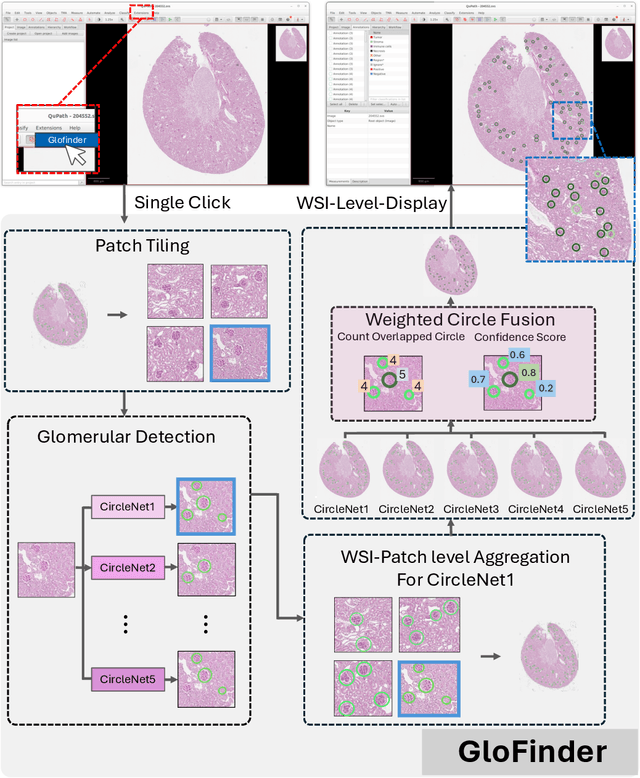
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has demonstrated significant success in automating the detection of glomeruli, the key functional units of the kidney, from whole slide images (WSIs) in kidney pathology. However, existing open-source tools are often distributed as source code or Docker containers, requiring advanced programming skills that hinder accessibility for non-programmers, such as clinicians. Additionally, current models are typically trained on a single dataset and lack flexibility in adjusting confidence levels for predictions. To overcome these challenges, we introduce GloFinder, a QuPath plugin designed for single-click automated glomeruli detection across entire WSIs with online editing through the graphical user interface (GUI). GloFinder employs CircleNet, an anchor-free detection framework utilizing circle representations for precise object localization, with models trained on approximately 160,000 manually annotated glomeruli. To further enhance accuracy, the plugin incorporates Weighted Circle Fusion (WCF), an ensemble method that combines confidence scores from multiple CircleNet models to produce refined predictions, achieving superior performance in glomerular detection. GloFinder enables direct visualization and editing of results in QuPath, facilitating seamless interaction for clinicians and providing a powerful tool for nephropathology research and clinical practice.
Glo-In-One-v2: Holistic Identification of Glomerular Cells, Tissues, and Lesions in Human and Mouse Histopathology
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Segmenting glomerular intraglomerular tissue and lesions traditionally depends on detailed morphological evaluations by expert nephropathologists, a labor-intensive process susceptible to interobserver variability. Our group previously developed the Glo-In-One toolkit for integrated detection and segmentation of glomeruli. In this study, we leverage the Glo-In-One toolkit to version 2 with fine-grained segmentation capabilities, curating 14 distinct labels for tissue regions, cells, and lesions across a dataset of 23,529 annotated glomeruli across human and mouse histopathology data. To our knowledge, this dataset is among the largest of its kind to date.In this study, we present a single dynamic head deep learning architecture designed to segment 14 classes within partially labeled images of human and mouse pathology data. Our model was trained using a training set derived from 368 annotated kidney whole-slide images (WSIs) to identify 5 key intraglomerular tissues covering Bowman's capsule, glomerular tuft, mesangium, mesangial cells, and podocytes. Additionally, the network segments 9 glomerular lesion classes including adhesion, capsular drop, global sclerosis, hyalinosis, mesangial lysis, microaneurysm, nodular sclerosis, mesangial expansion, and segmental sclerosis. The glomerulus segmentation model achieved a decent performance compared with baselines, and achieved a 76.5 % average Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC). Additional, transfer learning from rodent to human for glomerular lesion segmentation model has enhanced the average segmentation accuracy across different types of lesions by more than 3 %, as measured by Dice scores. The Glo-In-One-v2 model and trained weight have been made publicly available at https: //github.com/hrlblab/Glo-In-One_v2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge