Xiaorui Lin
AbdomenAtlas: A Large-Scale, Detailed-Annotated, & Multi-Center Dataset for Efficient Transfer Learning and Open Algorithmic Benchmarking
Jul 23, 2024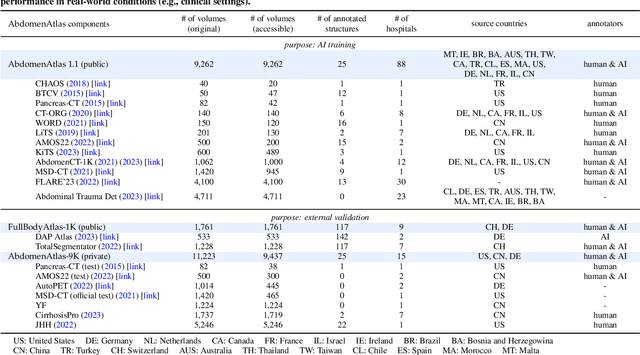


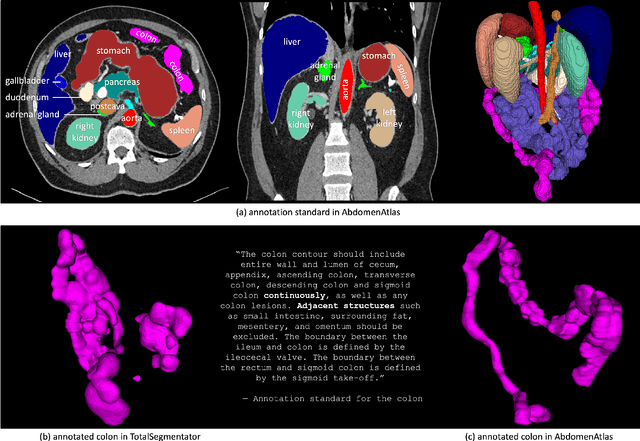
Abstract:We introduce the largest abdominal CT dataset (termed AbdomenAtlas) of 20,460 three-dimensional CT volumes sourced from 112 hospitals across diverse populations, geographies, and facilities. AbdomenAtlas provides 673K high-quality masks of anatomical structures in the abdominal region annotated by a team of 10 radiologists with the help of AI algorithms. We start by having expert radiologists manually annotate 22 anatomical structures in 5,246 CT volumes. Following this, a semi-automatic annotation procedure is performed for the remaining CT volumes, where radiologists revise the annotations predicted by AI, and in turn, AI improves its predictions by learning from revised annotations. Such a large-scale, detailed-annotated, and multi-center dataset is needed for two reasons. Firstly, AbdomenAtlas provides important resources for AI development at scale, branded as large pre-trained models, which can alleviate the annotation workload of expert radiologists to transfer to broader clinical applications. Secondly, AbdomenAtlas establishes a large-scale benchmark for evaluating AI algorithms -- the more data we use to test the algorithms, the better we can guarantee reliable performance in complex clinical scenarios. An ISBI & MICCAI challenge named BodyMaps: Towards 3D Atlas of Human Body was launched using a subset of our AbdomenAtlas, aiming to stimulate AI innovation and to benchmark segmentation accuracy, inference efficiency, and domain generalizability. We hope our AbdomenAtlas can set the stage for larger-scale clinical trials and offer exceptional opportunities to practitioners in the medical imaging community. Codes, models, and datasets are available at https://www.zongweiz.com/dataset
Detecting Adversarial Faces Using Only Real Face Self-Perturbations
May 04, 2023



Abstract:Adversarial attacks aim to disturb the functionality of a target system by adding specific noise to the input samples, bringing potential threats to security and robustness when applied to facial recognition systems. Although existing defense techniques achieve high accuracy in detecting some specific adversarial faces (adv-faces), new attack methods especially GAN-based attacks with completely different noise patterns circumvent them and reach a higher attack success rate. Even worse, existing techniques require attack data before implementing the defense, making it impractical to defend newly emerging attacks that are unseen to defenders. In this paper, we investigate the intrinsic generality of adv-faces and propose to generate pseudo adv-faces by perturbing real faces with three heuristically designed noise patterns. We are the first to train an adv-face detector using only real faces and their self-perturbations, agnostic to victim facial recognition systems, and agnostic to unseen attacks. By regarding adv-faces as out-of-distribution data, we then naturally introduce a novel cascaded system for adv-face detection, which consists of training data self-perturbations, decision boundary regularization, and a max-pooling-based binary classifier focusing on abnormal local color aberrations. Experiments conducted on LFW and CelebA-HQ datasets with eight gradient-based and two GAN-based attacks validate that our method generalizes to a variety of unseen adversarial attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge