Zijian Yang
Dynamic Acoustic Model Architecture Optimization in Training for ASR
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Architecture design is inherently complex. Existing approaches rely on either handcrafted rules, which demand extensive empirical expertise, or automated methods like neural architecture search, which are computationally intensive. In this paper, we introduce DMAO, an architecture optimization framework that employs a grow-and-drop strategy to automatically reallocate parameters during training. This reallocation shifts resources from less-utilized areas to those parts of the model where they are most beneficial. Notably, DMAO only introduces negligible training overhead at a given model complexity. We evaluate DMAO through experiments with CTC on LibriSpeech, TED-LIUM-v2 and Switchboard datasets. The results show that, using the same amount of training resources, our proposed DMAO consistently improves WER by up to 6% relatively across various architectures, model sizes, and datasets. Furthermore, we analyze the pattern of parameter redistribution and uncover insightful findings.
Label-Context-Dependent Internal Language Model Estimation for CTC
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Although connectionist temporal classification (CTC) has the label context independence assumption, it can still implicitly learn a context-dependent internal language model (ILM) due to modern powerful encoders. In this work, we investigate the implicit context dependency modeled in the ILM of CTC. To this end, we propose novel context-dependent ILM estimation methods for CTC based on knowledge distillation (KD) with theoretical justifications. Furthermore, we introduce two regularization methods for KD. We conduct experiments on Librispeech and TED-LIUM Release 2 datasets for in-domain and cross-domain evaluation, respectively. Experimental results show that context-dependent ILMs outperform the context-independent priors in cross-domain evaluation, indicating that CTC learns a context-dependent ILM. The proposed label-level KD with smoothing method surpasses other ILM estimation approaches, with more than 13% relative improvement in word error rate compared to shallow fusion.
When Feedback Empowers the Uplink: Integrating Adaptive Coding with Wireless Power Transfer
May 28, 2025Abstract:Energy consumption and device lifetime are critical concerns for battery-constrained IoT devices. This paper introduces the Feedback-Aided Coding and Energy Transfer (FACET) framework, which synergistically combines adaptive feedback channel coding with wireless power transfer. FACET leverages the saturation effect of feedback coding, where increasing downlink power yields diminishing returns, to design a dual-purpose feedback mechanism that simultaneously guides uplink coding and replenishes device energy. We characterize the inherent tradeoff between feedback precision and harvested power, and formulate a fairness-constrained min-max optimization problem to minimize worst-case net energy consumption. An efficient algorithm based on alternating optimization and Lagrangian duality is developed, with each subproblem admitting a closed-form solution. Simulations show that FACET nearly triples device lifetime compared to conventional feedback coding architectures, and remains robust across a wide range of power regimes. These results suggest that FACET not only improves communication efficiency but also redefines the role of feedback in energy-constrained IoT systems.
AutoMathKG: The automated mathematical knowledge graph based on LLM and vector database
May 19, 2025Abstract:A mathematical knowledge graph (KG) presents knowledge within the field of mathematics in a structured manner. Constructing a math KG using natural language is an essential but challenging task. There are two major limitations of existing works: first, they are constrained by corpus completeness, often discarding or manually supplementing incomplete knowledge; second, they typically fail to fully automate the integration of diverse knowledge sources. This paper proposes AutoMathKG, a high-quality, wide-coverage, and multi-dimensional math KG capable of automatic updates. AutoMathKG regards mathematics as a vast directed graph composed of Definition, Theorem, and Problem entities, with their reference relationships as edges. It integrates knowledge from ProofWiki, textbooks, arXiv papers, and TheoremQA, enhancing entities and relationships with large language models (LLMs) via in-context learning for data augmentation. To search for similar entities, MathVD, a vector database, is built through two designed embedding strategies using SBERT. To automatically update, two mechanisms are proposed. For knowledge completion mechanism, Math LLM is developed to interact with AutoMathKG, providing missing proofs or solutions. For knowledge fusion mechanism, MathVD is used to retrieve similar entities, and LLM is used to determine whether to merge with a candidate or add as a new entity. A wide range of experiments demonstrate the advanced performance and broad applicability of the AutoMathKG system, including superior reachability query results in MathVD compared to five baselines and robust mathematical reasoning capability in Math LLM.
GaussianCAD: Robust Self-Supervised CAD Reconstruction from Three Orthographic Views Using 3D Gaussian Splatting
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:The automatic reconstruction of 3D computer-aided design (CAD) models from CAD sketches has recently gained significant attention in the computer vision community. Most existing methods, however, rely on vector CAD sketches and 3D ground truth for supervision, which are often difficult to be obtained in industrial applications and are sensitive to noise inputs. We propose viewing CAD reconstruction as a specific instance of sparse-view 3D reconstruction to overcome these limitations. While this reformulation offers a promising perspective, existing 3D reconstruction methods typically require natural images and corresponding camera poses as inputs, which introduces two major significant challenges: (1) modality discrepancy between CAD sketches and natural images, and (2) difficulty of accurate camera pose estimation for CAD sketches. To solve these issues, we first transform the CAD sketches into representations resembling natural images and extract corresponding masks. Next, we manually calculate the camera poses for the orthographic views to ensure accurate alignment within the 3D coordinate system. Finally, we employ a customized sparse-view 3D reconstruction method to achieve high-quality reconstructions from aligned orthographic views. By leveraging raster CAD sketches for self-supervision, our approach eliminates the reliance on vector CAD sketches and 3D ground truth. Experiments on the Sub-Fusion360 dataset demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms previous approaches in CAD reconstruction performance and exhibits strong robustness to noisy inputs.
Efficient Supernet Training with Orthogonal Softmax for Scalable ASR Model Compression
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:ASR systems are deployed across diverse environments, each with specific hardware constraints. We use supernet training to jointly train multiple encoders of varying sizes, enabling dynamic model size adjustment to fit hardware constraints without redundant training. Moreover, we introduce a novel method called OrthoSoftmax, which applies multiple orthogonal softmax functions to efficiently identify optimal subnets within the supernet, avoiding resource-intensive search. This approach also enables more flexible and precise subnet selection by allowing selection based on various criteria and levels of granularity. Our results with CTC on Librispeech and TED-LIUM-v2 show that FLOPs-aware component-wise selection achieves the best overall performance. With the same number of training updates from one single job, WERs for all model sizes are comparable to or slightly better than those of individually trained models. Furthermore, we analyze patterns in the selected components and reveal interesting insights.
Classification Error Bound for Low Bayes Error Conditions in Machine Learning
Jan 27, 2025


Abstract:In statistical classification and machine learning, classification error is an important performance measure, which is minimized by the Bayes decision rule. In practice, the unknown true distribution is usually replaced with a model distribution estimated from the training data in the Bayes decision rule. This substitution introduces a mismatch between the Bayes error and the model-based classification error. In this work, we apply classification error bounds to study the relationship between the error mismatch and the Kullback-Leibler divergence in machine learning. Motivated by recent observations of low model-based classification errors in many machine learning tasks, bounding the Bayes error to be lower, we propose a linear approximation of the classification error bound for low Bayes error conditions. Then, the bound for class priors are discussed. Moreover, we extend the classification error bound for sequences. Using automatic speech recognition as a representative example of machine learning applications, this work analytically discusses the correlations among different performance measures with extended bounds, including cross-entropy loss, language model perplexity, and word error rate.
Investigating the Effect of Language Models in Sequence Discriminative Training for Neural Transducers
Oct 11, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we investigate the effect of language models (LMs) with different context lengths and label units (phoneme vs. word) used in sequence discriminative training for phoneme-based neural transducers. Both lattice-free and N-best-list approaches are examined. For lattice-free methods with phoneme-level LMs, we propose a method to approximate the context history to employ LMs with full-context dependency. This approximation can be extended to arbitrary context length and enables the usage of word-level LMs in lattice-free methods. Moreover, a systematic comparison is conducted across lattice-free and N-best-list-based methods. Experimental results on Librispeech show that using the word-level LM in training outperforms the phoneme-level LM. Besides, we find that the context size of the LM used for probability computation has a limited effect on performance. Moreover, our results reveal the pivotal importance of the hypothesis space quality in sequence discriminative training.
On the Relation between Internal Language Model and Sequence Discriminative Training for Neural Transducers
Sep 25, 2023Abstract:Internal language model (ILM) subtraction has been widely applied to improve the performance of the RNN-Transducer with external language model (LM) fusion for speech recognition. In this work, we show that sequence discriminative training has a strong correlation with ILM subtraction from both theoretical and empirical points of view. Theoretically, we derive that the global optimum of maximum mutual information (MMI) training shares a similar formula as ILM subtraction. Empirically, we show that ILM subtraction and sequence discriminative training achieve similar performance across a wide range of experiments on Librispeech, including both MMI and minimum Bayes risk (MBR) criteria, as well as neural transducers and LMs of both full and limited context. The benefit of ILM subtraction also becomes much smaller after sequence discriminative training. We also provide an in-depth study to show that sequence discriminative training has a minimal effect on the commonly used zero-encoder ILM estimation, but a joint effect on both encoder and prediction + joint network for posterior probability reshaping including both ILM and blank suppression.
Enhancing Model Performance in Multilingual Information Retrieval with Comprehensive Data Engineering Techniques
Feb 14, 2023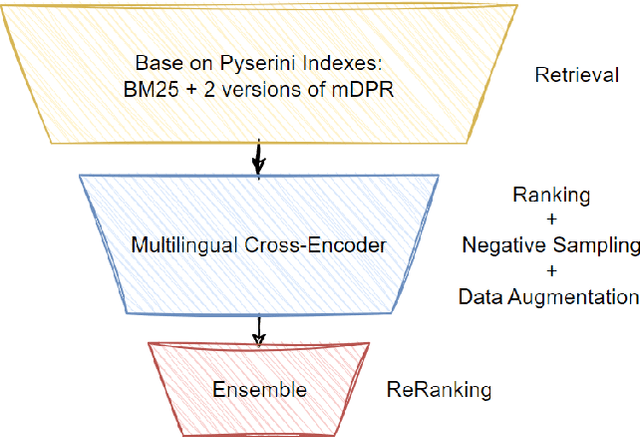


Abstract:In this paper, we present our solution to the Multilingual Information Retrieval Across a Continuum of Languages (MIRACL) challenge of WSDM CUP 2023\footnote{https://project-miracl.github.io/}. Our solution focuses on enhancing the ranking stage, where we fine-tune pre-trained multilingual transformer-based models with MIRACL dataset. Our model improvement is mainly achieved through diverse data engineering techniques, including the collection of additional relevant training data, data augmentation, and negative sampling. Our fine-tuned model effectively determines the semantic relevance between queries and documents, resulting in a significant improvement in the efficiency of the multilingual information retrieval process. Finally, Our team is pleased to achieve remarkable results in this challenging competition, securing 2nd place in the Surprise-Languages track with a score of 0.835 and 3rd place in the Known-Languages track with an average nDCG@10 score of 0.716 across the 16 known languages on the final leaderboard.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge