Zhongzhi Chen
Hunyuan-TurboS: Advancing Large Language Models through Mamba-Transformer Synergy and Adaptive Chain-of-Thought
May 21, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) rapidly advance, we introduce Hunyuan-TurboS, a novel large hybrid Transformer-Mamba Mixture of Experts (MoE) model. It synergistically combines Mamba's long-sequence processing efficiency with Transformer's superior contextual understanding. Hunyuan-TurboS features an adaptive long-short chain-of-thought (CoT) mechanism, dynamically switching between rapid responses for simple queries and deep "thinking" modes for complex problems, optimizing computational resources. Architecturally, this 56B activated (560B total) parameter model employs 128 layers (Mamba2, Attention, FFN) with an innovative AMF/MF block pattern. Faster Mamba2 ensures linear complexity, Grouped-Query Attention minimizes KV cache, and FFNs use an MoE structure. Pre-trained on 16T high-quality tokens, it supports a 256K context length and is the first industry-deployed large-scale Mamba model. Our comprehensive post-training strategy enhances capabilities via Supervised Fine-Tuning (3M instructions), a novel Adaptive Long-short CoT Fusion method, Multi-round Deliberation Learning for iterative improvement, and a two-stage Large-scale Reinforcement Learning process targeting STEM and general instruction-following. Evaluations show strong performance: overall top 7 rank on LMSYS Chatbot Arena with a score of 1356, outperforming leading models like Gemini-2.0-Flash-001 (1352) and o4-mini-2025-04-16 (1345). TurboS also achieves an average of 77.9% across 23 automated benchmarks. Hunyuan-TurboS balances high performance and efficiency, offering substantial capabilities at lower inference costs than many reasoning models, establishing a new paradigm for efficient large-scale pre-trained models.
Hunyuan-Large: An Open-Source MoE Model with 52 Billion Activated Parameters by Tencent
Nov 05, 2024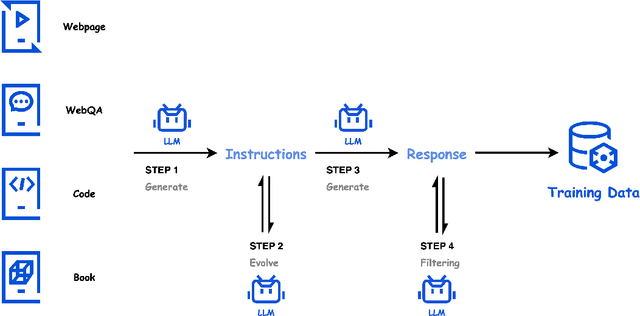
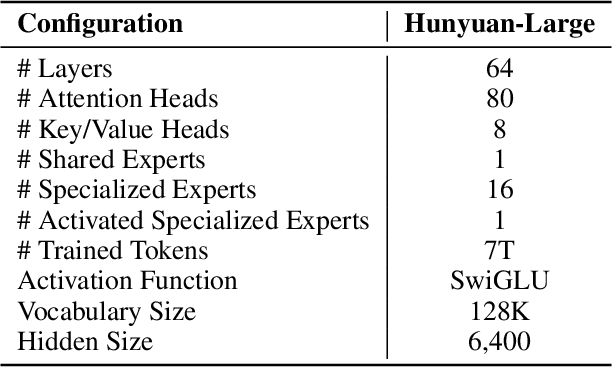
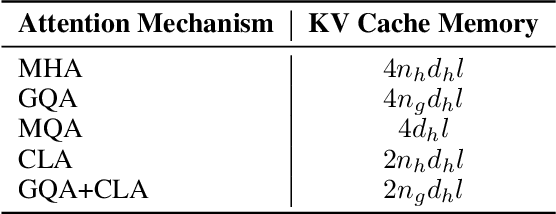
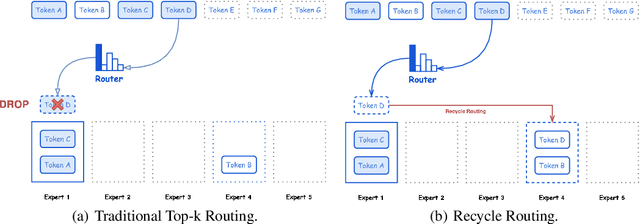
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Hunyuan-Large, which is currently the largest open-source Transformer-based mixture of experts model, with a total of 389 billion parameters and 52 billion activation parameters, capable of handling up to 256K tokens. We conduct a thorough evaluation of Hunyuan-Large's superior performance across various benchmarks including language understanding and generation, logical reasoning, mathematical problem-solving, coding, long-context, and aggregated tasks, where it outperforms LLama3.1-70B and exhibits comparable performance when compared to the significantly larger LLama3.1-405B model. Key practice of Hunyuan-Large include large-scale synthetic data that is orders larger than in previous literature, a mixed expert routing strategy, a key-value cache compression technique, and an expert-specific learning rate strategy. Additionally, we also investigate the scaling laws and learning rate schedule of mixture of experts models, providing valuable insights and guidances for future model development and optimization. The code and checkpoints of Hunyuan-Large are released to facilitate future innovations and applications. Codes: https://github.com/Tencent/Hunyuan-Large Models: https://huggingface.co/tencent/Tencent-Hunyuan-Large
Adaptive Activation Steering: A Tuning-Free LLM Truthfulness Improvement Method for Diverse Hallucinations Categories
May 26, 2024Abstract:Recent studies have indicated that Large Language Models (LLMs) harbor an inherent understanding of truthfulness, yet often fail to express fully and generate false statements. This gap between "knowing" and "telling" poses a challenge for ensuring the truthfulness of generated content. To address this, we introduce Adaptive Activation Steering (ACT), a tuning-free method that adaptively shift LLM's activations in "truthful" direction during inference. ACT addresses diverse categories of hallucinations by utilizing diverse steering vectors and adjusting the steering intensity adaptively. Applied as an add-on across various models, ACT significantly improves truthfulness in LLaMA ($\uparrow$ 142\%), LLaMA2 ($\uparrow$ 24\%), Alpaca ($\uparrow$ 36\%), Vicuna ($\uparrow$ 28\%), and LLaMA2-Chat ($\uparrow$ 19\%). Furthermore, we verify ACT's scalability across larger models (13B, 33B, 65B), underscoring the adaptability of ACT to large-scale language models.
Truth Forest: Toward Multi-Scale Truthfulness in Large Language Models through Intervention without Tuning
Dec 29, 2023Abstract:Despite the great success of large language models (LLMs) in various tasks, they suffer from generating hallucinations. We introduce Truth Forest, a method that enhances truthfulness in LLMs by uncovering hidden truth representations using multi-dimensional orthogonal probes. Specifically, it creates multiple orthogonal bases for modeling truth by incorporating orthogonal constraints into the probes. Moreover, we introduce Random Peek, a systematic technique considering an extended range of positions within the sequence, reducing the gap between discerning and generating truth features in LLMs. By employing this approach, we improved the truthfulness of Llama-2-7B from 40.8\% to 74.5\% on TruthfulQA. Likewise, significant improvements are observed in fine-tuned models. We conducted a thorough analysis of truth features using probes. Our visualization results show that orthogonal probes capture complementary truth-related features, forming well-defined clusters that reveal the inherent structure of the dataset. Code: \url{https://github.com/jongjyh/trfr}
AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities
Nov 21, 2022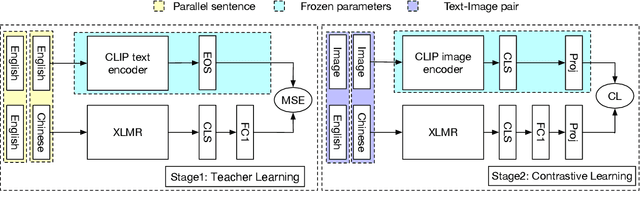
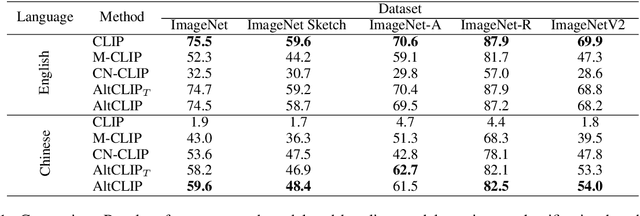
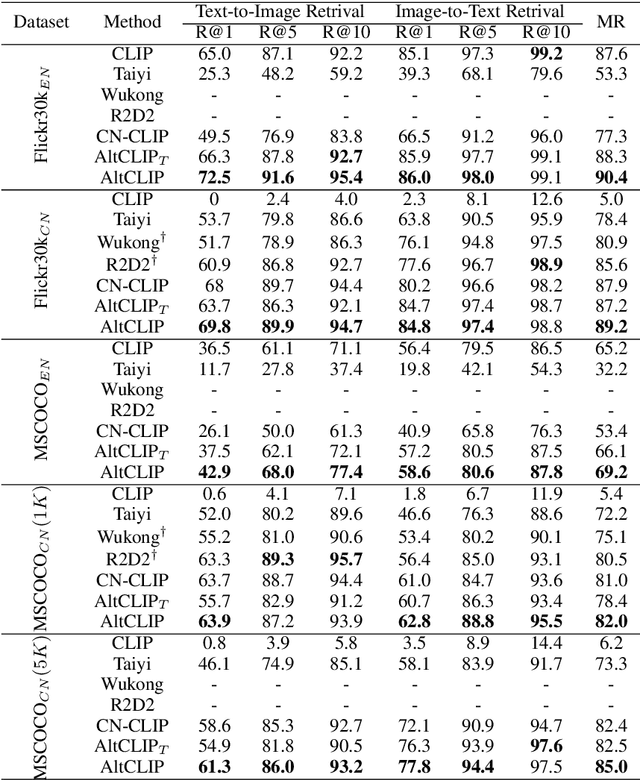
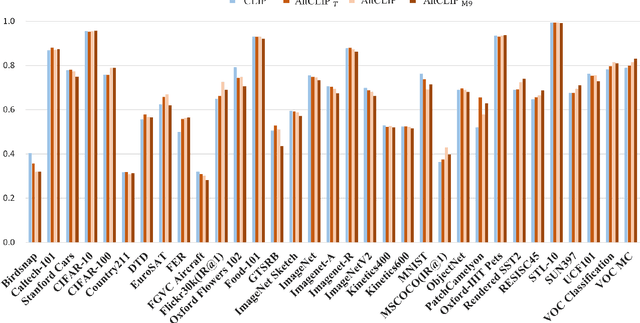
Abstract:In this work, we present a conceptually simple and effective method to train a strong bilingual/multilingual multimodal representation model. Starting from the pre-trained multimodal representation model CLIP released by OpenAI, we altered its text encoder with a pre-trained multilingual text encoder XLM-R, and aligned both languages and image representations by a two-stage training schema consisting of teacher learning and contrastive learning. We validate our method through evaluations of a wide range of tasks. We set new state-of-the-art performances on a bunch of tasks including ImageNet-CN, Flicker30k-CN, COCO-CN and XTD. Further, we obtain very close performances with CLIP on almost all tasks, suggesting that one can simply alter the text encoder in CLIP for extended capabilities such as multilingual understanding. Our models and code are available at https://github.com/FlagAI-Open/FlagAI.
Exploiting Global and Local Hierarchies for Hierarchical Text Classification
May 05, 2022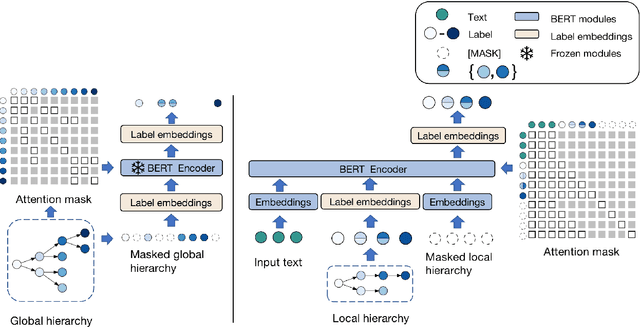
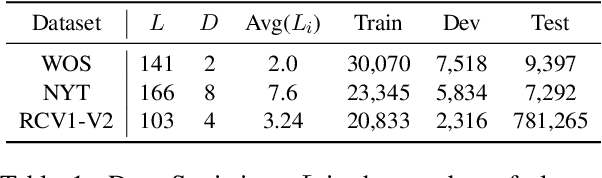
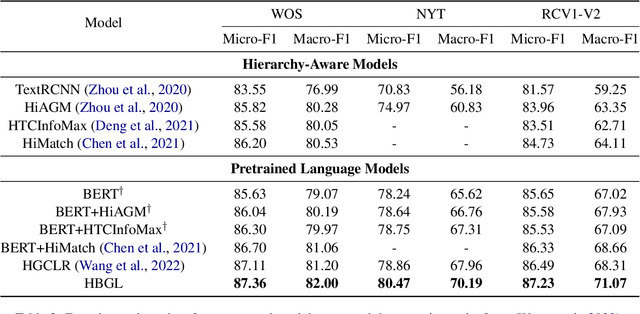
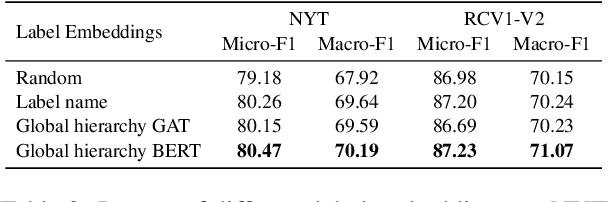
Abstract:Hierarchical text classification aims to leverage label hierarchy in multi-label text classification. Existing methods encode label hierarchy in a global view, where label hierarchy is treated as the static hierarchical structure containing all labels. Since global hierarchy is static and irrelevant to text samples, it makes these methods hard to exploit hierarchical information. Contrary to global hierarchy, local hierarchy as the structured target labels hierarchy corresponding to each text sample is dynamic and relevant to text samples, which is ignored in previous methods. To exploit global and local hierarchies, we propose Hierarchy-guided BERT with Global and Local hierarchies (HBGL), which utilizes the large-scale parameters and prior language knowledge of BERT to model both global and local hierarchies. Moreover, HBGL avoids the intentional fusion of semantic and hierarchical modules by directly modeling semantic and hierarchical information with BERT. Compared with the state-of-the-art method HGCLR, our method achieves significant improvement on three benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge