Fulong Ye
OmniTransfer: All-in-one Framework for Spatio-temporal Video Transfer
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Videos convey richer information than images or text, capturing both spatial and temporal dynamics. However, most existing video customization methods rely on reference images or task-specific temporal priors, failing to fully exploit the rich spatio-temporal information inherent in videos, thereby limiting flexibility and generalization in video generation. To address these limitations, we propose OmniTransfer, a unified framework for spatio-temporal video transfer. It leverages multi-view information across frames to enhance appearance consistency and exploits temporal cues to enable fine-grained temporal control. To unify various video transfer tasks, OmniTransfer incorporates three key designs: Task-aware Positional Bias that adaptively leverages reference video information to improve temporal alignment or appearance consistency; Reference-decoupled Causal Learning separating reference and target branches to enable precise reference transfer while improving efficiency; and Task-adaptive Multimodal Alignment using multimodal semantic guidance to dynamically distinguish and tackle different tasks. Extensive experiments show that OmniTransfer outperforms existing methods in appearance (ID and style) and temporal transfer (camera movement and video effects), while matching pose-guided methods in motion transfer without using pose, establishing a new paradigm for flexible, high-fidelity video generation.
DreamID-V:Bridging the Image-to-Video Gap for High-Fidelity Face Swapping via Diffusion Transformer
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Video Face Swapping (VFS) requires seamlessly injecting a source identity into a target video while meticulously preserving the original pose, expression, lighting, background, and dynamic information. Existing methods struggle to maintain identity similarity and attribute preservation while preserving temporal consistency. To address the challenge, we propose a comprehensive framework to seamlessly transfer the superiority of Image Face Swapping (IFS) to the video domain. We first introduce a novel data pipeline SyncID-Pipe that pre-trains an Identity-Anchored Video Synthesizer and combines it with IFS models to construct bidirectional ID quadruplets for explicit supervision. Building upon paired data, we propose the first Diffusion Transformer-based framework DreamID-V, employing a core Modality-Aware Conditioning module to discriminatively inject multi-model conditions. Meanwhile, we propose a Synthetic-to-Real Curriculum mechanism and an Identity-Coherence Reinforcement Learning strategy to enhance visual realism and identity consistency under challenging scenarios. To address the issue of limited benchmarks, we introduce IDBench-V, a comprehensive benchmark encompassing diverse scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate DreamID-V outperforms state-of-the-art methods and further exhibits exceptional versatility, which can be seamlessly adapted to various swap-related tasks.
DreamID: High-Fidelity and Fast diffusion-based Face Swapping via Triplet ID Group Learning
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we introduce DreamID, a diffusion-based face swapping model that achieves high levels of ID similarity, attribute preservation, image fidelity, and fast inference speed. Unlike the typical face swapping training process, which often relies on implicit supervision and struggles to achieve satisfactory results. DreamID establishes explicit supervision for face swapping by constructing Triplet ID Group data, significantly enhancing identity similarity and attribute preservation. The iterative nature of diffusion models poses challenges for utilizing efficient image-space loss functions, as performing time-consuming multi-step sampling to obtain the generated image during training is impractical. To address this issue, we leverage the accelerated diffusion model SD Turbo, reducing the inference steps to a single iteration, enabling efficient pixel-level end-to-end training with explicit Triplet ID Group supervision. Additionally, we propose an improved diffusion-based model architecture comprising SwapNet, FaceNet, and ID Adapter. This robust architecture fully unlocks the power of the Triplet ID Group explicit supervision. Finally, to further extend our method, we explicitly modify the Triplet ID Group data during training to fine-tune and preserve specific attributes, such as glasses and face shape. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DreamID outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of identity similarity, pose and expression preservation, and image fidelity. Overall, DreamID achieves high-quality face swapping results at 512*512 resolution in just 0.6 seconds and performs exceptionally well in challenging scenarios such as complex lighting, large angles, and occlusions.
AnyDressing: Customizable Multi-Garment Virtual Dressing via Latent Diffusion Models
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in garment-centric image generation from text and image prompts based on diffusion models are impressive. However, existing methods lack support for various combinations of attire, and struggle to preserve the garment details while maintaining faithfulness to the text prompts, limiting their performance across diverse scenarios. In this paper, we focus on a new task, i.e., Multi-Garment Virtual Dressing, and we propose a novel AnyDressing method for customizing characters conditioned on any combination of garments and any personalized text prompts. AnyDressing comprises two primary networks named GarmentsNet and DressingNet, which are respectively dedicated to extracting detailed clothing features and generating customized images. Specifically, we propose an efficient and scalable module called Garment-Specific Feature Extractor in GarmentsNet to individually encode garment textures in parallel. This design prevents garment confusion while ensuring network efficiency. Meanwhile, we design an adaptive Dressing-Attention mechanism and a novel Instance-Level Garment Localization Learning strategy in DressingNet to accurately inject multi-garment features into their corresponding regions. This approach efficiently integrates multi-garment texture cues into generated images and further enhances text-image consistency. Additionally, we introduce a Garment-Enhanced Texture Learning strategy to improve the fine-grained texture details of garments. Thanks to our well-craft design, AnyDressing can serve as a plug-in module to easily integrate with any community control extensions for diffusion models, improving the diversity and controllability of synthesized images. Extensive experiments show that AnyDressing achieves state-of-the-art results.
AltDiffusion: A Multilingual Text-to-Image Diffusion Model
Aug 23, 2023Abstract:Large Text-to-Image(T2I) diffusion models have shown a remarkable capability to produce photorealistic and diverse images based on text inputs. However, existing works only support limited language input, e.g., English, Chinese, and Japanese, leaving users beyond these languages underserved and blocking the global expansion of T2I models. Therefore, this paper presents AltDiffusion, a novel multilingual T2I diffusion model that supports eighteen different languages. Specifically, we first train a multilingual text encoder based on the knowledge distillation. Then we plug it into a pretrained English-only diffusion model and train the model with a two-stage schema to enhance the multilingual capability, including concept alignment and quality improvement stage on a large-scale multilingual dataset. Furthermore, we introduce a new benchmark, which includes Multilingual-General-18(MG-18) and Multilingual-Cultural-18(MC-18) datasets, to evaluate the capabilities of T2I diffusion models for generating high-quality images and capturing culture-specific concepts in different languages. Experimental results on both MG-18 and MC-18 demonstrate that AltDiffusion outperforms current state-of-the-art T2I models, e.g., Stable Diffusion in multilingual understanding, especially with respect to culture-specific concepts, while still having comparable capability for generating high-quality images. All source code and checkpoints could be found in https://github.com/superhero-7/AltDiffuson.
Whether you can locate or not? Interactive Referring Expression Generation
Aug 19, 2023



Abstract:Referring Expression Generation (REG) aims to generate unambiguous Referring Expressions (REs) for objects in a visual scene, with a dual task of Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) to locate the referred object. Existing methods construct REG models independently by using only the REs as ground truth for model training, without considering the potential interaction between REG and REC models. In this paper, we propose an Interactive REG (IREG) model that can interact with a real REC model, utilizing signals indicating whether the object is located and the visual region located by the REC model to gradually modify REs. Our experimental results on three RE benchmark datasets, RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and RefCOCOg show that IREG outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods on popular evaluation metrics. Furthermore, a human evaluation shows that IREG generates better REs with the capability of interaction.
SPRING: Situated Conversation Agent Pretrained with Multimodal Questions from Incremental Layout Graph
Jan 05, 2023



Abstract:Existing multimodal conversation agents have shown impressive abilities to locate absolute positions or retrieve attributes in simple scenarios, but they fail to perform well when complex relative positions and information alignments are involved, which poses a bottleneck in response quality. In this paper, we propose a Situated Conversation Agent Petrained with Multimodal Questions from INcremental Layout Graph (SPRING) with abilities of reasoning multi-hops spatial relations and connecting them with visual attributes in crowded situated scenarios. Specifically, we design two types of Multimodal Question Answering (MQA) tasks to pretrain the agent. All QA pairs utilized during pretraining are generated from novel Incremental Layout Graphs (ILG). QA pair difficulty labels automatically annotated by ILG are used to promote MQA-based Curriculum Learning. Experimental results verify the SPRING's effectiveness, showing that it significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches on both SIMMC 1.0 and SIMMC 2.0 datasets.
AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities
Nov 21, 2022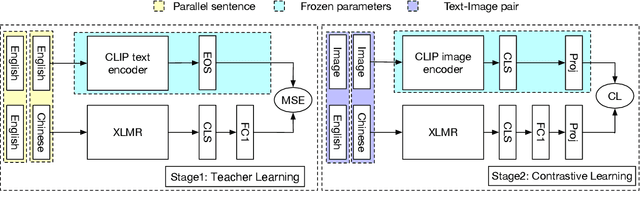
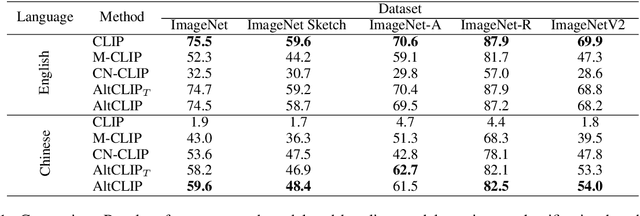
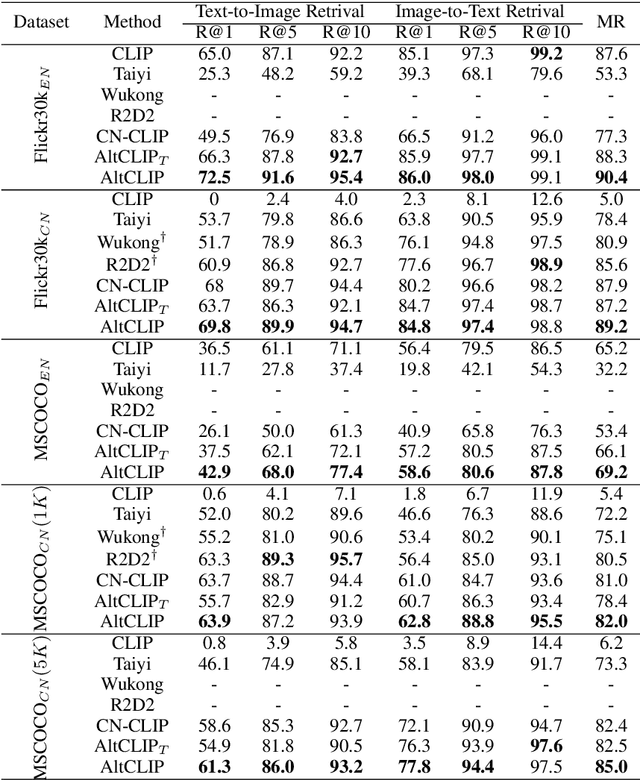
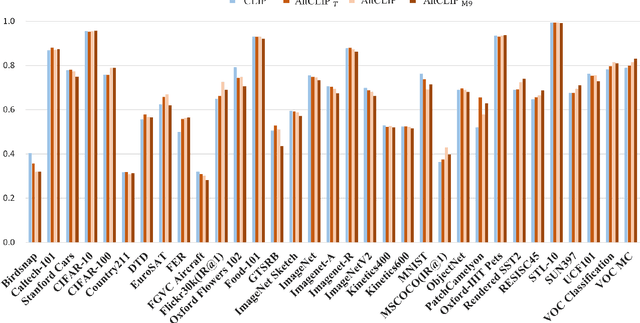
Abstract:In this work, we present a conceptually simple and effective method to train a strong bilingual/multilingual multimodal representation model. Starting from the pre-trained multimodal representation model CLIP released by OpenAI, we altered its text encoder with a pre-trained multilingual text encoder XLM-R, and aligned both languages and image representations by a two-stage training schema consisting of teacher learning and contrastive learning. We validate our method through evaluations of a wide range of tasks. We set new state-of-the-art performances on a bunch of tasks including ImageNet-CN, Flicker30k-CN, COCO-CN and XTD. Further, we obtain very close performances with CLIP on almost all tasks, suggesting that one can simply alter the text encoder in CLIP for extended capabilities such as multilingual understanding. Our models and code are available at https://github.com/FlagAI-Open/FlagAI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge