Caixia Yuan
Enhancing Complex Instruction Following for Large Language Models with Mixture-of-Contexts Fine-tuning
May 17, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in handling natural language tasks; however, they may struggle to consistently follow complex instructions including those involve multiple constraints. Post-training LLMs using supervised fine-tuning (SFT) is a standard approach to improve their ability to follow instructions. In addressing complex instruction following, existing efforts primarily focus on data-driven methods that synthesize complex instruction-output pairs for SFT. However, insufficient attention allocated to crucial sub-contexts may reduce the effectiveness of SFT. In this work, we propose transforming sequentially structured input instruction into multiple parallel instructions containing subcontexts. To support processing this multi-input, we propose MISO (Multi-Input Single-Output), an extension to currently dominant decoder-only transformer-based LLMs. MISO introduces a mixture-of-contexts paradigm that jointly considers the overall instruction-output alignment and the influence of individual sub-contexts to enhance SFT effectiveness. We apply MISO fine-tuning to complex instructionfollowing datasets and evaluate it with standard LLM inference. Empirical results demonstrate the superiority of MISO as a fine-tuning method for LLMs, both in terms of effectiveness in complex instruction-following scenarios and its potential for training efficiency.
Collab-Overcooked: Benchmarking and Evaluating Large Language Models as Collaborative Agents
Feb 27, 2025
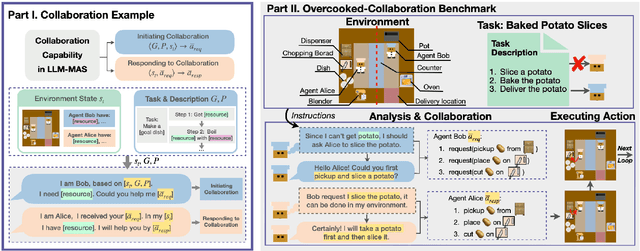

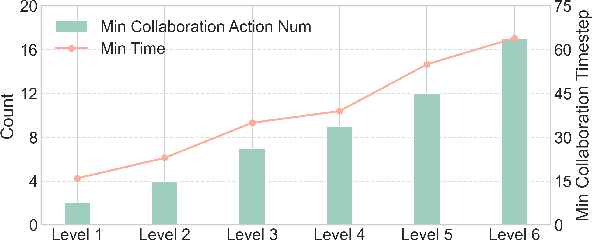
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) based agent systems have made great strides in real-world applications beyond traditional NLP tasks. This paper proposes a new LLM-powered Multi-Agent System (LLM-MAS) benchmark, Collab-Overcooked, built on the popular Overcooked-AI game with more applicable and challenging tasks in interactive environments. Collab-Overcooked extends existing benchmarks from two novel perspectives. First, it provides a multi-agent framework supporting diverse tasks and objectives and encourages collaboration through natural language communication. Second, it introduces a spectrum of process-oriented evaluation metrics to assess the fine-grained collaboration capabilities of different LLM agents, a dimension often overlooked in prior work. We conduct extensive experiments over 10 popular LLMs and show that, while the LLMs present a strong ability in goal interpretation, there is a significant discrepancy in active collaboration and continuous adaption that are critical for efficiently fulfilling complicated tasks. Notably, we highlight the strengths and weaknesses in LLM-MAS and provide insights for improving and evaluating LLM-MAS on a unified and open-sourced benchmark. Environments, 30 open-ended tasks, and an integrated evaluation package are now publicly available at https://github.com/YusaeMeow/Collab-Overcooked.
Circuit-tuning: A Mechanistic Approach for Identifying Parameter Redundancy and Fine-tuning Neural Networks
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:The study of mechanistic interpretability aims to reverse-engineer a model to explain its behaviors. While recent studies have focused on the static mechanism of a certain behavior, the training dynamics inside a model remain to be explored. In this work, we develop an interpretable method for fine-tuning and reveal the mechanism behind learning. We first propose the concept of node redundancy as an extension of intrinsic dimension and explain the idea behind circuit discovery from a fresh view. Based on the theory, we propose circuit-tuning, a two-stage algorithm that iteratively performs circuit discovery to mask out irrelevant edges and updates the remaining parameters responsible for a specific task. Experiments show that our method not only improves performance on a wide range of tasks but is also scalable while preserving general capabilities. We visualize and analyze the circuits before, during, and after fine-tuning, providing new insights into the self-organization mechanism of a neural network in the learning process.
Controlled Low-Rank Adaptation with Subspace Regularization for Continued Training on Large Language Models
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in natural language processing but face catastrophic forgetting when learning new tasks, where adaptation to a new domain leads to a substantial decline in performance on previous tasks. In this paper, we propose Controlled LoRA (CLoRA), a subspace regularization method on LoRA structure. Aiming to reduce the scale of output change while introduce minimal constraint on model capacity, CLoRA imposes constraint on the direction of updating matrix null space. Experimental results on commonly used LLM finetuning tasks reveal that CLoRA significantly outperforms existing LoRA subsequent methods on both in-domain and outdomain evaluations, highlighting the superority of CLoRA as a effective parameter-efficient finetuning method with catastrophic forgetting mitigating. Further investigation for model parameters indicates that CLoRA effectively balances the trade-off between model capacity and degree of forgetting.
Explicit Alignment and Many-to-many Entailment Based Reasoning for Conversational Machine Reading
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Conversational Machine Reading (CMR) requires answering a user's initial question through multi-turn dialogue interactions based on a given document. Although there exist many effective methods, they largely neglected the alignment between the document and the user-provided information, which significantly affects the intermediate decision-making and subsequent follow-up question generation. To address this issue, we propose a pipeline framework that (1) aligns the aforementioned two sides in an explicit way, (2)makes decisions using a lightweight many-to-many entailment reasoning module, and (3) directly generates follow-up questions based on the document and previously asked questions. Our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art in micro-accuracy and ranks the first place on the public leaderboard of the CMR benchmark dataset ShARC.
A Task-oriented Dialog Model with Task-progressive and Policy-aware Pre-training
Oct 01, 2023Abstract:Pre-trained conversation models (PCMs) have achieved promising progress in recent years. However, existing PCMs for Task-oriented dialog (TOD) are insufficient for capturing the sequential nature of the TOD-related tasks, as well as for learning dialog policy information. To alleviate these problems, this paper proposes a task-progressive PCM with two policy-aware pre-training tasks. The model is pre-trained through three stages where TOD-related tasks are progressively employed according to the task logic of the TOD system. A global policy consistency task is designed to capture the multi-turn dialog policy sequential relation, and an act-based contrastive learning task is designed to capture similarities among samples with the same dialog policy. Our model achieves better results on both MultiWOZ and In-Car end-to-end dialog modeling benchmarks with only 18\% parameters and 25\% pre-training data compared to the previous state-of-the-art PCM, GALAXY.
AKEM: Aligning Knowledge Base to Queries with Ensemble Model for Entity Recognition and Linking
Sep 13, 2023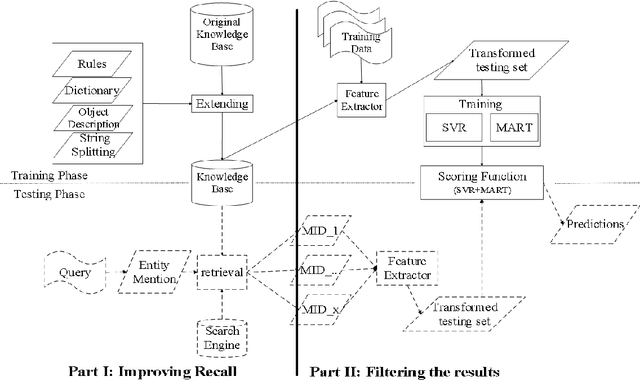
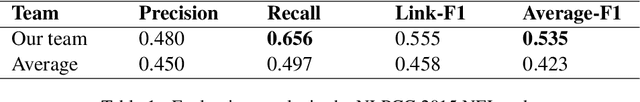
Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to address the Entity Recognition and Linking Challenge at NLPCC 2015. The task involves extracting named entity mentions from short search queries and linking them to entities within a reference Chinese knowledge base. To tackle this problem, we first expand the existing knowledge base and utilize external knowledge to identify candidate entities, thereby improving the recall rate. Next, we extract features from the candidate entities and utilize Support Vector Regression and Multiple Additive Regression Tree as scoring functions to filter the results. Additionally, we apply rules to further refine the results and enhance precision. Our method is computationally efficient and achieves an F1 score of 0.535.
An Asynchronous Updating Reinforcement Learning Framework for Task-oriented Dialog System
May 04, 2023


Abstract:Reinforcement learning has been applied to train the dialog systems in many works. Previous approaches divide the dialog system into multiple modules including DST (dialog state tracking) and DP (dialog policy), and train these modules simultaneously. However, different modules influence each other during training. The errors from DST might misguide the dialog policy, and the system action brings extra difficulties for the DST module. To alleviate this problem, we propose Asynchronous Updating Reinforcement Learning framework (AURL) that updates the DST module and the DP module asynchronously under a cooperative setting. Furthermore, curriculum learning is implemented to address the problem of unbalanced data distribution during reinforcement learning sampling, and multiple user models are introduced to increase the dialog diversity. Results on the public SSD-PHONE dataset show that our method achieves a compelling result with a 31.37% improvement on the dialog success rate. The code is publicly available via https://github.com/shunjiu/AURL.
SPRING: Situated Conversation Agent Pretrained with Multimodal Questions from Incremental Layout Graph
Jan 05, 2023



Abstract:Existing multimodal conversation agents have shown impressive abilities to locate absolute positions or retrieve attributes in simple scenarios, but they fail to perform well when complex relative positions and information alignments are involved, which poses a bottleneck in response quality. In this paper, we propose a Situated Conversation Agent Petrained with Multimodal Questions from INcremental Layout Graph (SPRING) with abilities of reasoning multi-hops spatial relations and connecting them with visual attributes in crowded situated scenarios. Specifically, we design two types of Multimodal Question Answering (MQA) tasks to pretrain the agent. All QA pairs utilized during pretraining are generated from novel Incremental Layout Graphs (ILG). QA pair difficulty labels automatically annotated by ILG are used to promote MQA-based Curriculum Learning. Experimental results verify the SPRING's effectiveness, showing that it significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches on both SIMMC 1.0 and SIMMC 2.0 datasets.
A Slot Is Not Built in One Utterance: Spoken Language Dialogs with Sub-Slots
Mar 21, 2022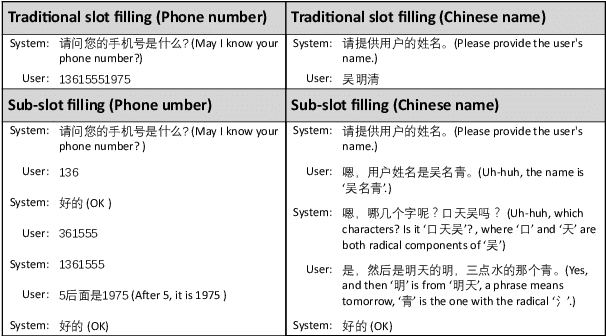
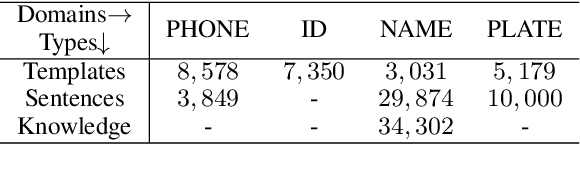
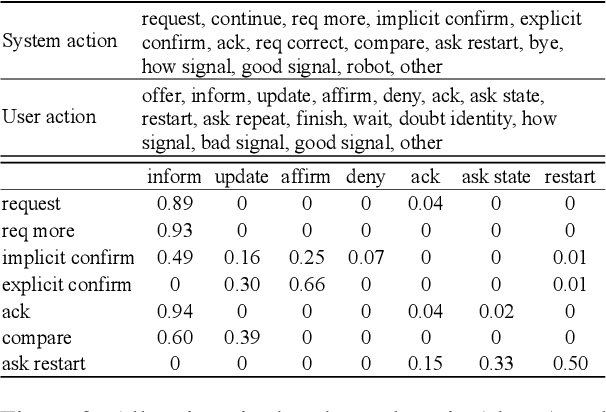
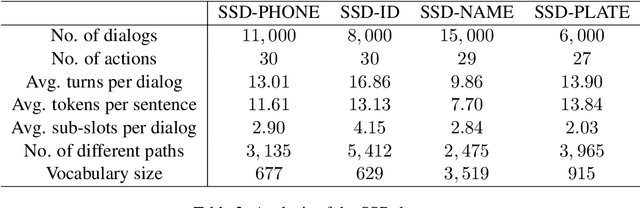
Abstract:A slot value might be provided segment by segment over multiple-turn interactions in a dialog, especially for some important information such as phone numbers and names. It is a common phenomenon in daily life, but little attention has been paid to it in previous work. To fill the gap, this paper defines a new task named Sub-Slot based Task-Oriented Dialog (SSTOD) and builds a Chinese dialog dataset SSD for boosting research on SSTOD. The dataset includes a total of 40K dialogs and 500K utterances from four different domains: Chinese names, phone numbers, ID numbers and license plate numbers. The data is well annotated with sub-slot values, slot values, dialog states and actions. We find some new linguistic phenomena and interactive manners in SSTOD which raise critical challenges of building dialog agents for the task. We test three state-of-the-art dialog models on SSTOD and find they cannot handle the task well on any of the four domains. We also investigate an improved model by involving slot knowledge in a plug-in manner. More work should be done to meet the new challenges raised from SSTOD which widely exists in real-life applications. The dataset and code are publicly available via https://github.com/shunjiu/SSTOD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge