Zhongying Deng
MedQ-Bench: Evaluating and Exploring Medical Image Quality Assessment Abilities in MLLMs
Oct 02, 2025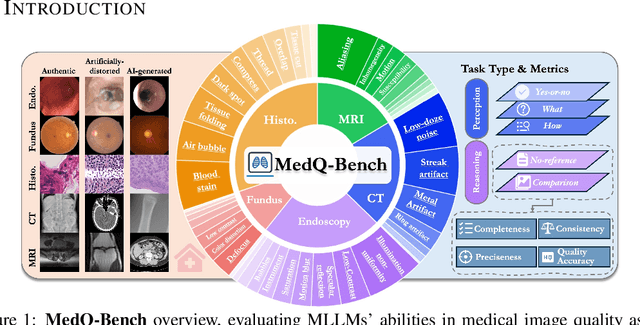
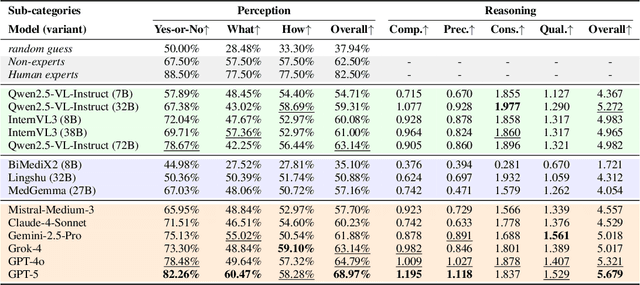
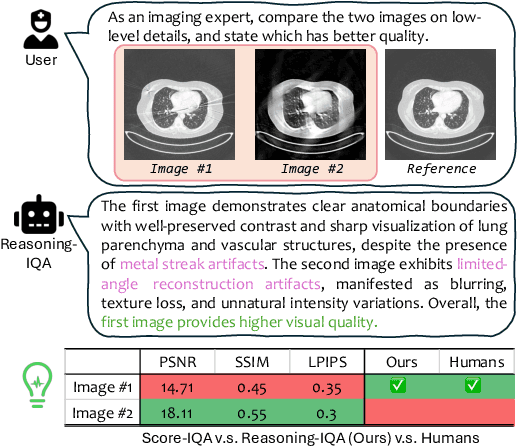
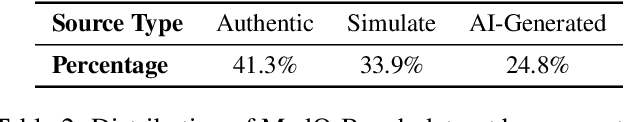
Abstract:Medical Image Quality Assessment (IQA) serves as the first-mile safety gate for clinical AI, yet existing approaches remain constrained by scalar, score-based metrics and fail to reflect the descriptive, human-like reasoning process central to expert evaluation. To address this gap, we introduce MedQ-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark that establishes a perception-reasoning paradigm for language-based evaluation of medical image quality with Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs). MedQ-Bench defines two complementary tasks: (1) MedQ-Perception, which probes low-level perceptual capability via human-curated questions on fundamental visual attributes; and (2) MedQ-Reasoning, encompassing both no-reference and comparison reasoning tasks, aligning model evaluation with human-like reasoning on image quality. The benchmark spans five imaging modalities and over forty quality attributes, totaling 2,600 perceptual queries and 708 reasoning assessments, covering diverse image sources including authentic clinical acquisitions, images with simulated degradations via physics-based reconstructions, and AI-generated images. To evaluate reasoning ability, we propose a multi-dimensional judging protocol that assesses model outputs along four complementary axes. We further conduct rigorous human-AI alignment validation by comparing LLM-based judgement with radiologists. Our evaluation of 14 state-of-the-art MLLMs demonstrates that models exhibit preliminary but unstable perceptual and reasoning skills, with insufficient accuracy for reliable clinical use. These findings highlight the need for targeted optimization of MLLMs in medical IQA. We hope that MedQ-Bench will catalyze further exploration and unlock the untapped potential of MLLMs for medical image quality evaluation.
A Survey of Scientific Large Language Models: From Data Foundations to Agent Frontiers
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) are transforming how knowledge is represented, integrated, and applied in scientific research, yet their progress is shaped by the complex nature of scientific data. This survey presents a comprehensive, data-centric synthesis that reframes the development of Sci-LLMs as a co-evolution between models and their underlying data substrate. We formulate a unified taxonomy of scientific data and a hierarchical model of scientific knowledge, emphasizing the multimodal, cross-scale, and domain-specific challenges that differentiate scientific corpora from general natural language processing datasets. We systematically review recent Sci-LLMs, from general-purpose foundations to specialized models across diverse scientific disciplines, alongside an extensive analysis of over 270 pre-/post-training datasets, showing why Sci-LLMs pose distinct demands -- heterogeneous, multi-scale, uncertainty-laden corpora that require representations preserving domain invariance and enabling cross-modal reasoning. On evaluation, we examine over 190 benchmark datasets and trace a shift from static exams toward process- and discovery-oriented assessments with advanced evaluation protocols. These data-centric analyses highlight persistent issues in scientific data development and discuss emerging solutions involving semi-automated annotation pipelines and expert validation. Finally, we outline a paradigm shift toward closed-loop systems where autonomous agents based on Sci-LLMs actively experiment, validate, and contribute to a living, evolving knowledge base. Collectively, this work provides a roadmap for building trustworthy, continually evolving artificial intelligence (AI) systems that function as a true partner in accelerating scientific discovery.
Conservation-preserved Fourier Neural Operator through Adaptive Correction
May 30, 2025

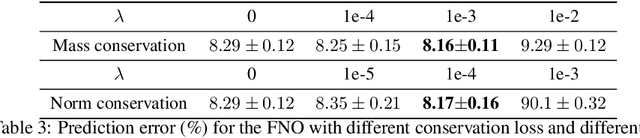
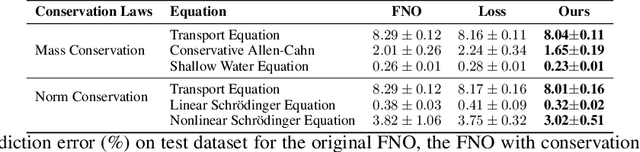
Abstract:Fourier Neural Operators (FNOs) have recently emerged as a promising and efficient approach for learning the numerical solutions to partial differential equations (PDEs) from data. However, standard FNO often fails to preserve key conservation laws, such as mass conservation, momentum conservation, norm conservation, etc., which are crucial for accurately modeling physical systems. Existing methods for incorporating these conservation laws into Fourier neural operators are achieved by designing related loss function or incorporating post-processing method at the training time. None of them can both exactly and adaptively correct the outputs to satisfy conservation laws, and our experiments show that these methods can lead to inferior performance while preserving conservation laws. In this work, we propose a novel adaptive correction approach to ensure the conservation of fundamental quantities. Our method introduces a learnable matrix to adaptively adjust the solution to satisfy the conservation law during training. It ensures that the outputs exactly satisfy the goal conservation law and allow for more flexibility and adaptivity for the model to correct the outputs. We theoretically show that applying our adaptive correction to an unconstrained FNO yields a solution with data loss no worse than that of the best conservation-satisfying FNO. We compare our approach with existing methods on a range of representative PDEs. Experiment results show that our method consistently outperform other methods.
Brain Foundation Models with Hypergraph Dynamic Adapter for Brain Disease Analysis
May 01, 2025Abstract:Brain diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and brain tumors, present profound challenges due to their complexity and societal impact. Recent advancements in brain foundation models have shown significant promise in addressing a range of brain-related tasks. However, current brain foundation models are limited by task and data homogeneity, restricted generalization beyond segmentation or classification, and inefficient adaptation to diverse clinical tasks. In this work, we propose SAM-Brain3D, a brain-specific foundation model trained on over 66,000 brain image-label pairs across 14 MRI sub-modalities, and Hypergraph Dynamic Adapter (HyDA), a lightweight adapter for efficient and effective downstream adaptation. SAM-Brain3D captures detailed brain-specific anatomical and modality priors for segmenting diverse brain targets and broader downstream tasks. HyDA leverages hypergraphs to fuse complementary multi-modal data and dynamically generate patient-specific convolutional kernels for multi-scale feature fusion and personalized patient-wise adaptation. Together, our framework excels across a broad spectrum of brain disease segmentation and classification tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, offering a new paradigm for brain disease analysis through multi-modal, multi-scale, and dynamic foundation modeling.
D2SA: Dual-Stage Distribution and Slice Adaptation for Efficient Test-Time Adaptation in MRI Reconstruction
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Variations in Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners and acquisition protocols cause distribution shifts that degrade reconstruction performance on unseen data. Test-time adaptation (TTA) offers a promising solution to address this discrepancies. However, previous single-shot TTA approaches are inefficient due to repeated training and suboptimal distributional models. Self-supervised learning methods are also limited by scarce date scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Dual-Stage Distribution and Slice Adaptation (D2SA) via MRI implicit neural representation (MR-INR) to improve MRI reconstruction performance and efficiency, which features two stages. In the first stage, an MR-INR branch performs patient-wise distribution adaptation by learning shared representations across slices and modelling patient-specific shifts with mean and variance adjustments. In the second stage, single-slice adaptation refines the output from frozen convolutional layers with a learnable anisotropic diffusion module, preventing over-smoothing and reducing computation. Experiments across four MRI distribution shifts demonstrate that our method can integrate well with various self-supervised learning (SSL) framework, improving performance and accelerating convergence under diverse conditions.
SegBook: A Simple Baseline and Cookbook for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 21, 2024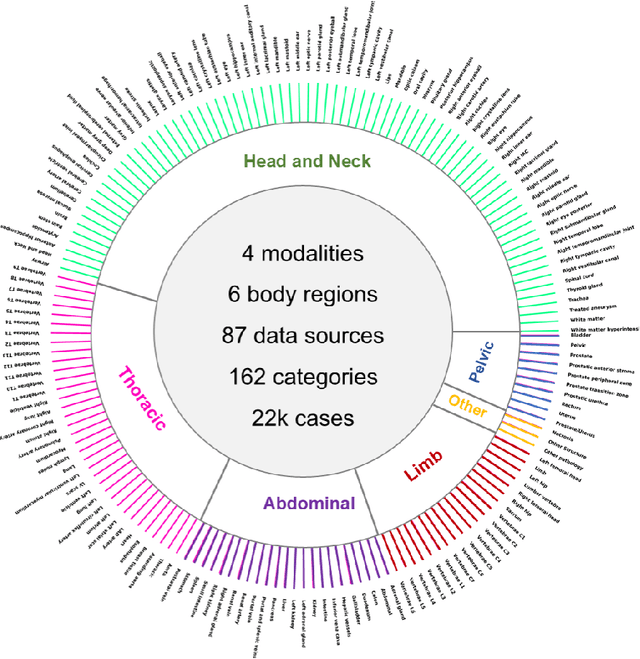
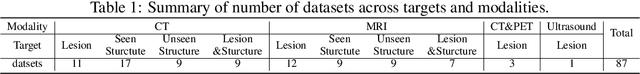
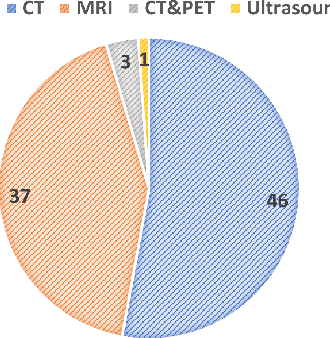
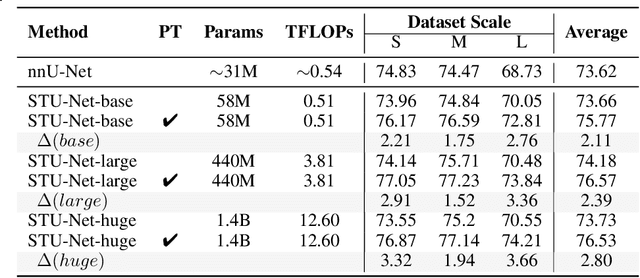
Abstract:Computed Tomography (CT) is one of the most popular modalities for medical imaging. By far, CT images have contributed to the largest publicly available datasets for volumetric medical segmentation tasks, covering full-body anatomical structures. Large amounts of full-body CT images provide the opportunity to pre-train powerful models, e.g., STU-Net pre-trained in a supervised fashion, to segment numerous anatomical structures. However, it remains unclear in which conditions these pre-trained models can be transferred to various downstream medical segmentation tasks, particularly segmenting the other modalities and diverse targets. To address this problem, a large-scale benchmark for comprehensive evaluation is crucial for finding these conditions. Thus, we collected 87 public datasets varying in modality, target, and sample size to evaluate the transfer ability of full-body CT pre-trained models. We then employed a representative model, STU-Net with multiple model scales, to conduct transfer learning across modalities and targets. Our experimental results show that (1) there may be a bottleneck effect concerning the dataset size in fine-tuning, with more improvement on both small- and large-scale datasets than medium-size ones. (2) Models pre-trained on full-body CT demonstrate effective modality transfer, adapting well to other modalities such as MRI. (3) Pre-training on the full-body CT not only supports strong performance in structure detection but also shows efficacy in lesion detection, showcasing adaptability across target tasks. We hope that this large-scale open evaluation of transfer learning can direct future research in volumetric medical image segmentation.
GMAI-VL & GMAI-VL-5.5M: A Large Vision-Language Model and A Comprehensive Multimodal Dataset Towards General Medical AI
Nov 21, 2024Abstract:Despite significant advancements in general artificial intelligence, such as GPT-4, their effectiveness in the medical domain (general medical AI, GMAI) remains constrained due to the absence of specialized medical knowledge. To address this challenge, we present GMAI-VL-5.5M, a comprehensive multimodal medical dataset created by converting hundreds of specialized medical datasets into meticulously constructed image-text pairs. This dataset features comprehensive task coverage, diverse modalities, and high-quality image-text data. Building upon this multimodal dataset, we propose GMAI-VL, a general medical vision-language model with a progressively three-stage training strategy. This approach significantly enhances the model's ability by integrating visual and textual information, thereby improving its ability to process multimodal data and support accurate diagnosis and clinical decision-making. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that GMAI-VL achieves state-of-the-art results across a wide range of multimodal medical tasks, such as visual question answering and medical image diagnosis. Our contributions include the development of the GMAI-VL-5.5M dataset, the introduction of the GMAI-VL model, and the establishment of new benchmarks in multiple medical domains. Code and dataset will be released at https://github.com/uni-medical/GMAI-VL.
Where Do We Stand with Implicit Neural Representations? A Technical and Performance Survey
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have emerged as a paradigm in knowledge representation, offering exceptional flexibility and performance across a diverse range of applications. INRs leverage multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) to model data as continuous implicit functions, providing critical advantages such as resolution independence, memory efficiency, and generalisation beyond discretised data structures. Their ability to solve complex inverse problems makes them particularly effective for tasks including audio reconstruction, image representation, 3D object reconstruction, and high-dimensional data synthesis. This survey provides a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art INR methods, introducing a clear taxonomy that categorises them into four key areas: activation functions, position encoding, combined strategies, and network structure optimisation. We rigorously analyse their critical properties, such as full differentiability, smoothness, compactness, and adaptability to varying resolutions while also examining their strengths and limitations in addressing locality biases and capturing fine details. Our experimental comparison offers new insights into the trade-offs between different approaches, showcasing the capabilities and challenges of the latest INR techniques across various tasks. In addition to identifying areas where current methods excel, we highlight key limitations and potential avenues for improvement, such as developing more expressive activation functions, enhancing positional encoding mechanisms, and improving scalability for complex, high-dimensional data. This survey serves as a roadmap for researchers, offering practical guidance for future exploration in the field of INRs. We aim to foster new methodologies by outlining promising research directions for INRs and applications.
GMAI-MMBench: A Comprehensive Multimodal Evaluation Benchmark Towards General Medical AI
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) are capable of handling diverse data types such as imaging, text, and physiological signals, and can be applied in various fields. In the medical field, LVLMs have a high potential to offer substantial assistance for diagnosis and treatment. Before that, it is crucial to develop benchmarks to evaluate LVLMs' effectiveness in various medical applications. Current benchmarks are often built upon specific academic literature, mainly focusing on a single domain, and lacking varying perceptual granularities. Thus, they face specific challenges, including limited clinical relevance, incomplete evaluations, and insufficient guidance for interactive LVLMs. To address these limitations, we developed the GMAI-MMBench, the most comprehensive general medical AI benchmark with well-categorized data structure and multi-perceptual granularity to date. It is constructed from 285 datasets across 39 medical image modalities, 18 clinical-related tasks, 18 departments, and 4 perceptual granularities in a Visual Question Answering (VQA) format. Additionally, we implemented a lexical tree structure that allows users to customize evaluation tasks, accommodating various assessment needs and substantially supporting medical AI research and applications. We evaluated 50 LVLMs, and the results show that even the advanced GPT-4o only achieves an accuracy of 52\%, indicating significant room for improvement. Moreover, we identified five key insufficiencies in current cutting-edge LVLMs that need to be addressed to advance the development of better medical applications. We believe that GMAI-MMBench will stimulate the community to build the next generation of LVLMs toward GMAI.
Bilevel Hypergraph Networks for Multi-Modal Alzheimer's Diagnosis
Mar 19, 2024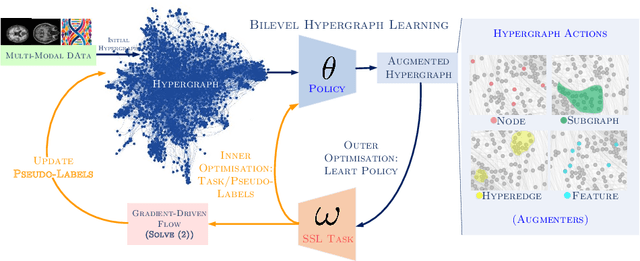
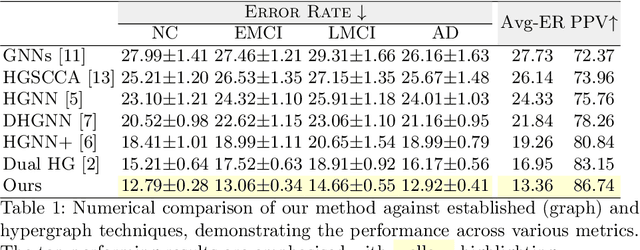
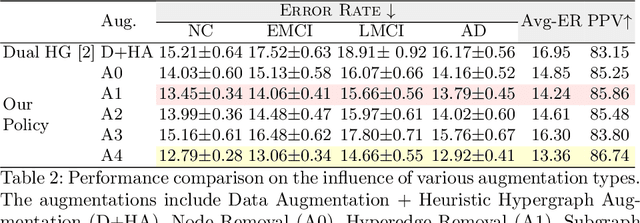
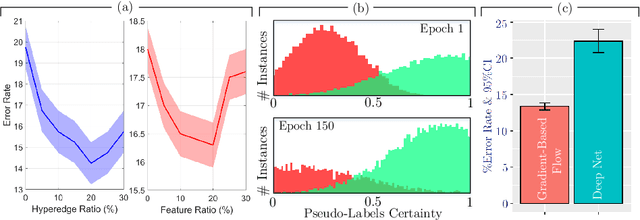
Abstract:Early detection of Alzheimer's disease's precursor stages is imperative for significantly enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life. This challenge is tackled through a semi-supervised multi-modal diagnosis framework. In particular, we introduce a new hypergraph framework that enables higher-order relations between multi-modal data, while utilising minimal labels. We first introduce a bilevel hypergraph optimisation framework that jointly learns a graph augmentation policy and a semi-supervised classifier. This dual learning strategy is hypothesised to enhance the robustness and generalisation capabilities of the model by fostering new pathways for information propagation. Secondly, we introduce a novel strategy for generating pseudo-labels more effectively via a gradient-driven flow. Our experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of our framework over current techniques in diagnosing Alzheimer's disease.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge