Zhihao Yuan
See the Forest and the Trees: A Synergistic Reasoning Framework for Knowledge-Based Visual Question Answering
Jul 23, 2025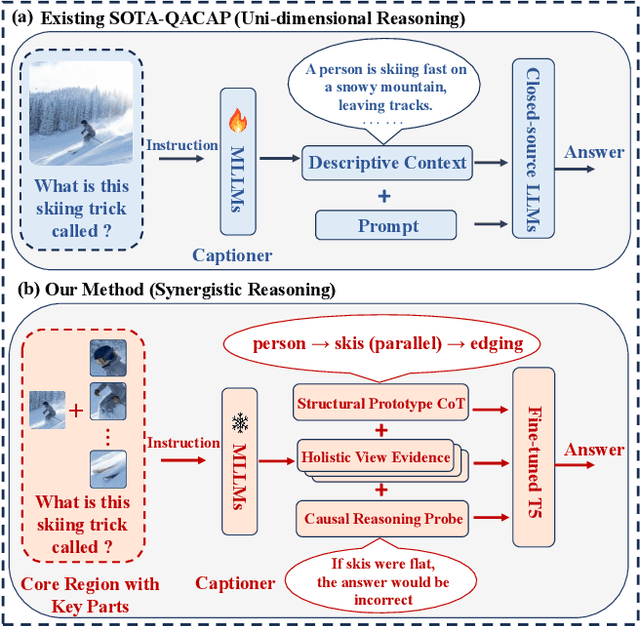



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have pushed the frontiers of Knowledge-Based Visual Question Answering (KBVQA), yet their reasoning is fundamentally bottlenecked by a reliance on uni-dimensional evidence. This "seeing only the trees, but not the forest" approach prevents robust, multi-faceted understanding. Inspired by the principle of seeing both the forest and trees, we propose Synergos-VQA, a novel synergistic reasoning framework. At its core, Synergos-VQA concurrently generates and fuses three complementary evidence streams at inference time: (1) Holistic Evidence to perceive the entire scene (the "forest"), (2) Structural Evidence from a prototype-driven module to identify key objects (the "trees"), and (3) Causal Evidence from a counterfactual probe to ensure the reasoning is robustly grounded. By synergistically fusing this multi-faceted evidence, our framework achieves a more comprehensive and reliable reasoning process. Extensive experiments show that Synergos-VQA decisively establishes a new state-of-the-art on three challenging benchmarks, including OK-VQA and A-OKVQA. Furthermore, our approach demonstrates strong plug-and-play capabilities, significantly boosting various open-source MLLMs and proving that superior methodological design can outperform sheer model scale.
Empowering Large Language Models with 3D Situation Awareness
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Driven by the great success of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the 2D image domain, their applications in 3D scene understanding has emerged as a new trend. A key difference between 3D and 2D is that the situation of an egocentric observer in 3D scenes can change, resulting in different descriptions (e.g., ''left" or ''right"). However, current LLM-based methods overlook the egocentric perspective and simply use datasets from a global viewpoint. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach to automatically generate a situation-aware dataset by leveraging the scanning trajectory during data collection and utilizing Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to produce high-quality captions and question-answer pairs. Furthermore, we introduce a situation grounding module to explicitly predict the position and orientation of observer's viewpoint, thereby enabling LLMs to ground situation description in 3D scenes. We evaluate our approach on several benchmarks, demonstrating that our method effectively enhances the 3D situational awareness of LLMs while significantly expanding existing datasets and reducing manual effort.
PiSA: A Self-Augmented Data Engine and Training Strategy for 3D Understanding with Large Models
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:3D Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have recently made substantial advancements. However, their potential remains untapped, primarily due to the limited quantity and suboptimal quality of 3D datasets. Current approaches attempt to transfer knowledge from 2D MLLMs to expand 3D instruction data, but still face modality and domain gaps. To this end, we introduce PiSA-Engine (Point-Self-Augmented-Engine), a new framework for generating instruction point-language datasets enriched with 3D spatial semantics. We observe that existing 3D MLLMs offer a comprehensive understanding of point clouds for annotation, while 2D MLLMs excel at cross-validation by providing complementary information. By integrating holistic 2D and 3D insights from off-the-shelf MLLMs, PiSA-Engine enables a continuous cycle of high-quality data generation. We select PointLLM as the baseline and adopt this co-evolution training framework to develop an enhanced 3D MLLM, termed PointLLM-PiSA. Additionally, we identify limitations in previous 3D benchmarks, which often feature coarse language captions and insufficient category diversity, resulting in inaccurate evaluations. To address this gap, we further introduce PiSA-Bench, a comprehensive 3D benchmark covering six key aspects with detailed and diverse labels. Experimental results demonstrate PointLLM-PiSA's state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot 3D object captioning and generative classification on our PiSA-Bench, achieving significant improvements of 46.45% (+8.33%) and 63.75% (+16.25%), respectively. We will release the code, datasets, and benchmark.
Generative Semantic Communication for Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:Semantic communication is a promising technology to improve communication efficiency by transmitting only the semantic information of the source data. However, traditional semantic communication methods primarily focus on data reconstruction tasks, which may not be efficient for emerging generative tasks such as text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. To address this limitation, this paper develops a novel generative semantic communication framework for TTS synthesis, leveraging generative artificial intelligence technologies. Firstly, we utilize a pre-trained large speech model called WavLM and the residual vector quantization method to construct two semantic knowledge bases (KBs) at the transmitter and receiver, respectively. The KB at the transmitter enables effective semantic extraction, while the KB at the receiver facilitates lifelike speech synthesis. Then, we employ a transformer encoder and a diffusion model to achieve efficient semantic coding without introducing significant communication overhead. Finally, numerical results demonstrate that our framework achieves much higher fidelity for the generated speech than four baselines, in both cases with additive white Gaussian noise channel and Rayleigh fading channel.
Instance-free Text to Point Cloud Localization with Relative Position Awareness
Apr 27, 2024Abstract:Text-to-point-cloud cross-modal localization is an emerging vision-language task critical for future robot-human collaboration. It seeks to localize a position from a city-scale point cloud scene based on a few natural language instructions. In this paper, we address two key limitations of existing approaches: 1) their reliance on ground-truth instances as input; and 2) their neglect of the relative positions among potential instances. Our proposed model follows a two-stage pipeline, including a coarse stage for text-cell retrieval and a fine stage for position estimation. In both stages, we introduce an instance query extractor, in which the cells are encoded by a 3D sparse convolution U-Net to generate the multi-scale point cloud features, and a set of queries iteratively attend to these features to represent instances. In the coarse stage, a row-column relative position-aware self-attention (RowColRPA) module is designed to capture the spatial relations among the instance queries. In the fine stage, a multi-modal relative position-aware cross-attention (RPCA) module is developed to fuse the text and point cloud features along with spatial relations for improving fine position estimation. Experiment results on the KITTI360Pose dataset demonstrate that our model achieves competitive performance with the state-of-the-art models without taking ground-truth instances as input.
GSmoothFace: Generalized Smooth Talking Face Generation via Fine Grained 3D Face Guidance
Dec 12, 2023



Abstract:Although existing speech-driven talking face generation methods achieve significant progress, they are far from real-world application due to the avatar-specific training demand and unstable lip movements. To address the above issues, we propose the GSmoothFace, a novel two-stage generalized talking face generation model guided by a fine-grained 3d face model, which can synthesize smooth lip dynamics while preserving the speaker's identity. Our proposed GSmoothFace model mainly consists of the Audio to Expression Prediction (A2EP) module and the Target Adaptive Face Translation (TAFT) module. Specifically, we first develop the A2EP module to predict expression parameters synchronized with the driven speech. It uses a transformer to capture the long-term audio context and learns the parameters from the fine-grained 3D facial vertices, resulting in accurate and smooth lip-synchronization performance. Afterward, the well-designed TAFT module, empowered by Morphology Augmented Face Blending (MAFB), takes the predicted expression parameters and target video as inputs to modify the facial region of the target video without distorting the background content. The TAFT effectively exploits the identity appearance and background context in the target video, which makes it possible to generalize to different speakers without retraining. Both quantitative and qualitative experiments confirm the superiority of our method in terms of realism, lip synchronization, and visual quality. See the project page for code, data, and request pre-trained models: https://zhanghm1995.github.io/GSmoothFace.
Visual Programming for Zero-shot Open-Vocabulary 3D Visual Grounding
Nov 26, 2023



Abstract:3D Visual Grounding (3DVG) aims at localizing 3D object based on textual descriptions. Conventional supervised methods for 3DVG often necessitate extensive annotations and a predefined vocabulary, which can be restrictive. To address this issue, we propose a novel visual programming approach for zero-shot open-vocabulary 3DVG, leveraging the capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Our approach begins with a unique dialog-based method, engaging with LLMs to establish a foundational understanding of zero-shot 3DVG. Building on this, we design a visual program that consists of three types of modules, i.e., view-independent, view-dependent, and functional modules. These modules, specifically tailored for 3D scenarios, work collaboratively to perform complex reasoning and inference. Furthermore, we develop an innovative language-object correlation module to extend the scope of existing 3D object detectors into open-vocabulary scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our zero-shot approach can outperform some supervised baselines, marking a significant stride towards effective 3DVG.
Toward Explainable and Fine-Grained 3D Grounding through Referring Textual Phrases
Jul 05, 2022



Abstract:Recent progress on 3D scene understanding has explored visual grounding (3DVG) to localize a target object through a language description. However, existing methods only consider the dependency between the entire sentence and the target object, thus ignoring fine-grained relationships between contexts and non-target ones. In this paper, we extend 3DVG to a more reliable and explainable task, called 3D Phrase Aware Grounding (3DPAG). The 3DPAG task aims to localize the target object in the 3D scenes by explicitly identifying all phrase-related objects and then conducting reasoning according to contextual phrases. To tackle this problem, we label about 400K phrase-level annotations from 170K sentences in available 3DVG datasets, i.e., Nr3D, Sr3D and ScanRefer. By tapping on these developed datasets, we propose a novel framework, i.e., PhraseRefer, which conducts phrase-aware and object-level representation learning through phrase-object alignment optimization as well as phrase-specific pre-training. In our setting, we extend previous 3DVG methods to the phrase-aware scenario and provide metrics to measure the explainability of the 3DPAG task. Extensive results confirm that 3DPAG effectively boosts the 3DVG, and PhraseRefer achieves state-of-the-arts across three datasets, i.e., 63.0%, 54.4% and 55.5% overall accuracy on Sr3D, Nr3D and ScanRefer, respectively.
X-Trans2Cap: Cross-Modal Knowledge Transfer using Transformer for 3D Dense Captioning
Apr 06, 2022



Abstract:3D dense captioning aims to describe individual objects by natural language in 3D scenes, where 3D scenes are usually represented as RGB-D scans or point clouds. However, only exploiting single modal information, e.g., point cloud, previous approaches fail to produce faithful descriptions. Though aggregating 2D features into point clouds may be beneficial, it introduces an extra computational burden, especially in inference phases. In this study, we investigate a cross-modal knowledge transfer using Transformer for 3D dense captioning, X-Trans2Cap, to effectively boost the performance of single-modal 3D caption through knowledge distillation using a teacher-student framework. In practice, during the training phase, the teacher network exploits auxiliary 2D modality and guides the student network that only takes point clouds as input through the feature consistency constraints. Owing to the well-designed cross-modal feature fusion module and the feature alignment in the training phase, X-Trans2Cap acquires rich appearance information embedded in 2D images with ease. Thus, a more faithful caption can be generated only using point clouds during the inference. Qualitative and quantitative results confirm that X-Trans2Cap outperforms previous state-of-the-art by a large margin, i.e., about +21 and about +16 absolute CIDEr score on ScanRefer and Nr3D datasets, respectively.
CLEVR3D: Compositional Language and Elementary Visual Reasoning for Question Answering in 3D Real-World Scenes
Dec 31, 2021



Abstract:3D scene understanding is a relatively emerging research field. In this paper, we introduce the Visual Question Answering task in 3D real-world scenes (VQA-3D), which aims to answer all possible questions given a 3D scene. To tackle this problem, the first VQA-3D dataset, namely CLEVR3D, is proposed, which contains 60K questions in 1,129 real-world scenes. Specifically, we develop a question engine leveraging 3D scene graph structures to generate diverse reasoning questions, covering the questions of objects' attributes (i.e., size, color, and material) and their spatial relationships. Built upon this dataset, we further design the first VQA-3D baseline model, TransVQA3D. The TransVQA3D model adopts well-designed Transformer architectures to achieve superior VQA-3D performance, compared with the pure language baseline and previous 3D reasoning methods directly applied to 3D scenarios. Experimental results verify that taking VQA-3D as an auxiliary task can boost the performance of 3D scene understanding, including scene graph analysis for the node-wise classification and whole-graph recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge