Gui Gui
When UAV Meets Federated Learning: Latency Minimization via Joint Trajectory Design and Resource Allocation
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a pivotal solution for training machine learning models over wireless networks, particularly for Internet of Things (IoT) devices with limited computation resources. Despite its benefits, the efficiency of FL is often restricted by the communication quality between IoT devices and the central server. To address this issue, we introduce an innovative approach by deploying an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) as a mobile FL server to enhance the training process of FL. By leveraging the UAV's maneuverability, we establish robust line-of-sight connections with IoT devices, significantly improving communication capacity. To improve the overall training efficiency, we formulate a latency minimization problem by jointly optimizing the bandwidth allocation, computing frequencies, transmit power for both the UAV and IoT devices, and the UAV's trajectory. Then, an efficient alternating optimization algorithm is developed to solve it efficiently. Furthermore, we analyze the convergence and computational complexity of the proposed algorithm. Finally, numerical results demonstrate that our proposed scheme not only outperforms existing benchmark schemes in terms of latency but also achieves training efficiency that closely approximate the ideal scenario.
Generative Semantic Communication for Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:Semantic communication is a promising technology to improve communication efficiency by transmitting only the semantic information of the source data. However, traditional semantic communication methods primarily focus on data reconstruction tasks, which may not be efficient for emerging generative tasks such as text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. To address this limitation, this paper develops a novel generative semantic communication framework for TTS synthesis, leveraging generative artificial intelligence technologies. Firstly, we utilize a pre-trained large speech model called WavLM and the residual vector quantization method to construct two semantic knowledge bases (KBs) at the transmitter and receiver, respectively. The KB at the transmitter enables effective semantic extraction, while the KB at the receiver facilitates lifelike speech synthesis. Then, we employ a transformer encoder and a diffusion model to achieve efficient semantic coding without introducing significant communication overhead. Finally, numerical results demonstrate that our framework achieves much higher fidelity for the generated speech than four baselines, in both cases with additive white Gaussian noise channel and Rayleigh fading channel.
Scalable Federated Unlearning via Isolated and Coded Sharding
Jan 29, 2024

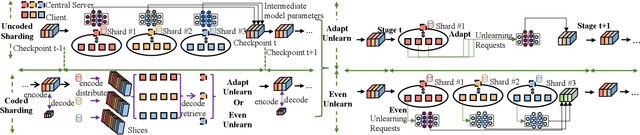

Abstract:Federated unlearning has emerged as a promising paradigm to erase the client-level data effect without affecting the performance of collaborative learning models. However, the federated unlearning process often introduces extensive storage overhead and consumes substantial computational resources, thus hindering its implementation in practice. To address this issue, this paper proposes a scalable federated unlearning framework based on isolated sharding and coded computing. We first divide distributed clients into multiple isolated shards across stages to reduce the number of clients being affected. Then, to reduce the storage overhead of the central server, we develop a coded computing mechanism by compressing the model parameters across different shards. In addition, we provide the theoretical analysis of time efficiency and storage effectiveness for the isolated and coded sharding. Finally, extensive experiments on two typical learning tasks, i.e., classification and generation, demonstrate that our proposed framework can achieve better performance than three state-of-the-art frameworks in terms of accuracy, retraining time, storage overhead, and F1 scores for resisting membership inference attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge