Zhihao Lin
On Geometric Structures for Policy Parameterization in Continuous Control
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Standard stochastic policies for continuous control often rely on ad-hoc boundary-enforcing transformations (e.g., tanh) which can distort the underlying optimization landscape and introduce gradient pathologies. While alternative parameterizations on the unit manifold (e.g., directional distributions) are theoretically appealing, their computational complexity (often requiring special functions or rejection sampling) has limited their practical use. We propose a novel, computationally efficient action generation paradigm that preserves the structural benefits of operating on a unit manifold. Our method decomposes the action into a deterministic directional vector and a learnable concentration scalar, enabling efficient interpolation between the target direction and uniform noise on the unit manifold. This design can reduce policy head parameters by nearly 50\% (from $2d$ to $d+1$) and maintains a simple $O(d)$ sampling complexity, avoiding costly sampling procedures. Empirically, our method matches or exceeds state-of-the-art methods on standard continuous control benchmarks, with significant improvements (e.g., +37.6\% and +112\%) on high-dimensional locomotion tasks. Ablation studies confirm that both the unit-norm normalization and the adaptive concentration mechanism are essential to the method's success. These findings suggest that robust, efficient control can be achieved by explicitly respecting the structure of bounded action spaces, rather than relying on complex, unbounded distributions. Code is available in supplementary materials.
PrefPoE: Advantage-Guided Preference Fusion for Learning Where to Explore
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Exploration in reinforcement learning remains a critical challenge, as naive entropy maximization often results in high variance and inefficient policy updates. We introduce \textbf{PrefPoE}, a novel \textit{Preference-Product-of-Experts} framework that performs intelligent, advantage-guided exploration via the first principled application of product-of-experts (PoE) fusion for single-task exploration-exploitation balancing. By training a preference network to concentrate probability mass on high-advantage actions and fusing it with the main policy through PoE, PrefPoE creates a \textbf{soft trust region} that stabilizes policy updates while maintaining targeted exploration. Across diverse control tasks spanning both continuous and discrete action spaces, PrefPoE demonstrates consistent improvements: +321\% on HalfCheetah-v4 (1276~$\rightarrow$~5375), +69\% on Ant-v4, +276\% on LunarLander-v2, with consistently enhanced training stability and sample efficiency. Unlike standard PPO, which suffers from entropy collapse, PrefPoE sustains adaptive exploration through its unique dynamics, thereby preventing premature convergence and enabling superior performance. Our results establish that learning \textit{where to explore} through advantage-guided preferences is as crucial as learning how to act, offering a general framework for enhancing policy gradient methods across the full spectrum of reinforcement learning domains. Code and pretrained models are available in supplementary materials.
Adaptive Evolutionary Framework for Safe, Efficient, and Cooperative Autonomous Vehicle Interactions
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Modern transportation systems face significant challenges in ensuring road safety, given serious injuries caused by road accidents. The rapid growth of autonomous vehicles (AVs) has prompted new traffic designs that aim to optimize interactions among AVs. However, effective interactions between AVs remains challenging due to the absence of centralized control. Besides, there is a need for balancing multiple factors, including passenger demands and overall traffic efficiency. Traditional rule-based, optimization-based, and game-theoretic approaches each have limitations in addressing these challenges. Rule-based methods struggle with adaptability and generalization in complex scenarios, while optimization-based methods often require high computational resources. Game-theoretic approaches, such as Stackelberg and Nash games, suffer from limited adaptability and potential inefficiencies in cooperative settings. This paper proposes an Evolutionary Game Theory (EGT)-based framework for AV interactions that overcomes these limitations by utilizing a decentralized and adaptive strategy evolution mechanism. A causal evaluation module (CEGT) is introduced to optimize the evolutionary rate, balancing mutation and evolution by learning from historical interactions. Simulation results demonstrate the proposed CEGT outperforms EGT and popular benchmark games in terms of lower collision rates, improved safety distances, higher speeds, and overall better performance compared to Nash and Stackelberg games across diverse scenarios and parameter settings.
Attention and Risk-Aware Decision Framework for Safe Autonomous Driving
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving has attracted great interest due to its potential capability in full-unsupervised driving. Model-based and learning-based methods are widely used in autonomous driving. Model-based methods rely on pre-defined models of the environment and may struggle with unforeseen events. Proximal policy optimization (PPO), an advanced learning-based method, can adapt to the above limits by learning from interactions with the environment. However, existing PPO faces challenges with poor training results, and low training efficiency in long sequences. Moreover, the poor training results are equivalent to collisions in driving tasks. To solve these issues, this paper develops an improved PPO by introducing the risk-aware mechanism, a risk-attention decision network, a balanced reward function, and a safety-assisted mechanism. The risk-aware mechanism focuses on highlighting areas with potential collisions, facilitating safe-driving learning of the PPO. The balanced reward function adjusts rewards based on the number of surrounding vehicles, promoting efficient exploration of the control strategy during training. Additionally, the risk-attention network enhances the PPO to hold channel and spatial attention for the high-risk areas of input images. Moreover, the safety-assisted mechanism supervises and prevents the actions with risks of collisions during the lane keeping and lane changing. Simulation results on a physical engine demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms benchmark algorithms in collision avoidance, achieving higher peak reward with less training time, and shorter driving time remaining on the risky areas among multiple testing traffic flow scenarios.
Efficient and Safe Planner for Automated Driving on Ramps Considering Unsatisfication
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Automated driving on ramps presents significant challenges due to the need to balance both safety and efficiency during lane changes. This paper proposes an integrated planner for automated vehicles (AVs) on ramps, utilizing an unsatisfactory level metric for efficiency and arrow-cluster-based sampling for safety. The planner identifies optimal times for the AV to change lanes, taking into account the vehicle's velocity as a key factor in efficiency. Additionally, the integrated planner employs arrow-cluster-based sampling to evaluate collision risks and select an optimal lane-changing curve. Extensive simulations were conducted in a ramp scenario to verify the planner's efficient and safe performance. The results demonstrate that the proposed planner can effectively select an appropriate lane-changing time point and a safe lane-changing curve for AVs, without incurring any collisions during the maneuver.
Evaluating Scenario-based Decision-making for Interactive Autonomous Driving Using Rational Criteria: A Survey
Jan 03, 2025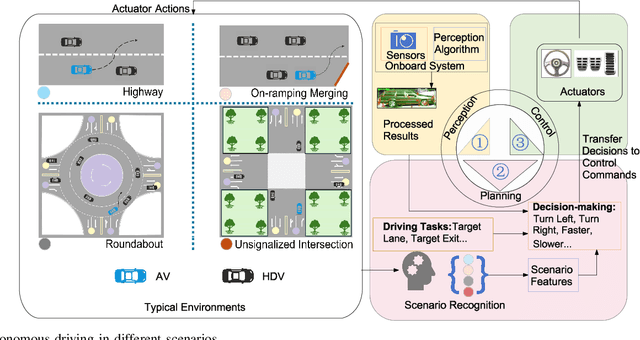
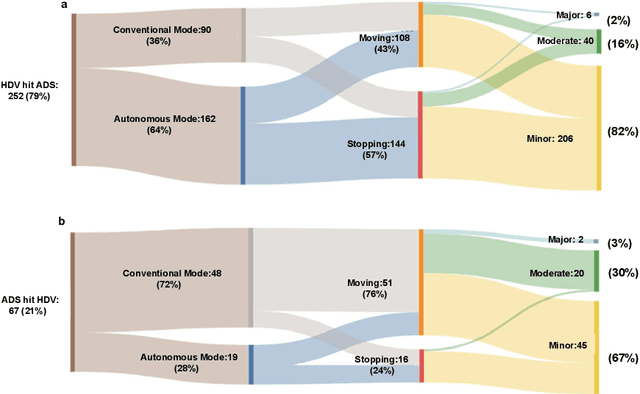
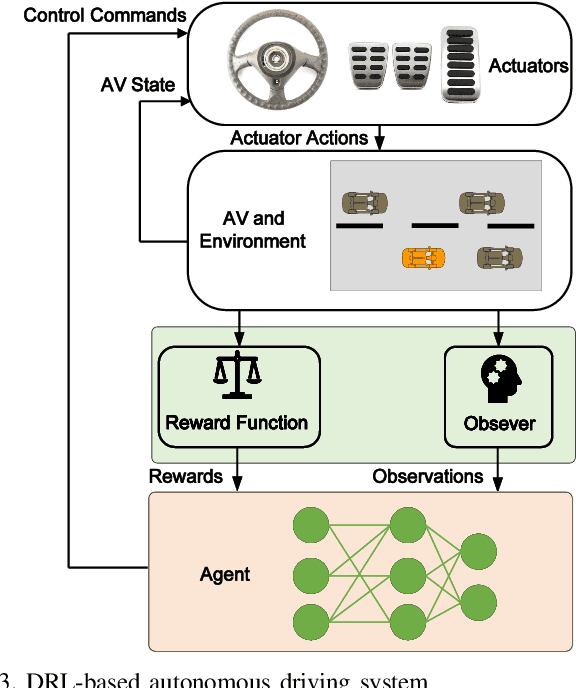
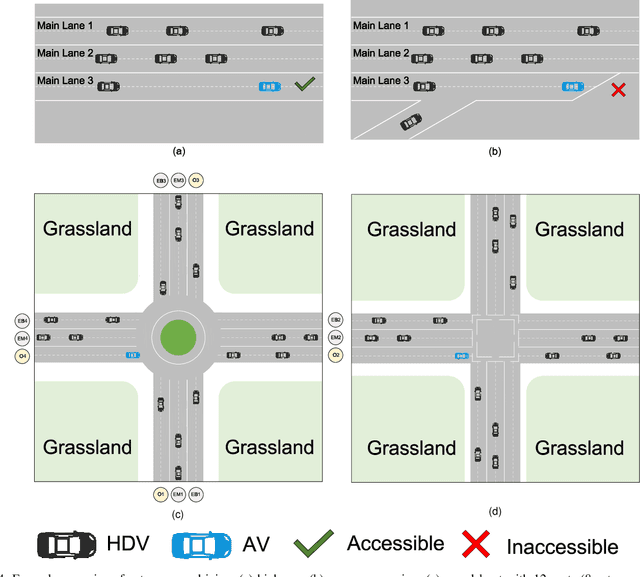
Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AVs) can significantly promote the advances in road transport mobility in terms of safety, reliability, and decarbonization. However, ensuring safety and efficiency in interactive during within dynamic and diverse environments is still a primary barrier to large-scale AV adoption. In recent years, deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has emerged as an advanced AI-based approach, enabling AVs to learn decision-making strategies adaptively from data and interactions. DRL strategies are better suited than traditional rule-based methods for handling complex, dynamic, and unpredictable driving environments due to their adaptivity. However, varying driving scenarios present distinct challenges, such as avoiding obstacles on highways and reaching specific exits at intersections, requiring different scenario-specific decision-making algorithms. Many DRL algorithms have been proposed in interactive decision-making. However, a rationale review of these DRL algorithms across various scenarios is lacking. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation is essential to assess these algorithms from multiple perspectives, including those of vehicle users and vehicle manufacturers. This survey reviews the application of DRL algorithms in autonomous driving across typical scenarios, summarizing road features and recent advancements. The scenarios include highways, on-ramp merging, roundabouts, and unsignalized intersections. Furthermore, DRL-based algorithms are evaluated based on five rationale criteria: driving safety, driving efficiency, training efficiency, unselfishness, and interpretability (DDTUI). Each criterion of DDTUI is specifically analyzed in relation to the reviewed algorithms. Finally, the challenges for future DRL-based decision-making algorithms are summarized.
Multi-frame Detection via Graph Neural Networks: A Link Prediction Approach
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Multi-frame detection algorithms can effectively utilize the correlation between consecutive echoes to improve the detection performance of weak targets. Existing efficient multi-frame detection algorithms are typically based on three sequential steps: plot extraction via a relative low primary threshold, track search and track detection. However, these three-stage processing algorithms may result in a notable loss of detection performance and do not fully leverage the available echo information across frames. As to applying graph neural networks in multi-frame detection, the algorithms are primarily based on node classification tasks, which cannot directly output target tracks. In this paper, we reformulate the multi-frame detection problem as a link prediction task in graphs. First, we perform a rough association of multi-frame observations that exceed the low threshold to construct observation association graphs. Subsequently, a multi-feature link prediction network is designed based on graph neural networks, which integrates multi-dimensional information, including echo structure, Doppler information, and spatio-temporal coupling of plots. By leveraging the principle of link prediction, we unifies the processes of track search and track detection into one step to reduce performance loss and directly output target tracks. Experimental results show that, compared with traditional single-frame and multi-frame detection algorithms, the proposed algorithm improves the detection performance of weak targets while suppressing false alarms. Additionally, interpretable analysis indicates that the designed network effectively integrates the utilized features, allowing for accurate associations between targets and false alarms.
PathSeeker: Exploring LLM Security Vulnerabilities with a Reinforcement Learning-Based Jailbreak Approach
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained widespread use, accompanied by increasing concerns over their security. Traditional jailbreak attacks rely on internal model details or have limitations when exploring the unsafe behavior of the victim model, limiting their generalizability. In this paper, we introduce PathSeeker, a novel black-box jailbreak method inspired by the concept of escaping a security maze. This work is inspired by the game of rats escaping a maze. We think that each LLM has its unique "security maze", and attackers attempt to find the exit learning from the received feedback and their accumulated experience to compromise the target LLM's security defences. Our approach leverages multi-agent reinforcement learning, where smaller models collaborate to guide the main LLM in performing mutation operations to achieve the attack objectives. By progressively modifying inputs based on the model's feedback, our system induces richer, harmful responses. During our manual attempts to perform jailbreak attacks, we found that the vocabulary of the response of the target model gradually became richer and eventually produced harmful responses. Based on the observation, we also introduce a reward mechanism that exploits the expansion of vocabulary richness in LLM responses to weaken security constraints. Our method outperforms five state-of-the-art attack techniques when tested across 13 commercial and open-source LLMs, achieving high attack success rates, especially in strongly aligned commercial models like GPT-4o-mini, Claude-3.5, and GLM-4-air with strong safety alignment. This study aims to improve the understanding of LLM security vulnerabilities and we hope that this sturdy can contribute to the development of more robust defenses.
NAS-BNN: Neural Architecture Search for Binary Neural Networks
Aug 28, 2024



Abstract:Binary Neural Networks (BNNs) have gained extensive attention for their superior inferencing efficiency and compression ratio compared to traditional full-precision networks. However, due to the unique characteristics of BNNs, designing a powerful binary architecture is challenging and often requires significant manpower. A promising solution is to utilize Neural Architecture Search (NAS) to assist in designing BNNs, but current NAS methods for BNNs are relatively straightforward and leave a performance gap between the searched models and manually designed ones. To address this gap, we propose a novel neural architecture search scheme for binary neural networks, named NAS-BNN. We first carefully design a search space based on the unique characteristics of BNNs. Then, we present three training strategies, which significantly enhance the training of supernet and boost the performance of all subnets. Our discovered binary model family outperforms previous BNNs for a wide range of operations (OPs) from 20M to 200M. For instance, we achieve 68.20% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet with only 57M OPs. In addition, we validate the transferability of these searched BNNs on the object detection task, and our binary detectors with the searched BNNs achieve a novel state-of-the-art result, e.g., 31.6% mAP with 370M OPs, on MS COCO dataset. The source code and models will be released at https://github.com/VDIGPKU/NAS-BNN.
Enhanced Visual SLAM for Collision-free Driving with Lightweight Autonomous Cars
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:The paper presents a vision-based obstacle avoidance strategy for lightweight self-driving cars that can be run on a CPU-only device using a single RGB-D camera. The method consists of two steps: visual perception and path planning. The visual perception part uses ORBSLAM3 enhanced with optical flow to estimate the car's poses and extract rich texture information from the scene. In the path planning phase, we employ a method combining a control Lyapunov function and control barrier function in the form of quadratic program (CLF-CBF-QP) together with an obstacle shape reconstruction process (SRP) to plan safe and stable trajectories. To validate the performance and robustness of the proposed method, simulation experiments were conducted with a car in various complex indoor environments using the Gazebo simulation environment. Our method can effectively avoid obstacles in the scenes. The proposed algorithm outperforms benchmark algorithms in achieving more stable and shorter trajectories across multiple simulated scenes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge