Shuja Ansari
Evaluating Scenario-based Decision-making for Interactive Autonomous Driving Using Rational Criteria: A Survey
Jan 03, 2025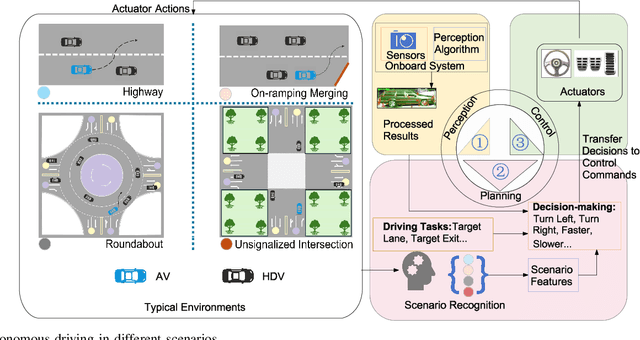
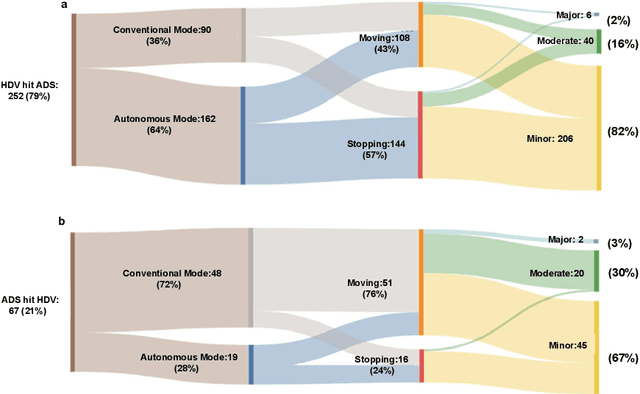
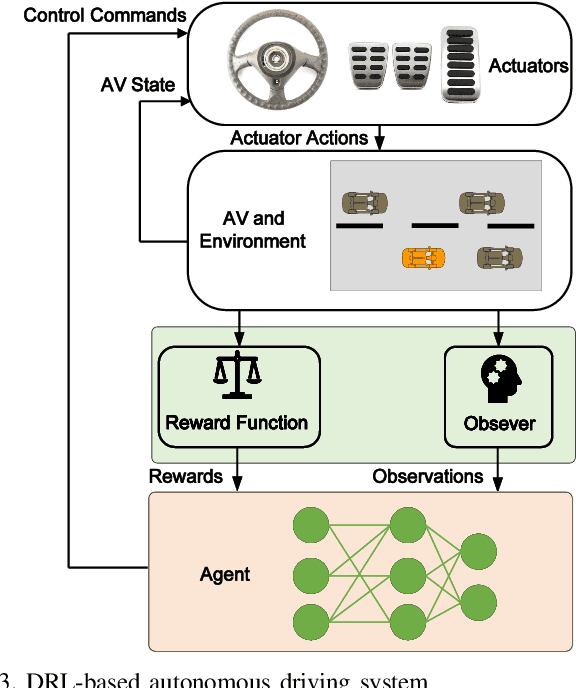
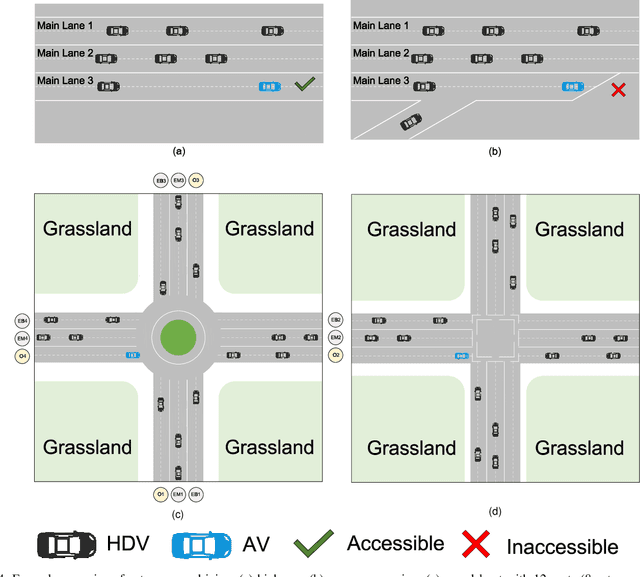
Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AVs) can significantly promote the advances in road transport mobility in terms of safety, reliability, and decarbonization. However, ensuring safety and efficiency in interactive during within dynamic and diverse environments is still a primary barrier to large-scale AV adoption. In recent years, deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has emerged as an advanced AI-based approach, enabling AVs to learn decision-making strategies adaptively from data and interactions. DRL strategies are better suited than traditional rule-based methods for handling complex, dynamic, and unpredictable driving environments due to their adaptivity. However, varying driving scenarios present distinct challenges, such as avoiding obstacles on highways and reaching specific exits at intersections, requiring different scenario-specific decision-making algorithms. Many DRL algorithms have been proposed in interactive decision-making. However, a rationale review of these DRL algorithms across various scenarios is lacking. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation is essential to assess these algorithms from multiple perspectives, including those of vehicle users and vehicle manufacturers. This survey reviews the application of DRL algorithms in autonomous driving across typical scenarios, summarizing road features and recent advancements. The scenarios include highways, on-ramp merging, roundabouts, and unsignalized intersections. Furthermore, DRL-based algorithms are evaluated based on five rationale criteria: driving safety, driving efficiency, training efficiency, unselfishness, and interpretability (DDTUI). Each criterion of DDTUI is specifically analyzed in relation to the reviewed algorithms. Finally, the challenges for future DRL-based decision-making algorithms are summarized.
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Assisted Cross-Layer Authentication for Secure and Efficient Vehicular Communications
Mar 15, 2023



Abstract:Intelligent transportation systems increasingly depend on wireless communication, facilitating real-time vehicular communication. In this context, message authentication is crucial for establishing secure and reliable communication. However, security solutions must consider the dynamic nature of vehicular communication links, which fluctuate between line-of-sight (LoS) and non-line-of-sight (NLoS). In this paper, we propose a lightweight cross-layer authentication scheme that employs public-key infrastructure-based authentication for initial legitimacy detection while using keyed-based physical-layer re-authentication for message verification. However, the latter's detection probability (P_d) decreases with the reduction of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Therefore, we examine using Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) to enhance the SNR value directed toward the designated vehicle and consequently improve the P_d, especially for NLoS scenarios. We conducted theoretical analysis and practical implementation of the proposed scheme using a 1-bit RIS, consisting of 64 x 64 reflective units. Experimental results show a significant improvement in the P_d, increasing from 0.82 to 0.96 at SNR = - 6 dB for an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system with 128 subcarriers. We also conducted informal and formal security analyses, using Burrows-Abadi-Needham (BAN)-logic, to prove the scheme's ability to resist passive and active attacks. Finally, the computation and communication comparisons demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed scheme compared to traditional crypto-based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge