Chongfeng Wei
Free Energy-Inspired Cognitive Risk Integration for AV Navigation in Pedestrian-Rich Environments
Jul 28, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in autonomous vehicle (AV) behavior planning have shown impressive social interaction capabilities when interacting with other road users. However, achieving human-like prediction and decision-making in interactions with vulnerable road users remains a key challenge in complex multi-agent interactive environments. Existing research focuses primarily on crowd navigation for small mobile robots, which cannot be directly applied to AVs due to inherent differences in their decision-making strategies and dynamic boundaries. Moreover, pedestrians in these multi-agent simulations follow fixed behavior patterns that cannot dynamically respond to AV actions. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes a novel framework for modeling interactions between the AV and multiple pedestrians. In this framework, a cognitive process modeling approach inspired by the Free Energy Principle is integrated into both the AV and pedestrian models to simulate more realistic interaction dynamics. Specifically, the proposed pedestrian Cognitive-Risk Social Force Model adjusts goal-directed and repulsive forces using a fused measure of cognitive uncertainty and physical risk to produce human-like trajectories. Meanwhile, the AV leverages this fused risk to construct a dynamic, risk-aware adjacency matrix for a Graph Convolutional Network within a Soft Actor-Critic architecture, allowing it to make more reasonable and informed decisions. Simulation results indicate that our proposed framework effectively improves safety, efficiency, and smoothness of AV navigation compared to the state-of-the-art method.
Socially-Aware Autonomous Driving: Inferring Yielding Intentions for Safer Interactions
Apr 28, 2025



Abstract:Since the emergence of autonomous driving technology, it has advanced rapidly over the past decade. It is becoming increasingly likely that autonomous vehicles (AVs) would soon coexist with human-driven vehicles (HVs) on the roads. Currently, safety and reliable decision-making remain significant challenges, particularly when AVs are navigating lane changes and interacting with surrounding HVs. Therefore, precise estimation of the intentions of surrounding HVs can assist AVs in making more reliable and safe lane change decision-making. This involves not only understanding their current behaviors but also predicting their future motions without any direct communication. However, distinguishing between the passing and yielding intentions of surrounding HVs still remains ambiguous. To address the challenge, we propose a social intention estimation algorithm rooted in Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), coupled with a decision-making framework employing Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithms. To evaluate the method's performance, the proposed framework can be tested and applied in a lane-changing scenario within a simulated environment. Furthermore, the experiment results demonstrate how our approach enhances the ability of AVs to navigate lane changes safely and efficiently on roads.
Evaluating Scenario-based Decision-making for Interactive Autonomous Driving Using Rational Criteria: A Survey
Jan 03, 2025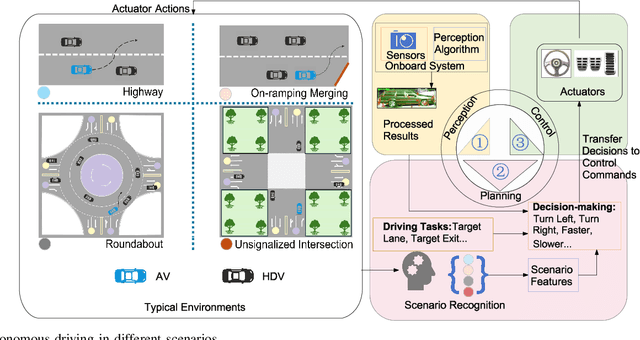
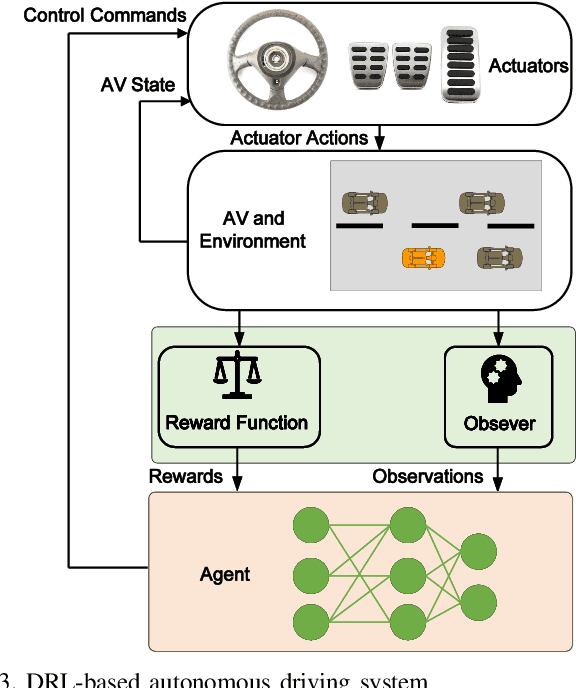
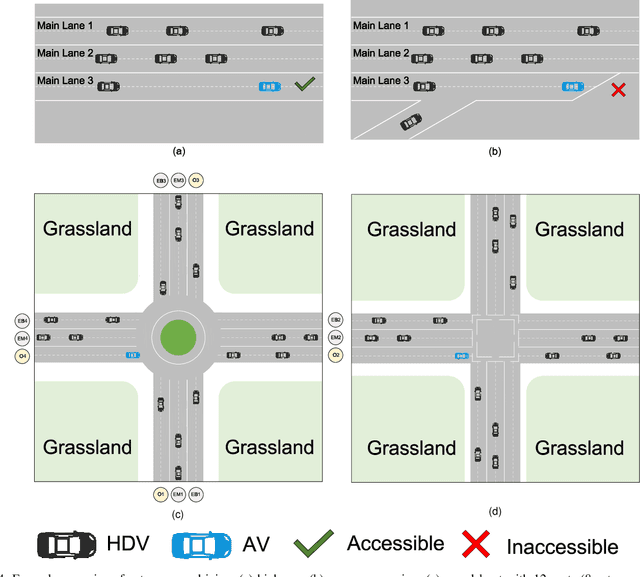
Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AVs) can significantly promote the advances in road transport mobility in terms of safety, reliability, and decarbonization. However, ensuring safety and efficiency in interactive during within dynamic and diverse environments is still a primary barrier to large-scale AV adoption. In recent years, deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has emerged as an advanced AI-based approach, enabling AVs to learn decision-making strategies adaptively from data and interactions. DRL strategies are better suited than traditional rule-based methods for handling complex, dynamic, and unpredictable driving environments due to their adaptivity. However, varying driving scenarios present distinct challenges, such as avoiding obstacles on highways and reaching specific exits at intersections, requiring different scenario-specific decision-making algorithms. Many DRL algorithms have been proposed in interactive decision-making. However, a rationale review of these DRL algorithms across various scenarios is lacking. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation is essential to assess these algorithms from multiple perspectives, including those of vehicle users and vehicle manufacturers. This survey reviews the application of DRL algorithms in autonomous driving across typical scenarios, summarizing road features and recent advancements. The scenarios include highways, on-ramp merging, roundabouts, and unsignalized intersections. Furthermore, DRL-based algorithms are evaluated based on five rationale criteria: driving safety, driving efficiency, training efficiency, unselfishness, and interpretability (DDTUI). Each criterion of DDTUI is specifically analyzed in relation to the reviewed algorithms. Finally, the challenges for future DRL-based decision-making algorithms are summarized.
Social Interaction-Aware Dynamical Models and Decision Making for Autonomous Vehicles
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Interaction-aware Autonomous Driving (IAAD) is a rapidly growing field of research that focuses on the development of autonomous vehicles (AVs) that are capable of interacting safely and efficiently with human road users. This is a challenging task, as it requires the autonomous vehicle to be able to understand and predict the behaviour of human road users. In this literature review, the current state of IAAD research is surveyed in this work. Commencing with an examination of terminology, attention is drawn to challenges and existing models employed for modelling the behaviour of drivers and pedestrians. Next, a comprehensive review is conducted on various techniques proposed for interaction modelling, encompassing cognitive methods, machine learning approaches, and game-theoretic methods. The conclusion is reached through a discussion of potential advantages and risks associated with IAAD, along with the illumination of pivotal research inquiries necessitating future exploration.
Interaction-aware Decision-making for Automated Vehicles using Social Value Orientation
Jul 12, 2022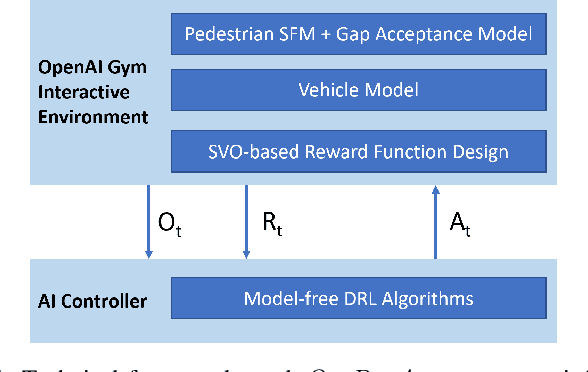
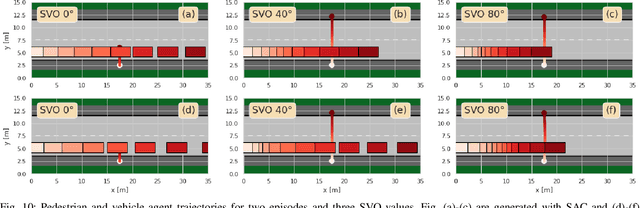
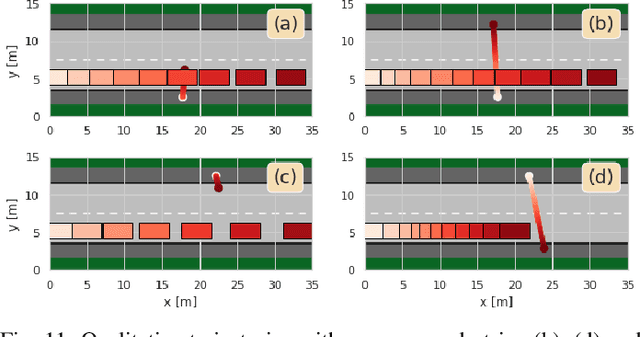
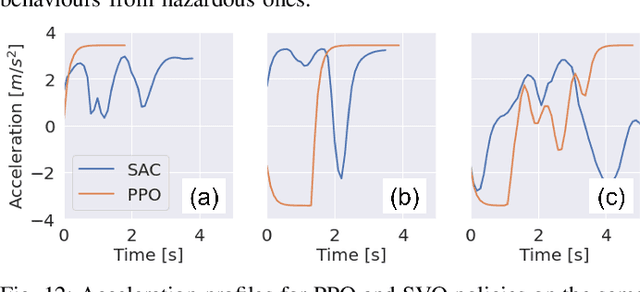
Abstract:Motion control algorithms in the presence of pedestrians are critical for the development of safe and reliable Autonomous Vehicles (AVs). Traditional motion control algorithms rely on manually designed decision-making policies which neglect the mutual interactions between AVs and pedestrians. On the other hand, recent advances in Deep Reinforcement Learning allow for the automatic learning of policies without manual designs. To tackle the problem of decision-making in the presence of pedestrians, the authors introduce a framework based on Social Value Orientation and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) that is capable of generating decision-making policies with different driving styles. The policy is trained using state-of-the-art DRL algorithms in a simulated environment. A novel computationally-efficient pedestrian model that is suitable for DRL training is also introduced. We perform experiments to validate our framework and we conduct a comparative analysis of the policies obtained with two different model-free Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Simulations results show how the developed model exhibits natural driving behaviours, such as short-stopping, to facilitate the pedestrian's crossing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge