Fei Ding
Alibaba Group
PoseStreamer: A Multi-modal Framework for 3D Tracking of Unseen Moving Objects
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Six degree of freedom (6DoF) pose estimation for novel objects is a critical task in computer vision, yet it faces significant challenges in high-speed and low-light scenarios where standard RGB cameras suffer from motion blur. While event cameras offer a promising solution due to their high temporal resolution, current 6DoF pose estimation methods typically yield suboptimal performance in high-speed object moving scenarios. To address this gap, we propose PoseStreamer, a robust multi-modal 6DoF pose estimation framework designed specifically on high-speed moving scenarios. Our approach integrates three core components: an Adaptive Pose Memory Queue that utilizes historical orientation cues for temporal consistency, an Object-centric 2D Tracker that provides strong 2D priors to boost 3D center recall, and a Ray Pose Filter for geometric refinement along camera rays. Furthermore, we introduce MoCapCube6D, a novel multi-modal dataset constructed to benchmark performance under rapid motion. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PoseStreamer not only achieves superior accuracy in high-speed moving scenarios, but also exhibits strong generalizability as a template-free framework for unseen moving objects.
PoseStreamer: A Multi-modal Framework for 6DoF Pose Estimation of Unseen Moving Objects
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Six degree of freedom (6DoF) pose estimation for novel objects is a critical task in computer vision, yet it faces significant challenges in high-speed and low-light scenarios where standard RGB cameras suffer from motion blur. While event cameras offer a promising solution due to their high temporal resolution, current 6DoF pose estimation methods typically yield suboptimal performance in high-speed object moving scenarios. To address this gap, we propose PoseStreamer, a robust multi-modal 6DoF pose estimation framework designed specifically on high-speed moving scenarios. Our approach integrates three core components: an Adaptive Pose Memory Queue that utilizes historical orientation cues for temporal consistency, an Object-centric 2D Tracker that provides strong 2D priors to boost 3D center recall, and a Ray Pose Filter for geometric refinement along camera rays. Furthermore, we introduce MoCapCube6D, a novel multi-modal dataset constructed to benchmark performance under rapid motion. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PoseStreamer not only achieves superior accuracy in high-speed moving scenarios, but also exhibits strong generalizability as a template-free framework for unseen moving objects.
SilverTorch: A Unified Model-based System to Democratize Large-Scale Recommendation on GPUs
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Serving deep learning based recommendation models (DLRM) at scale is challenging. Existing systems rely on CPU-based ANN indexing and filtering services, suffering from non-negligible costs and forgoing joint optimization opportunities. Such inefficiency makes them difficult to support more complex model architectures, such as learned similarities and multi-task retrieval. In this paper, we propose SilverTorch, a model-based system for serving recommendation models on GPUs. SilverTorch unifies model serving by replacing standalone indexing and filtering services with layers of served models. We propose a Bloom index algorithm on GPUs for feature filtering and a tensor-native fused Int8 ANN kernel on GPUs for nearest neighbor search. We further co-design the ANN search index and filtering index to reduce GPU memory utilization and eliminate unnecessary computation. Benefit from SilverTorch's serving paradigm, we introduce a OverArch scoring layer and a Value Model to aggregate results across multi-tasks. These advancements improve the accuracy for retrieval and enable future studies for serving more complex models. For ranking, SilverTorch's design accelerates item embedding calculation by caching the pre-calculated embeddings inside the serving model. Our evaluation on the industry-scale datasets show that SilverTorch achieves up to 5.6x lower latency and 23.7x higher throughput compared to the state-of-the-art approaches. We also demonstrate that SilverTorch's solution is 13.35x more cost-efficient than CPU-based solution while improving accuracy via serving more complex models. SilverTorch serves over hundreds of models online across major products and recommends contents for billions of daily active users.
USO: Unified Style and Subject-Driven Generation via Disentangled and Reward Learning
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Existing literature typically treats style-driven and subject-driven generation as two disjoint tasks: the former prioritizes stylistic similarity, whereas the latter insists on subject consistency, resulting in an apparent antagonism. We argue that both objectives can be unified under a single framework because they ultimately concern the disentanglement and re-composition of content and style, a long-standing theme in style-driven research. To this end, we present USO, a Unified Style-Subject Optimized customization model. First, we construct a large-scale triplet dataset consisting of content images, style images, and their corresponding stylized content images. Second, we introduce a disentangled learning scheme that simultaneously aligns style features and disentangles content from style through two complementary objectives, style-alignment training and content-style disentanglement training. Third, we incorporate a style reward-learning paradigm denoted as SRL to further enhance the model's performance. Finally, we release USO-Bench, the first benchmark that jointly evaluates style similarity and subject fidelity across multiple metrics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that USO achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models along both dimensions of subject consistency and style similarity. Code and model: https://github.com/bytedance/USO
Improved Supervised Fine-Tuning for Large Language Models to Mitigate Catastrophic Forgetting
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), while enhancing large language models(LLMs)' instruction-following capabilities and domain-specific task adaptability, often diminishes their general capabilities. Moreover, due to the inaccessibility of original pre-training data, catastrophic forgetting tends to be exacerbated when third-party practitioners implement SFT on open-sourced models. To address this challenge, we propose a novel, more cost-effective SFT method which could effectively reduce the risk of catastrophic forgetting without access to original SFT data. Our approach begins by reconstructing the likely SFT instruction distribution of the base model, followed by a multi-model screening process to select optimal data, which is then mixed with new data for SFT. Experimental results demonstrate that our method preserves generalization capabilities in general domains while improving task-specific performance.
Multi-Layer GRPO: Enhancing Reasoning and Self-Correction in Large Language Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:The Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm has demonstrated considerable success in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), as evidenced by DeepSeek-R1. However, the absence of intermediate supervision in GRPO frequently leads to inefficient exploration dynamics. A single error in a complex reasoning chain can invalidate the entire solution, resulting in abrupt reward vanishing and compromising training stability.To address these challenges, we propose MGRPO (Multi-layer GRPO). MGRPO operates in two layers: the first layer employs standard GRPO to generate an initial response. This response, along with the original query, is then fed into a second-layer GRPO process. This second layer is specifically trained to identify and correct errors in the initial response, effectively creating a self-correction loop. This mechanism provides implicit process-level supervision by rewarding successful error correction, without requiring an explicit, densely-annotated reward model. Experimental results on several mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that MGRPO significantly outperforms standard GRPO, achieving superior performance by fostering both reasoning and self-correction abilities.
Socially-Aware Autonomous Driving: Inferring Yielding Intentions for Safer Interactions
Apr 28, 2025



Abstract:Since the emergence of autonomous driving technology, it has advanced rapidly over the past decade. It is becoming increasingly likely that autonomous vehicles (AVs) would soon coexist with human-driven vehicles (HVs) on the roads. Currently, safety and reliable decision-making remain significant challenges, particularly when AVs are navigating lane changes and interacting with surrounding HVs. Therefore, precise estimation of the intentions of surrounding HVs can assist AVs in making more reliable and safe lane change decision-making. This involves not only understanding their current behaviors but also predicting their future motions without any direct communication. However, distinguishing between the passing and yielding intentions of surrounding HVs still remains ambiguous. To address the challenge, we propose a social intention estimation algorithm rooted in Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), coupled with a decision-making framework employing Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithms. To evaluate the method's performance, the proposed framework can be tested and applied in a lane-changing scenario within a simulated environment. Furthermore, the experiment results demonstrate how our approach enhances the ability of AVs to navigate lane changes safely and efficiently on roads.
DreamO: A Unified Framework for Image Customization
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Recently, extensive research on image customization (e.g., identity, subject, style, background, etc.) demonstrates strong customization capabilities in large-scale generative models. However, most approaches are designed for specific tasks, restricting their generalizability to combine different types of condition. Developing a unified framework for image customization remains an open challenge. In this paper, we present DreamO, an image customization framework designed to support a wide range of tasks while facilitating seamless integration of multiple conditions. Specifically, DreamO utilizes a diffusion transformer (DiT) framework to uniformly process input of different types. During training, we construct a large-scale training dataset that includes various customization tasks, and we introduce a feature routing constraint to facilitate the precise querying of relevant information from reference images. Additionally, we design a placeholder strategy that associates specific placeholders with conditions at particular positions, enabling control over the placement of conditions in the generated results. Moreover, we employ a progressive training strategy consisting of three stages: an initial stage focused on simple tasks with limited data to establish baseline consistency, a full-scale training stage to comprehensively enhance the customization capabilities, and a final quality alignment stage to correct quality biases introduced by low-quality data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed DreamO can effectively perform various image customization tasks with high quality and flexibly integrate different types of control conditions.
Less-to-More Generalization: Unlocking More Controllability by In-Context Generation
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Although subject-driven generation has been extensively explored in image generation due to its wide applications, it still has challenges in data scalability and subject expansibility. For the first challenge, moving from curating single-subject datasets to multiple-subject ones and scaling them is particularly difficult. For the second, most recent methods center on single-subject generation, making it hard to apply when dealing with multi-subject scenarios. In this study, we propose a highly-consistent data synthesis pipeline to tackle this challenge. This pipeline harnesses the intrinsic in-context generation capabilities of diffusion transformers and generates high-consistency multi-subject paired data. Additionally, we introduce UNO, which consists of progressive cross-modal alignment and universal rotary position embedding. It is a multi-image conditioned subject-to-image model iteratively trained from a text-to-image model. Extensive experiments show that our method can achieve high consistency while ensuring controllability in both single-subject and multi-subject driven generation.
VMix: Improving Text-to-Image Diffusion Model with Cross-Attention Mixing Control
Dec 30, 2024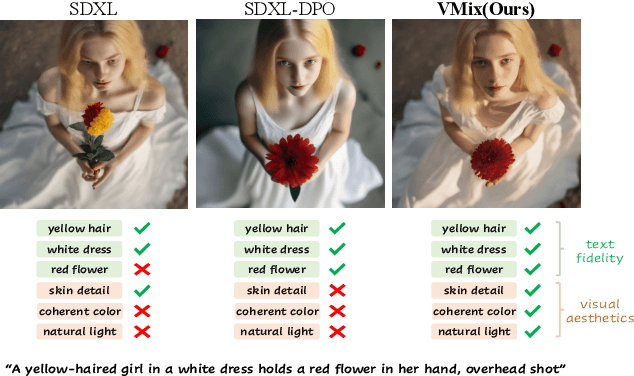
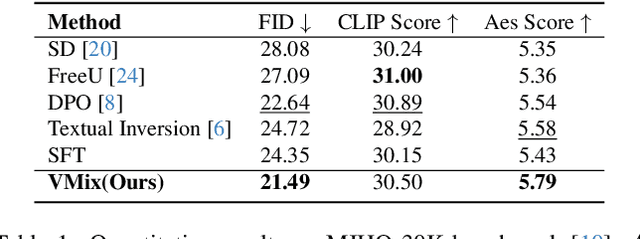
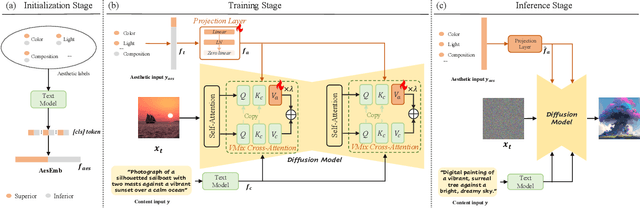
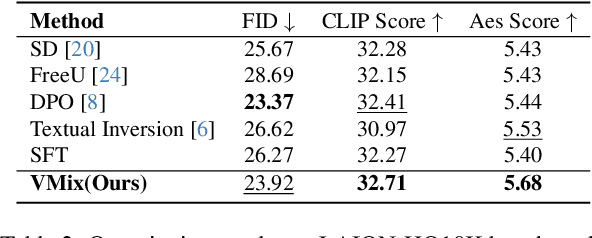
Abstract:While diffusion models show extraordinary talents in text-to-image generation, they may still fail to generate highly aesthetic images. More specifically, there is still a gap between the generated images and the real-world aesthetic images in finer-grained dimensions including color, lighting, composition, etc. In this paper, we propose Cross-Attention Value Mixing Control (VMix) Adapter, a plug-and-play aesthetics adapter, to upgrade the quality of generated images while maintaining generality across visual concepts by (1) disentangling the input text prompt into the content description and aesthetic description by the initialization of aesthetic embedding, and (2) integrating aesthetic conditions into the denoising process through value-mixed cross-attention, with the network connected by zero-initialized linear layers. Our key insight is to enhance the aesthetic presentation of existing diffusion models by designing a superior condition control method, all while preserving the image-text alignment. Through our meticulous design, VMix is flexible enough to be applied to community models for better visual performance without retraining. To validate the effectiveness of our method, we conducted extensive experiments, showing that VMix outperforms other state-of-the-art methods and is compatible with other community modules (e.g., LoRA, ControlNet, and IPAdapter) for image generation. The project page is https://vmix-diffusion.github.io/VMix/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge